Nissan 240sx Idle Problems: Troubleshooting Guide
Nissan 240SX Idle Problems: A Troubleshooting Guide
The Nissan 240SX, a darling of the drift and tuner scenes, is known for its robust SR20DET or KA24DE engine and rear-wheel-drive platform. However, like any vehicle of its age, the 240SX can suffer from idle issues. These problems can range from a slightly high idle to a wildly fluctuating or even stalling engine. Understanding the common causes and how to diagnose them is crucial for keeping your 240SX running smoothly.
Understanding the Idle Control System
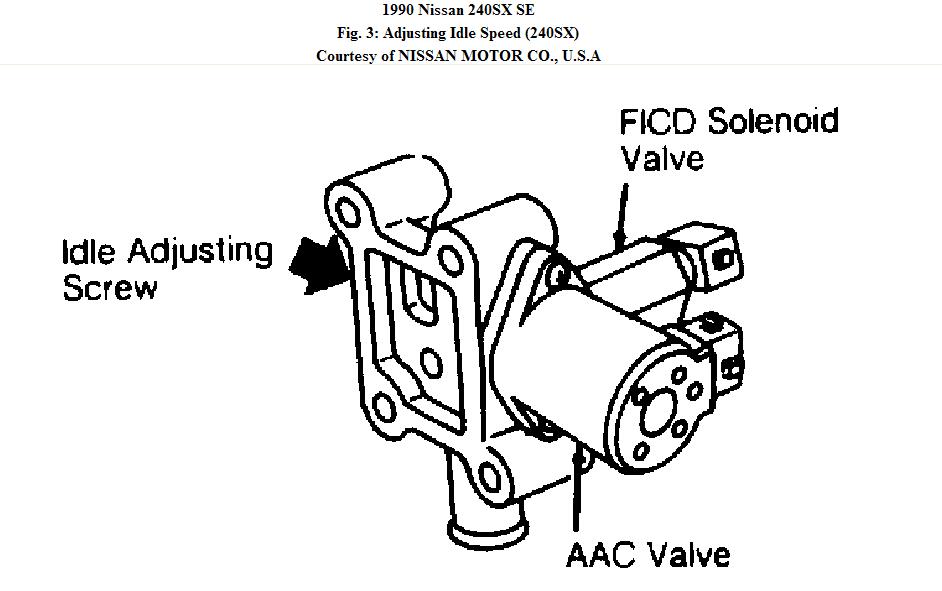
Before diving into specific troubleshooting steps, it's essential to grasp the basics of the 240SX's idle control system. The Engine Control Unit (ECU) is the brain of the operation, constantly monitoring various sensors and adjusting the Idle Air Control Valve (IACV) (also known as the Auxiliary Air Regulator or AAC valve in some models) to maintain a target idle speed. This target speed varies depending on engine temperature, electrical load (e.g., headlights, A/C), and other factors. The IACV bypasses the throttle plate, allowing air to flow into the engine even when the throttle is closed. The ECU adjusts the IACV's opening to precisely control the amount of bypassed air, and thus, the idle speed.
Several sensors provide crucial information to the ECU for idle control:
- Coolant Temperature Sensor (CTS): Informs the ECU about the engine's temperature. A cold engine requires a higher idle speed for stable operation.
- Throttle Position Sensor (TPS): Indicates the throttle's position. Although primarily for throttle response, the ECU needs to know when the throttle is fully closed for proper idle control.
- Mass Air Flow Sensor (MAF) (SR20DET models): Measures the amount of air entering the engine. A faulty MAF can skew fuel calculations and affect idle.
- Oxygen Sensor (O2 Sensor): Monitors the oxygen content in the exhaust. While primarily for fuel mixture control, an inaccurate O2 sensor can indirectly affect idle.
- Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS): Informs the ECU about vehicle speed. This is mainly for idle-up circuits and preventing stalling when coming to a stop.
Common Causes of Idle Problems and Troubleshooting Steps
Let's explore the common culprits behind 240SX idle issues and the steps to diagnose them:
1. Vacuum Leaks
Vacuum leaks are perhaps the most frequent cause of idle problems. Unmetered air entering the engine throws off the air-fuel ratio, leading to a high or erratic idle.
Troubleshooting:
- Visual Inspection: Carefully examine all vacuum hoses for cracks, splits, or disconnections. Pay close attention to hoses connected to the intake manifold, brake booster, IACV, and PCV valve.
- Spray Test: With the engine running, carefully spray small amounts of carburetor cleaner or starter fluid around vacuum hoses and intake manifold gaskets. If the idle speed changes when you spray a specific area, you've likely found a leak. Be extremely cautious when using flammable sprays near a hot engine!
- Smoke Test: A smoke test is a more professional method that involves introducing smoke into the intake system and observing where it escapes. This can pinpoint even small, difficult-to-find leaks.
