Intake Manifold Installation And Airflow Optimization Techniques
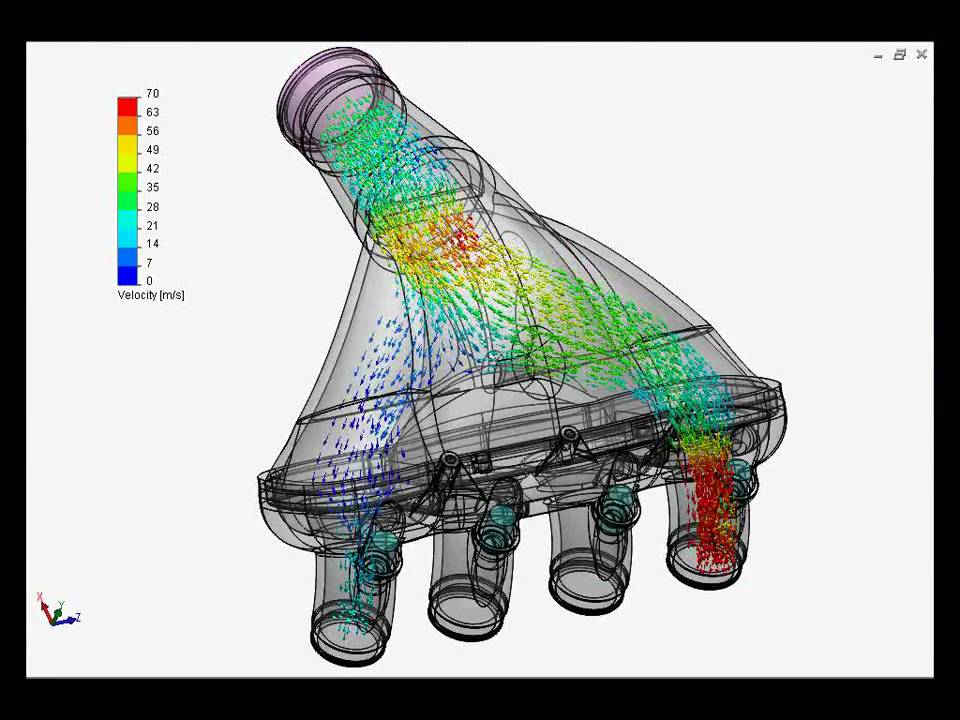
Upgrading your intake manifold can significantly improve your engine's performance by optimizing airflow. This article provides a comprehensive guide to intake manifold installation and airflow optimization techniques, suitable for both beginners and experienced car enthusiasts.
Understanding the Intake Manifold
The intake manifold is a crucial component of your engine's air intake system. Its primary function is to distribute air evenly to each cylinder, ensuring efficient combustion. The design and condition of the intake manifold directly impact engine performance, including horsepower, torque, and fuel efficiency.
A poorly designed or malfunctioning intake manifold can restrict airflow, leading to reduced engine power and poor fuel economy. Upgrading to a higher-performance intake manifold or optimizing the existing one can alleviate these issues.
Signs You May Need a New Intake Manifold
Several indicators suggest your intake manifold might need replacement or attention:
- Decreased engine performance: Noticeable loss of power and acceleration.
- Poor fuel economy: A sudden drop in miles per gallon.
- Rough idling: The engine vibrates or sputters when idle.
- Vacuum leaks: Hissing sounds or error codes related to vacuum leaks.
- Check engine light: Illuminated due to issues related to air-fuel mixture.
Intake Manifold Installation: A Step-by-Step Guide
Installing a new intake manifold requires careful attention and the right tools. Always consult your vehicle's service manual for specific instructions and torque specifications. Here's a general guide to the process:
1. Preparation and Safety
Before starting, disconnect the negative battery cable to prevent electrical shocks. Gather all necessary tools, including sockets, wrenches, torque wrench, screwdrivers, and a gasket scraper. Ensure you have a clean and well-lit workspace.
2. Removal of the Old Intake Manifold
a. Disconnect Sensors and Hoses: Carefully disconnect all sensors, vacuum lines, and fuel lines attached to the intake manifold. Label each connection to avoid confusion during reassembly.
b. Remove Throttle Body: Detach the throttle body from the intake manifold. Clean the throttle body thoroughly while it's removed.
c. Remove Fuel Rail: Disconnect the fuel rail and remove the fuel injectors. Handle fuel injectors with care.
d. Unbolt the Intake Manifold: Loosen and remove the intake manifold bolts in a specific sequence, typically starting from the center and working outwards. This prevents warping.
e. Remove the Old Manifold: Carefully lift the old intake manifold off the engine. Be cautious of any remaining coolant or debris.
