Fuel Temperature Sensor Nissan Sentra
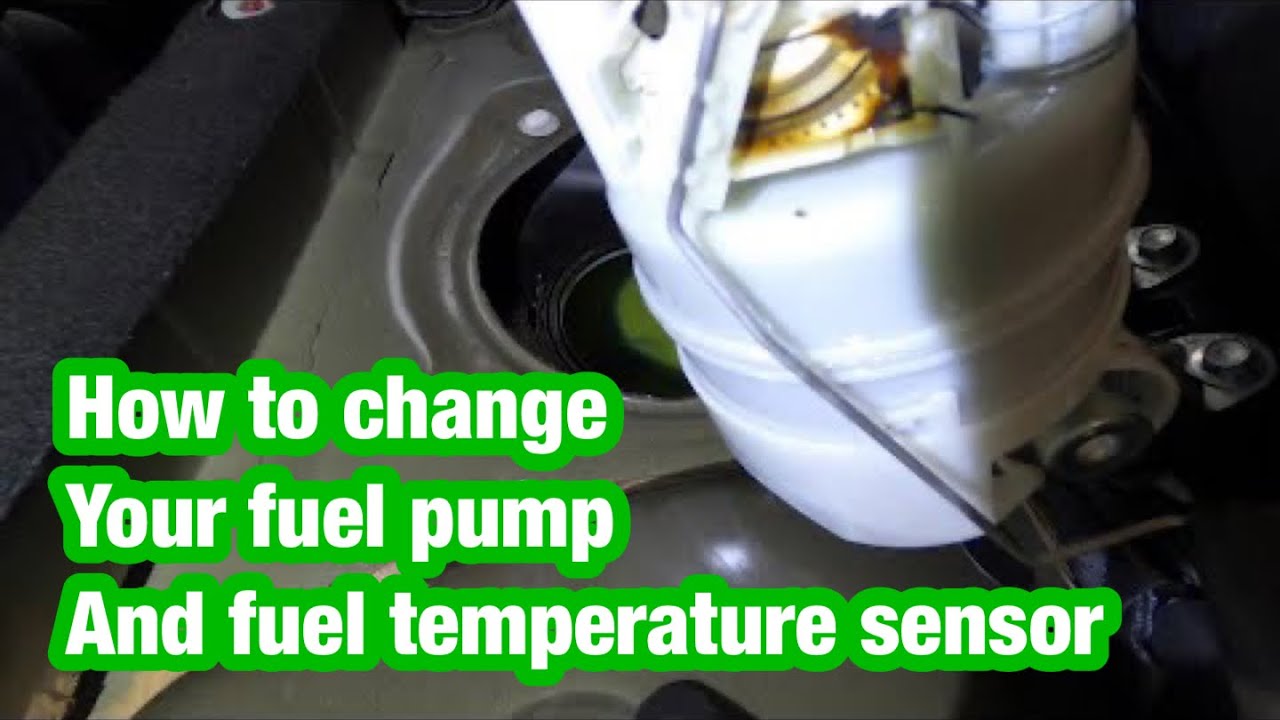
Okay, so you're here because you're having trouble with your Nissan Sentra and you suspect it might be the fuel temperature sensor. You're in the right place. Let's break down what this sensor does, the symptoms you might be seeing, and how to troubleshoot and potentially fix the problem. Think of me as your friendly neighborhood mechanic – I'm here to guide you through it.
What is the Fuel Temperature Sensor and Why is it Important?
The fuel temperature sensor (FTS) in your Nissan Sentra is a small but crucial component of the engine management system. Its primary job is to measure the temperature of the fuel flowing through the fuel rail or in the fuel tank (depending on the specific model year and engine). This information is then relayed to the Engine Control Module (ECM), sometimes also referred to as the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). The ECM uses this data, along with information from other sensors, to optimize engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions.
Think of it like this: the ECM is the "brain" of your engine, and the fuel temperature sensor is one of its key "senses." Just like you wouldn't want to try and bake a cake without knowing the oven temperature, the ECM needs to know the fuel temperature to properly control the air-fuel mixture, ignition timing, and other parameters. Cooler fuel is denser than warmer fuel, impacting how well it atomizes and burns. Without accurate fuel temperature data, the engine can run poorly, resulting in:
- Reduced fuel economy
- Poor engine performance (hesitation, stalling)
- Increased emissions
- Difficulty starting (especially in hot or cold weather)
- Illumination of the Check Engine Light
Common Symptoms of a Failing Fuel Temperature Sensor
Now, let's dive into the symptoms that might indicate your fuel temperature sensor is on its way out. Keep in mind that some of these symptoms can also be caused by other issues, so it's important to properly diagnose the problem before replacing the sensor. Here are some of the most common signs:
Check Engine Light (CEL)
This is often the first and most obvious sign. A faulty fuel temperature sensor will usually trigger a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) related to fuel temperature. Common codes include:
- P0180: Fuel Temperature Sensor A Circuit Malfunction
- P0181: Fuel Temperature Sensor A Circuit Range/Performance
- P0182: Fuel Temperature Sensor A Circuit Low Input
- P0183: Fuel Temperature Sensor A Circuit High Input
You'll need an OBD-II scanner to read these codes. Many auto parts stores will scan your car for free, or you can invest in your own scanner (they're relatively inexpensive). Write down the code(s) you find, as this will help you narrow down the problem.