Common Vacuum Leak Locations:
- Intake manifold gasket
- Throttle body gasket
- Vacuum hoses to the brake booster
- Vacuum hoses to the IACV
- PCV valve and hose
- Fuel injector O-rings
2. Faulty Idle Air Control Valve (IACV)
A malfunctioning IACV can prevent the ECU from properly regulating idle speed. The IACV motor can fail, the valve itself can become clogged with carbon deposits, or the wiring to the IACV can be damaged.
Troubleshooting:
- Visual Inspection: Check the IACV connector for corrosion or damage. Inspect the wiring harness for breaks or shorts.
- IACV Cleaning: Remove the IACV and thoroughly clean it with carburetor cleaner. Use a soft brush to remove carbon deposits. Ensure the valve moves freely after cleaning.
- IACV Function Test: With the IACV removed, manually move the valve. It should move smoothly. You can also apply 12V power to the IACV terminals (refer to the factory service manual for the correct polarity) to observe its movement.
- Voltage Test: Use a multimeter to check the voltage at the IACV connector with the ignition on. Refer to the factory service manual for the correct voltage readings.
- Resistance Test: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance across the IACV terminals. Compare your readings to the specifications in the factory service manual.
3. Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Issues
An improperly adjusted or faulty TPS can send incorrect signals to the ECU, affecting idle speed. The ECU needs to know when the throttle is fully closed to engage idle control.
Troubleshooting:
- TPS Adjustment: Use a multimeter to check the voltage at the TPS connector with the throttle closed. Adjust the TPS until the voltage is within the specified range (refer to the factory service manual).
- TPS Resistance Test: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance of the TPS as you slowly open and close the throttle. The resistance should change smoothly and linearly. Jerky or erratic changes indicate a faulty TPS.
- Visual Inspection: Check the TPS connector and wiring for damage.
4. Coolant Temperature Sensor (CTS) Problems
A faulty CTS can cause the ECU to misinterpret the engine's temperature, leading to incorrect idle speed adjustments. The engine might idle too high when warm or stall when cold.
Troubleshooting:
- Resistance Test: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance of the CTS at different engine temperatures. Compare your readings to the values in the factory service manual.
- Visual Inspection: Check the CTS connector and wiring for damage.
5. Mass Air Flow Sensor (MAF) Issues (SR20DET Models)
A dirty or failing MAF sensor can provide inaccurate air flow readings to the ECU, resulting in a poor air-fuel mixture and unstable idle.
Troubleshooting:
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the MAF sensor for physical damage or contamination.
- MAF Cleaning: Carefully clean the MAF sensor with MAF sensor cleaner. Do not use carburetor cleaner or other harsh solvents!
- MAF Voltage Test: With the engine running, use a multimeter to check the voltage output of the MAF sensor as you increase the engine speed. The voltage should increase smoothly and proportionally. Refer to the factory service manual for the correct voltage range.
- MAF Data Monitoring: If you have access to a scan tool, monitor the MAF sensor readings while the engine is running. Compare the readings to expected values.
6. Fuel System Problems
While less common, fuel system issues can indirectly affect idle. A clogged fuel filter, weak fuel pump, or faulty fuel injectors can lead to a lean air-fuel mixture and unstable idle.
Troubleshooting:
- Fuel Pressure Test: Use a fuel pressure gauge to check the fuel pressure at the fuel rail. The pressure should be within the specified range.
- Fuel Injector Inspection: Inspect the fuel injectors for leaks or damage. Consider having them professionally cleaned and flow-tested.
- Fuel Filter Replacement: Replace the fuel filter as part of regular maintenance.
7. Electrical Issues
Loose or corroded electrical connections can disrupt the signals from sensors to the ECU, leading to idle problems. Grounding issues are particularly common in older vehicles.
Troubleshooting:
- Visual Inspection: Thoroughly inspect all wiring harnesses, connectors, and ground connections for corrosion, damage, or looseness.
- Grounding Verification: Ensure all engine and chassis grounds are clean and securely fastened. Add additional ground straps if necessary.
- Voltage Drop Test: Use a multimeter to measure the voltage drop across various circuits. Excessive voltage drop indicates a wiring problem.
Using a Scan Tool
A scan tool can be a valuable tool for diagnosing idle problems. It allows you to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitor sensor data in real-time, and perform actuator tests. While older 240SX models might not have the most sophisticated diagnostic capabilities, a basic scan tool can still provide valuable information.
Conclusion
Troubleshooting idle problems on a Nissan 240SX can be a challenging but rewarding task. By understanding the idle control system, systematically checking for common issues, and using appropriate diagnostic tools, you can often identify and resolve the problem yourself. Remember to consult the factory service manual for specific procedures and specifications. Safety is paramount, so always disconnect the battery before working on the electrical system and take precautions when working around flammable fluids. Good luck!
