Hydro E-brake System Design And Installation Guide
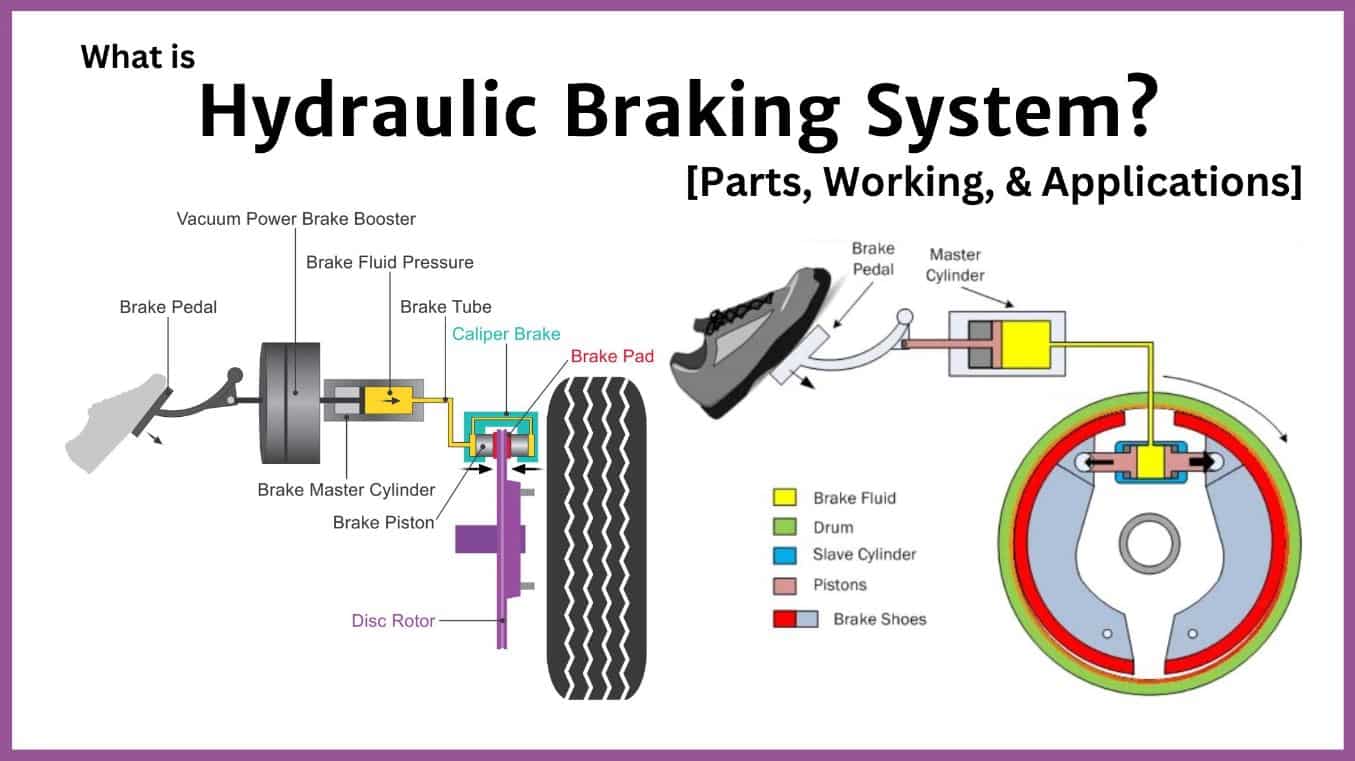
Understanding Hydro E-Brake Systems: A Design and Installation Guide
Are you looking to enhance the braking performance of your vehicle, especially in performance driving scenarios like drifting or rally? A hydraulic e-brake (hydro e-brake) system might be the solution you need. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the design considerations and installation process of a hydro e-brake system, providing you with the knowledge to make informed decisions and potentially tackle this project yourself. We'll cover everything from the fundamental principles to practical tips, ensuring a safe and effective installation.