3. Cleaning the Mating Surfaces
Thoroughly clean the engine's mating surface where the intake manifold sits. Use a gasket scraper to remove any old gasket material. Ensure the surface is smooth and free of debris to ensure a proper seal.
4. Installing the New Intake Manifold
a. Install New Gaskets: Place the new intake manifold gaskets onto the engine. Ensure they are properly aligned.
b. Position the Intake Manifold: Carefully position the new intake manifold onto the engine, aligning it with the gaskets and bolt holes.
c. Install the Bolts: Install the intake manifold bolts and tighten them in the correct sequence, according to the manufacturer's specifications. Use a torque wrench to ensure proper torque to avoid warping or leaks. Over-tightening can damage the manifold or engine block.
d. Reinstall Fuel Rail and Injectors: Reinstall the fuel rail and fuel injectors, ensuring they are properly seated and connected.
e. Reinstall Throttle Body: Reattach the throttle body to the intake manifold and tighten the bolts.
f. Reconnect Sensors and Hoses: Reconnect all sensors, vacuum lines, and fuel lines, referring to your labels to ensure proper connections.
5. Final Checks and Startup
Double-check all connections and ensure everything is properly secured. Reconnect the negative battery cable. Start the engine and listen for any leaks or unusual noises. Monitor the engine temperature and performance.
Airflow Optimization Techniques
Once the intake manifold is installed, you can further optimize airflow to maximize engine performance. Here are several techniques to consider:
1. Port Matching
Port matching involves aligning the intake manifold ports with the cylinder head ports. Misalignment can create turbulence and restrict airflow. Carefully grind or machine the intake manifold ports to match the cylinder head ports, creating a smooth transition for airflow.
2. Polishing
Polishing the intake manifold runners can reduce friction and improve airflow. A smooth surface minimizes air resistance, allowing for more efficient air delivery to the cylinders. Use abrasive tools and polishing compounds to achieve a mirror-like finish.
3. Using a Cold Air Intake
A cold air intake (CAI) system replaces the factory airbox with a system designed to draw cooler air into the engine. Cooler air is denser and contains more oxygen, which can improve combustion and increase horsepower. Be sure to choose a CAI system designed specifically for your vehicle.
4. Upgrading the Throttle Body
The throttle body controls the amount of air entering the intake manifold. Upgrading to a larger throttle body can increase airflow, especially at higher RPMs. This can result in improved throttle response and increased horsepower.
5. Tuning the Engine Control Unit (ECU)
After making modifications to the intake system, it's essential to tune the ECU to optimize the air-fuel ratio and ignition timing. A professional tuner can adjust the ECU settings to maximize the benefits of the airflow improvements. A dyno tune is highly recommended for best results.
6. Intake Manifold Spacers
Intake manifold spacers, also known as thermal intake gaskets, are designed to reduce heat transfer from the engine to the intake manifold. Keeping the intake manifold cooler can result in denser air, improving engine performance. These are generally inexpensive and easy to install.
Choosing the Right Intake Manifold
Selecting the correct intake manifold is crucial for achieving optimal performance gains. Consider the following factors when choosing an intake manifold:
- Engine Type: Ensure the intake manifold is designed specifically for your engine type (e.g., inline-four, V6, V8).
- Application: Determine whether you need a manifold for street, track, or off-road use. Different manifolds offer different performance characteristics.
- Performance Goals: Consider your desired performance gains (e.g., increased horsepower, torque, or fuel efficiency).
- Budget: Intake manifolds range in price from a few hundred dollars to several thousand. Set a budget and choose a manifold that fits your needs and financial constraints.
- Material: Intake manifolds are typically made of aluminum or composite materials. Aluminum offers excellent heat dissipation, while composite materials are lighter and can reduce heat soak.
Troubleshooting Common Intake Manifold Problems
Even with careful installation and optimization, intake manifold problems can sometimes arise. Here are some common issues and their potential solutions:
- Vacuum Leaks: Check all connections and gaskets for leaks. Use a vacuum gauge to diagnose vacuum leaks and replace any damaged components.
- Coolant Leaks: Inspect the intake manifold and gaskets for coolant leaks. Ensure the intake manifold bolts are properly torqued.
- Poor Idle: A faulty intake manifold can cause a rough or unstable idle. Check for vacuum leaks and ensure the throttle body is clean.
- Reduced Power: Restricted airflow can lead to reduced power. Check for obstructions in the intake manifold and ensure the air filter is clean.
Conclusion
Upgrading your intake manifold and optimizing airflow can significantly enhance your engine's performance. By following the steps outlined in this guide and addressing any potential issues, you can unlock your engine's full potential and enjoy improved horsepower, torque, and fuel efficiency. Always consult with a qualified mechanic or tuner for expert advice and assistance. Remember safety first, and happy tuning!