Poor Fuel Economy
If you notice a sudden or gradual decrease in your gas mileage, a faulty fuel temperature sensor could be the culprit. The ECM might be miscalculating the proper air-fuel mixture, causing the engine to burn more fuel than necessary.
Engine Hesitation or Stalling
The engine might hesitate or stumble during acceleration, or it might even stall completely, especially at idle. This is because the ECM is struggling to maintain the correct air-fuel ratio without accurate fuel temperature data.
Difficulty Starting
A bad fuel temperature sensor can make it difficult to start the engine, particularly in extreme weather conditions. In hot weather, the fuel might vaporize too quickly, making it hard to ignite. In cold weather, the fuel might not vaporize sufficiently, also hindering starting.
Rough Idle
The engine might idle roughly, with noticeable vibrations or fluctuations in RPM. This is another sign that the ECM is having trouble maintaining a stable air-fuel mixture.
Troubleshooting the Fuel Temperature Sensor
Before you rush out and buy a new sensor, let's do some basic troubleshooting. Here's a step-by-step guide:
- Read the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve any stored codes. As mentioned earlier, this will give you a starting point.
- Inspect the Wiring and Connectors: Carefully examine the wiring harness and connector leading to the fuel temperature sensor. Look for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires, corrosion, or loose connections. Clean the connector with electrical contact cleaner.
- Check the Sensor Resistance: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance of the fuel temperature sensor. You'll need to consult your vehicle's repair manual or a reliable online resource to find the correct resistance values for your specific sensor at different temperatures. If the resistance is significantly different from the expected value, the sensor is likely faulty.
- Check the Sensor Voltage: With the ignition on but the engine off, use a multimeter to check the voltage at the sensor connector. You should find a reference voltage (usually 5 volts) from the ECM. If there's no voltage, there might be a problem with the wiring or the ECM.
Tools You'll Need
- OBD-II Scanner
- Multimeter
- Socket set or wrench set (to remove the sensor)
- Electrical contact cleaner
- Wiring diagram (optional, but helpful)
- Safety glasses
- Gloves
Replacing the Fuel Temperature Sensor
If your troubleshooting steps indicate that the fuel temperature sensor is indeed faulty, the next step is to replace it. Here's a general guide, but always refer to your vehicle's repair manual for specific instructions, as the location and removal procedure can vary slightly depending on the model year and engine.
- Disconnect the Negative Battery Cable: This is crucial for safety.
- Locate the Fuel Temperature Sensor: The sensor is typically located either on the fuel rail (near the fuel injectors) or in the fuel tank. Consult your repair manual to find its exact location.
- Disconnect the Electrical Connector: Carefully disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor. You might need to press a release tab.
- Remove the Old Sensor: Use a socket or wrench to carefully remove the sensor. Be prepared for a small amount of fuel to leak out. Have a rag handy to catch any spills.
- Install the New Sensor: Apply a small amount of Teflon tape to the threads of the new sensor (if recommended by the manufacturer). Install the new sensor and tighten it to the specified torque (if applicable).
- Reconnect the Electrical Connector: Reconnect the electrical connector to the sensor. Make sure it's securely attached.
- Reconnect the Negative Battery Cable: Reconnect the negative battery cable.
- Clear the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Use your OBD-II scanner to clear any stored DTCs.
- Test Drive the Vehicle: Take the vehicle for a test drive to see if the problem has been resolved. Monitor the engine performance and fuel economy.
Important Considerations During Replacement
- Safety First: Fuel is flammable. Work in a well-ventilated area and avoid sparks or open flames.
- Proper Torque: Overtightening the new sensor can damage it or the surrounding components. Use a torque wrench and tighten to the specified torque if available.
- Quality Parts: Use a high-quality replacement sensor from a reputable brand. Aftermarket sensors can vary in quality.
- Consult a Professional: If you're not comfortable performing this repair yourself, don't hesitate to take your car to a qualified mechanic.
Estimated Repair Costs
The cost of replacing a fuel temperature sensor can vary depending on several factors, including:
- The cost of the sensor itself: Aftermarket sensors can range from $20 to $80. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) sensors will typically be more expensive, costing upwards of $100 or more.
- Labor costs (if you're having a mechanic do the work): Labor rates vary depending on your location and the mechanic's hourly rate. Expect to pay between $50 and $150 for labor, depending on the complexity of the job. The location of the sensor plays a big role in labor costs.
Therefore, the total cost of replacing a fuel temperature sensor can range from $70 to $250 or more, depending on whether you do it yourself or have a mechanic do it for you.
Preventative Maintenance
While fuel temperature sensor failures aren't always preventable, you can take steps to minimize the risk:
- Use High-Quality Fuel: Using fuel from reputable sources can help prevent contamination and buildup in the fuel system.
- Regular Fuel Filter Replacement: A clogged fuel filter can put stress on the fuel system and potentially affect the fuel temperature sensor. Follow the manufacturer's recommended replacement interval.
- Address Check Engine Lights Promptly: Don't ignore a Check Engine Light. Addressing problems early can prevent them from escalating and potentially damaging other components.
Final Thoughts
A faulty fuel temperature sensor can cause a variety of problems in your Nissan Sentra, but with a little knowledge and some basic troubleshooting skills, you can often diagnose and fix the issue yourself. Remember to prioritize safety, consult your vehicle's repair manual, and use high-quality replacement parts. If you're not comfortable doing the work yourself, don't hesitate to seek help from a qualified mechanic. Good luck, and happy motoring!