What is a Hydraulic E-Brake?
Unlike a traditional cable-operated emergency brake, a hydro e-brake uses hydraulic pressure to actuate the rear brakes. This provides significantly more stopping power and finer control, particularly beneficial in situations requiring controlled rear-wheel lockup. Imagine trying to initiate a drift using a standard e-brake cable – it's often sluggish and lacks the precision needed. A hydro e-brake addresses this by delivering instant and powerful braking force, making it a valuable tool for experienced drivers.
Why Choose a Hydro E-Brake?
The advantages of a hydraulic e-brake system extend beyond just increased stopping power. Consider these key benefits:
- Increased Stopping Power: Hydraulic systems offer a significant mechanical advantage over cable systems, resulting in much greater braking force.
- Improved Control: The direct hydraulic connection allows for precise modulation of braking force, offering superior control during drifts, turns, and other maneuvers.
- Faster Response Time: Hydro e-brakes engage almost instantly, providing quicker reaction times in critical situations.
- Reduced Cable Stretch: Eliminating cables eliminates the issue of cable stretch and subsequent adjustments needed with traditional e-brakes.
- More Consistent Performance: Hydraulic systems are less susceptible to wear and tear, maintaining consistent performance over time.
Designing Your Hydro E-Brake System
Before you start tearing apart your vehicle, careful planning is crucial. A well-designed system is essential for both safety and optimal performance. Here are some key considerations:
Master Cylinder Selection
The master cylinder is the heart of your hydro e-brake system. Choosing the right one is paramount. Factors to consider include:
- Bore Size: The bore size of the master cylinder determines the amount of fluid displaced per stroke. A larger bore will result in more braking force but require more pedal travel. A smaller bore will offer less force but require less travel. Finding the right balance is key. Generally, a bore size similar to or slightly larger than your existing brake master cylinder is a good starting point.
- Reservoir Size: Ensure the master cylinder reservoir is large enough to accommodate the fluid displacement of your rear brake calipers. Insufficient reservoir capacity can lead to air being drawn into the system, causing brake failure.
- Mounting Configuration: Verify that the master cylinder's mounting configuration is compatible with your vehicle's interior. You may need to fabricate a custom bracket.
- Brand and Quality: Opt for reputable brands known for their reliability and quality. Poorly manufactured master cylinders can compromise safety.
Line and Fitting Selection
The lines and fittings connecting the master cylinder to the rear brake calipers are equally important. Consider these factors:
- Line Type: Use DOT-approved brake lines specifically designed for hydraulic brake systems. Stainless steel braided lines are highly recommended for their durability and resistance to expansion, which can improve brake feel. Avoid using non-DOT-approved lines, as they may not withstand the pressures involved.
- Line Size: Choose the correct line size for your system. Typically, -3 AN or -4 AN lines are used for hydro e-brakes. Consult with your supplier to determine the optimal size for your specific application.
- Fitting Type: Use high-quality AN fittings to ensure a secure and leak-free connection. Ensure the fittings are compatible with your chosen brake lines. Flare fittings are also acceptable, but require careful flaring to avoid leaks.
- Line Routing: Plan the routing of your brake lines carefully, avoiding sharp bends and potential chafing points. Secure the lines with clamps or brackets to prevent movement and damage.
E-Brake Handle and Mounting
The e-brake handle should be comfortable to grip and easy to operate. Consider the following:
- Handle Length: A longer handle provides more leverage, making it easier to lock the rear wheels. However, it may also take up more space in the cabin.
- Handle Angle: Choose a handle angle that is comfortable for your driving position.
- Mounting Location: Select a mounting location that is easily accessible and does not interfere with other controls. Ideally, it should be within easy reach of your steering wheel.
- Handle Quality: Choose a sturdy, well-built handle that can withstand repeated use.
