High-flow Fuel Filter Upgrade And System Pressure Testing
Hey folks, let's talk about something crucial for your engine's performance and longevity: fuel. More specifically, getting the right amount of clean fuel to your engine. If you're experiencing issues like sluggish acceleration, stalling, or a general lack of power, you might be facing fuel delivery problems. Two common culprits? A clogged or inadequate fuel filter and low fuel system pressure.
The Case for a High-Flow Fuel Filter
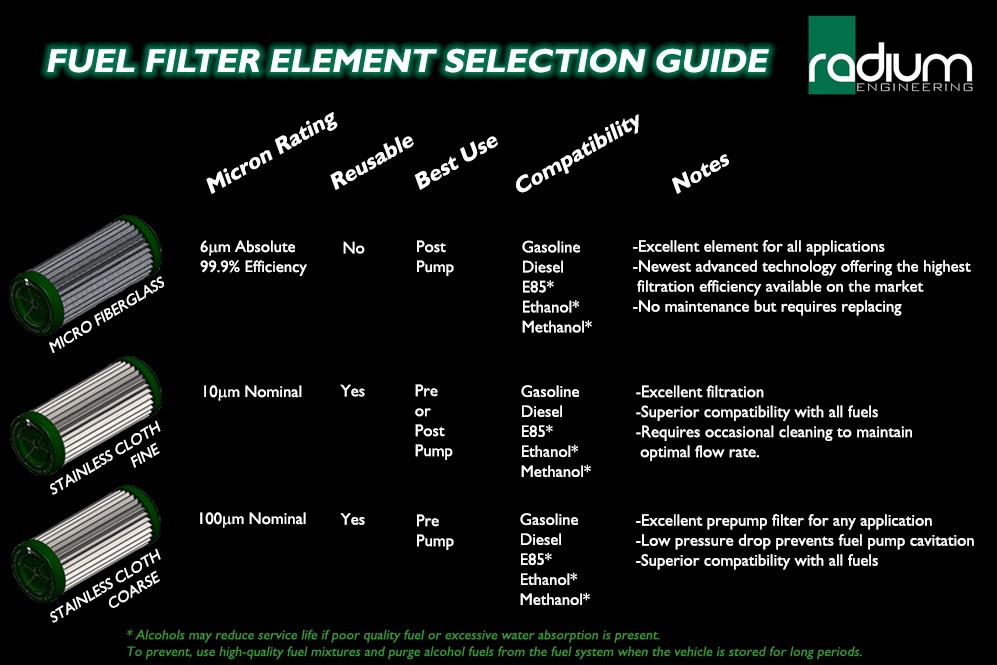
First, let's dive into the fuel filter. Its job is simple: to prevent contaminants like rust, dirt, and debris from reaching your fuel injectors and other sensitive components. A standard fuel filter does a decent job, but if you've upgraded your engine with performance parts, frequently drive in dusty environments, or simply want to ensure optimal fuel delivery, a high-flow fuel filter can be a smart upgrade. Think of it as giving your fuel system a performance boost.
When is a High-Flow Filter Necessary?
Here are some scenarios where a high-flow filter becomes more than just a nice-to-have:
- Modified Engines: If you've added a turbocharger, supercharger, or made other significant engine modifications that increase fuel demand, a high-flow filter can help prevent fuel starvation.
- Older Vehicles: Older fuel tanks can accumulate rust and sediment over time. A high-flow filter with a finer micron rating can provide better protection.
- Ethanol Blends (E85): Ethanol can be corrosive and can loosen deposits in your fuel system. A high-flow filter with compatibility for ethanol blends is crucial.
- Performance Driving: If you frequently track your car or engage in aggressive driving, a high-flow filter can ensure consistent fuel delivery under demanding conditions.
Choosing the Right High-Flow Filter
Not all high-flow filters are created equal. Here's what to consider:
- Micron Rating: This indicates the size of particles the filter can trap. A lower micron rating means finer filtration, but it can also restrict flow if not properly designed. Find a balance between filtration and flow rate.
- Flow Rate: Make sure the filter's flow rate meets or exceeds your engine's fuel requirements. Consult your vehicle's specifications or a performance shop for recommendations.
- Material: Look for filters made from durable materials like stainless steel or reinforced paper.
- Compatibility: Verify the filter is compatible with your fuel type (gasoline, diesel, ethanol).
- Size and Fitment: Ensure the filter is the correct size and has the appropriate fittings for your fuel lines.
Installing a High-Flow Fuel Filter: A DIY Guide (with Caution!)
Replacing a fuel filter can be a DIY project, but it requires caution and some basic mechanical skills. Fuel is flammable and can be dangerous. If you're not comfortable working with fuel systems, it's best to leave this to a professional.
Tools Needed:
- Safety glasses
- Gloves
- Wrench set
- Fuel line disconnect tool (if necessary)
- Catch pan
- Shop towels
- New fuel filter
Steps:
- Safety First: Disconnect the negative battery cable to prevent sparks. Work in a well-ventilated area and have a fire extinguisher nearby.
