Material Science Analysis Of Budget Coilover Components
Coilovers are a popular upgrade for vehicles, offering adjustable ride height and damping, which can significantly improve handling and performance. However, the performance and longevity of a coilover system heavily rely on the quality of its components. This article delves into the material science analysis of budget coilover components, examining the materials used, their properties, and the potential implications for performance and durability. Understanding these aspects is crucial for making informed decisions when selecting coilovers, especially when considering budget-friendly options.
Understanding Coilover Components and Material Selection
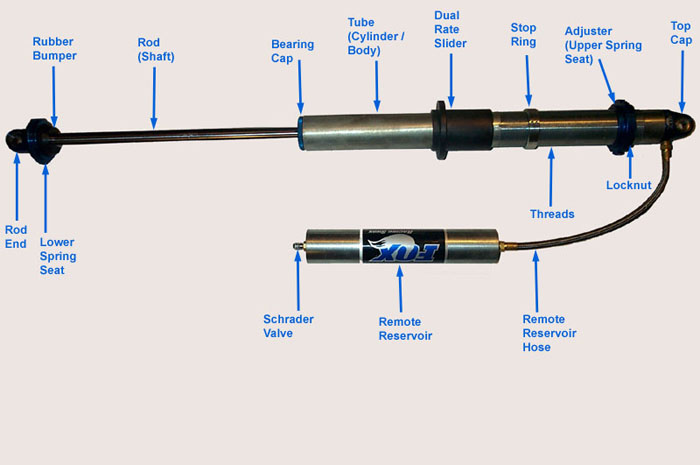
A typical coilover system consists of several key components, each with specific material requirements. The primary components we'll analyze are:
- Springs: Responsible for supporting the vehicle's weight and absorbing impacts.
- Shock Absorber (Damper): Controls the rate of compression and rebound, managing suspension movement.
- Coilover Body: The housing for the shock absorber, often threaded for height adjustment.
- Mounts: Connect the coilover to the vehicle's chassis.
Material selection plays a critical role in the performance and lifespan of each component. High-quality materials can withstand stress, resist corrosion, and maintain their properties over time. In contrast, budget coilovers often utilize less expensive materials, which can compromise performance and durability.
Spring Material Analysis
Coilover springs are typically made from steel alloys, with the most common being variations of spring steel. Higher-end coilovers often utilize alloys with higher tensile strength and fatigue resistance, allowing for thinner coils and lighter overall weight, while still maintaining the necessary load-bearing capacity. Common alloys include:
- SAE 9254: A silicon-manganese spring steel known for its good strength and toughness.
- Chrome Silicon Steel: Offers improved fatigue resistance and high-temperature performance compared to standard carbon steel.
Budget coilovers may use lower-grade steel, which can lead to several issues:
- Reduced Spring Rate Consistency: The spring rate (the amount of force required to compress the spring a certain distance) may deviate significantly from the advertised value, leading to inconsistent handling.
- Premature Sagging: The spring may lose its height over time, reducing ride height and potentially affecting handling.
- Increased Risk of Fracture: Lower-grade steel is more susceptible to fatigue and fracture, especially under repeated stress.
The manufacturing process of the spring also affects its quality. Shot peening, a process that introduces compressive stress to the surface of the spring, can significantly improve fatigue life. Budget coilovers may skip or inadequately perform this step, further reducing spring lifespan.
Shock Absorber Material Analysis
The shock absorber body is usually made from steel or aluminum. Aluminum is lighter and offers better heat dissipation, but it's also more expensive. Steel is more common in budget coilovers due to its lower cost. Internal components, such as the piston and valves, are typically made from steel or aluminum, with seals made from rubber or synthetic elastomers.
The quality of the materials used in the shock absorber affects its ability to control damping and dissipate heat. Budget coilovers often use:
- Lower-Quality Steel: Prone to corrosion and wear, potentially leading to leaks and reduced damping performance.