Brake Calipers (If Upgrading)
While not always necessary, upgrading your rear brake calipers can significantly improve braking performance, especially if you're increasing the power output of your vehicle. Consider these factors:
- Caliper Size: Choose calipers that are appropriately sized for your vehicle's rear axle and braking requirements. Larger calipers typically provide more stopping power.
- Piston Count: Calipers with more pistons generally provide more even pad pressure and improved braking performance.
- Rotor Size: Ensure that the new calipers are compatible with your existing or upgraded brake rotors.
Hydro E-Brake Installation: Step-by-Step Guide
Disclaimer: Brake systems are critical safety components. If you are not comfortable working on brakes, seek professional assistance. Improper installation can lead to brake failure and serious injury.
- Preparation: Gather all necessary tools and materials, including the master cylinder, brake lines, fittings, e-brake handle, brake fluid (DOT 4 or DOT 5.1 recommended), wrenches, screwdrivers, a flaring tool (if needed), a brake bleeder kit, and safety glasses.
- Mounting the E-Brake Handle: Securely mount the e-brake handle in your chosen location. Ensure it is stable and within easy reach.
- Mounting the Master Cylinder: Install the hydro e-brake master cylinder. This may require fabricating a custom bracket to properly position and secure it.
- Running Brake Lines: Carefully route the brake lines from the master cylinder to the rear brake calipers. Secure the lines with clamps or brackets to prevent movement and chafing. Avoid sharp bends.
- Connecting Fittings: Connect the brake lines to the master cylinder and rear brake calipers using appropriate AN fittings or flare fittings. Ensure all connections are tight and leak-free.
- Bleeding the System: This is a critical step. Bleed the entire hydraulic system to remove any air. Start with the rear brake calipers farthest from the master cylinder and work your way closer. Use a brake bleeder kit to ensure a thorough bleed. Continue bleeding until you see a steady stream of brake fluid with no air bubbles.
- Testing: After bleeding the system, test the e-brake thoroughly in a safe environment. Ensure the rear wheels lock up smoothly and evenly when the e-brake is engaged. Check for any leaks.
- Adjustments: Adjust the e-brake handle and master cylinder as needed to achieve optimal performance and feel.
Important Considerations During Installation
- Safety First: Always wear safety glasses when working on brake systems. Brake fluid is corrosive and can cause eye irritation.
- Cleanliness: Keep all components clean and free from debris. Contamination can compromise the performance of the hydraulic system.
- Torque Specifications: Follow torque specifications for all fittings and fasteners. Over-tightening can damage components, while under-tightening can lead to leaks.
- Double-Check Connections: Before driving the vehicle, double-check all connections to ensure they are tight and leak-free.
- Professional Assistance: If you are unsure about any aspect of the installation process, seek professional assistance from a qualified mechanic.
Troubleshooting Common Hydro E-Brake Issues
Even with careful installation, issues can sometimes arise. Here are some common problems and their potential solutions:
- Soft or Spongy Pedal: This is often caused by air in the system. Re-bleed the entire system thoroughly.
- E-Brake Not Engaging: Check for leaks in the system. Ensure the master cylinder is properly primed and functioning. Adjust the handle and master cylinder linkage.
- Uneven Rear Wheel Lockup: This could be due to uneven brake pad wear, a faulty caliper, or air trapped in one of the rear brake lines. Inspect the brake pads and calipers and bleed the system again.
- Leaks: Inspect all fittings and connections for leaks. Tighten any loose fittings or replace damaged components.
Conclusion
Installing a hydro e-brake system can significantly enhance the braking performance and control of your vehicle. By carefully considering the design aspects and following the installation steps outlined in this guide, you can achieve a safe and effective upgrade. Remember to prioritize safety and seek professional assistance if needed. With a well-designed and properly installed hydro e-brake, you'll be well-equipped to tackle any performance driving challenge. Always prioritize safety and ensure your brake system is functioning optimally before driving your vehicle.