- Locate the Fuel Filter: Consult your vehicle's repair manual to find the location of the fuel filter. It's often located along the fuel line, either under the vehicle or in the engine bay.
- Relieve Fuel Pressure: This is crucial to prevent fuel from spraying everywhere. Consult your vehicle's repair manual for the proper procedure to relieve fuel pressure. Some vehicles have a Schrader valve on the fuel rail that can be used to release pressure.
- Disconnect Fuel Lines: Carefully disconnect the fuel lines from the old filter. Use a fuel line disconnect tool if necessary. Have a catch pan ready to catch any spilled fuel.
- Remove Old Filter: Remove the old filter from its mounting bracket.
- Install New Filter: Install the new filter in the mounting bracket, ensuring it's oriented correctly (follow the arrow on the filter).
- Connect Fuel Lines: Reconnect the fuel lines to the new filter, making sure they are securely attached.
- Reconnect Battery: Reconnect the negative battery cable.
- Check for Leaks: Turn the ignition key to the "on" position (without starting the engine) to allow the fuel pump to prime the system. Check for any fuel leaks around the filter connections. If you find any leaks, tighten the connections or re-seat the fuel lines.
- Start the Engine: Start the engine and let it idle for a few minutes. Check again for leaks.
Approximate Cost: A high-flow fuel filter can range from $30 to $150, depending on the brand and features. Professional installation can add another $50 to $150, depending on labor rates.
Fuel System Pressure Testing: Diagnosing Fuel Delivery Issues
Now, let's move on to fuel system pressure. Even with a clean, high-flow filter, your engine might still suffer from fuel delivery problems if the fuel pump isn't providing adequate pressure. Low fuel pressure can cause a variety of issues, from poor performance to a complete no-start condition.
Symptoms of Low Fuel Pressure
- Sluggish acceleration
- Stalling, especially under load
- Hesitation when accelerating
- Poor fuel economy
- Rough idling
- Difficulty starting
- Check engine light (with codes related to fuel trim or lean conditions)
Performing a Fuel System Pressure Test
Testing fuel system pressure requires a fuel pressure gauge. You can purchase one at most auto parts stores for around $30-$100, or rent one.
Tools Needed:
- Fuel pressure gauge
- Safety glasses
- Gloves
- Shop towels
Steps:
- Safety First: Disconnect the negative battery cable. Work in a well-ventilated area.
- Locate the Fuel Rail Test Port: Most vehicles have a test port (usually a Schrader valve) on the fuel rail. Consult your vehicle's repair manual to find its location.
- Connect the Fuel Pressure Gauge: Connect the fuel pressure gauge to the test port. Make sure the connection is secure to prevent fuel leaks.
- Reconnect Battery: Reconnect the negative battery cable.
- Turn the Ignition On: Turn the ignition key to the "on" position (without starting the engine) to allow the fuel pump to prime the system.
- Read the Fuel Pressure: Observe the fuel pressure reading on the gauge. Compare the reading to your vehicle's specifications. You can find this information in your repair manual or online.
- Start the Engine: Start the engine and let it idle. Observe the fuel pressure reading again. It should remain within the specified range.
- Check Pressure Under Load: If possible, have someone rev the engine while you observe the fuel pressure. The pressure should not drop significantly.
- Fuel Pressure Regulator Test: Disconnect the vacuum line from the fuel pressure regulator (if equipped). The fuel pressure should increase slightly. If it doesn't, the regulator may be faulty.
- Disconnect the Gauge: Carefully disconnect the fuel pressure gauge from the test port, using a shop towel to catch any spilled fuel.
Interpreting the Results
If the fuel pressure is below the specified range, it could indicate:
- A weak or failing fuel pump
- A clogged fuel filter (even with a high-flow filter, debris can accumulate)
- A faulty fuel pressure regulator
- A leak in the fuel lines
- A clogged fuel injector(s)
If the fuel pressure is above the specified range, it could indicate:
- A faulty fuel pressure regulator
- A blocked return line (if equipped)
What to Do Next?
If you suspect low fuel pressure, the next step is to further diagnose the cause. This might involve:
- Testing the fuel pump's electrical circuit
- Checking for fuel leaks
- Inspecting the fuel lines for damage or blockage
- Testing the fuel pressure regulator
- Having your fuel injectors professionally cleaned or tested
Approximate Cost: Fuel system diagnosis and repair costs can vary widely depending on the cause of the problem. Replacing a fuel pump can range from $300 to $1000, including parts and labor. A fuel pressure regulator replacement might cost $100 to $300. Fuel injector cleaning or replacement can also add to the expense.
Final Thoughts
Maintaining a healthy fuel system is essential for your engine's performance and longevity. Upgrading to a high-flow fuel filter and regularly testing fuel system pressure are valuable steps you can take to prevent problems and ensure your engine receives the fuel it needs. Remember, safety is paramount when working with fuel systems. If you're unsure about any of these procedures, it's always best to consult a qualified mechanic. Good luck!