- Inferior Seals: Leakage of shock oil is a common problem with budget coilovers, leading to a loss of damping and eventual failure.
- Basic Piston Design: Simpler piston designs may not provide precise damping control across a wide range of speeds and conditions.
- Inadequate Oil: Cheaper shock oil can break down quickly under high temperatures, reducing damping performance and potentially damaging internal components.
Heat dissipation is crucial for maintaining consistent damping performance. Overheating can cause the shock oil to thin out, reducing its effectiveness. Aluminum shock bodies and larger oil reservoirs help to dissipate heat more efficiently. Budget coilovers may lack these features, leading to inconsistent damping performance under demanding conditions.
Coilover Body Material Analysis
The coilover body, typically made of steel or aluminum, houses the shock absorber and provides the threaded section for height adjustment. Aluminum offers weight savings and corrosion resistance, while steel is more affordable and stronger. Budget coilovers frequently employ steel bodies for cost savings.
Here's a material science perspective:
- Thread Quality: Poorly manufactured threads can be difficult to adjust and prone to seizing. Low-quality steel threads are also more susceptible to corrosion, further exacerbating this issue.
- Corrosion Resistance: Steel bodies are susceptible to rust and corrosion, especially in harsh environments. Budget coilovers may have inadequate protective coatings, leading to premature failure.
- Wall Thickness: Insufficient wall thickness can lead to bending or deformation under stress, affecting the shock absorber's performance.
Mount Material Analysis
Coilover mounts connect the system to the vehicle's chassis and are typically made from steel or aluminum. Bushings, which dampen vibrations and allow for some movement, are usually made from rubber or polyurethane.
Material deficiencies in mounts can lead to the following:
- Weak Mounting Points: Low-quality steel or improperly welded mounts can fail under stress, potentially leading to a dangerous situation.
- Bushing Degradation: Cheap rubber bushings can degrade quickly, leading to increased noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH). Polyurethane bushings are more durable but can transmit more vibration.
- Corrosion: Steel mounts are susceptible to corrosion, which can weaken the structure and make them difficult to remove.
The Trade-offs of Budget Coilovers
Choosing budget coilovers often involves significant trade-offs in material quality and manufacturing precision. While the initial cost may be appealing, the long-term consequences can include reduced performance, decreased durability, and potential safety concerns.
Investing in higher-quality coilovers, even if it means spending more upfront, can ultimately save money and provide a better driving experience in the long run.
Here's a summary of the key differences:
- Material Quality: Budget coilovers often use lower-grade steel, rubber, and plastics, leading to reduced strength, fatigue resistance, and corrosion resistance.
- Manufacturing Precision: Tolerances may be looser, leading to inconsistent damping performance and potential fitment issues.
- Durability: Budget coilovers are more likely to fail prematurely due to material degradation, corrosion, or component failure.
- Performance: Damping performance may be inconsistent, and spring rates may deviate from the advertised values, leading to unpredictable handling.
Making an Informed Decision
When selecting coilovers, it's important to consider your needs and budget. If you're primarily concerned with improving the appearance of your vehicle and don't plan on aggressive driving, budget coilovers may suffice. However, if you're looking for improved handling, performance, and durability, investing in higher-quality coilovers is generally recommended.
Here are some tips for making an informed decision:
- Research the Materials: Look for coilovers that use high-quality materials, such as SAE 9254 steel for springs and aluminum for shock bodies.
- Read Reviews: See what other users have to say about the performance and durability of the coilovers you're considering.
- Consider the Warranty: A longer warranty indicates that the manufacturer has confidence in the product's quality.
- Don't Just Focus on Price: Consider the long-term cost of ownership, including potential repairs and replacements. The cheapest option might not always be the best value.
- Consult with Experts: Talk to experienced mechanics or suspension specialists for their recommendations.
Ultimately, the best choice depends on your specific needs and priorities. By understanding the material science behind coilover components, you can make a more informed decision and choose a system that meets your requirements for performance, durability, and value.
