Oem Fog Light Wattage And Beam Pattern Specifications
Fog lights, those low-mounted auxiliary lights on your vehicle, play a crucial role in improving visibility during adverse weather conditions like fog, heavy rain, and snow. Understanding their wattage and beam pattern specifications, particularly for Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) fog lights, is essential for maintaining optimal performance and safety. This article will delve into the technical aspects of OEM fog light specifications, helping you make informed decisions when replacing or upgrading them.
Wattage Specifications: Power and Performance
Wattage, measured in watts (W), is a direct indicator of the electrical power consumed by the fog light. It's a key factor influencing the light's brightness and heat output. OEM fog lights are designed with specific wattage ratings to comply with safety standards and vehicle electrical system limitations. Straying significantly from these OEM specifications can lead to several issues.
OEM Standard Wattage: Why It Matters
OEM fog lights typically range from 35W to 55W per bulb. This range is carefully chosen by the vehicle manufacturer to strike a balance between brightness, energy consumption, and heat generation. Using a bulb with a significantly higher wattage than the OEM specification can overload the vehicle's electrical system, potentially causing:
- Blown fuses: The increased current draw can exceed the fuse's capacity, leading to frequent fuse failures.
- Damaged wiring: Excessive heat can melt or damage the wiring harness connected to the fog lights.
- Reduced bulb lifespan: Overdriving the bulb can significantly shorten its lifespan.
- Headlight switch or relay failure: The increased load can damage the switch or relay controlling the fog lights.
Conversely, using a bulb with a significantly lower wattage than the OEM specification may result in insufficient brightness, defeating the purpose of fog lights altogether.
Understanding Electrical Load and Resistance
To fully grasp the importance of wattage, it's helpful to understand the relationship between voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) according to Ohm's Law: V = IR. The wattage (P) is then calculated as P = VI. When replacing fog light bulbs, you are essentially changing the resistance (R) in the circuit. If you use a bulb with lower resistance (higher wattage), the current (I) increases, potentially overloading the system. OEM bulbs are selected to maintain the correct resistance for the given voltage and circuit design.
For example, a 55W bulb operating at 12V draws approximately 4.6 amps (55W / 12V ≈ 4.6A). If you were to install an 80W bulb, the current draw would increase to approximately 6.7 amps (80W / 12V ≈ 6.7A). This 2.1 amp increase could easily trip a 5 amp fuse.
LED Replacements: A Modern Alternative
LED (Light Emitting Diode) fog lights have become increasingly popular as replacements for traditional halogen bulbs. LEDs offer several advantages, including:
- Lower power consumption: LEDs produce more light per watt than halogen bulbs, resulting in less strain on the electrical system.
- Longer lifespan: LEDs typically last significantly longer than halogen bulbs.
- Brighter light output: LEDs can produce a brighter, more focused beam.
However, when choosing LED replacements, it's crucial to consider the equivalent wattage. Many LED manufacturers advertise their bulbs based on the equivalent light output compared to a halogen bulb. For example, an LED bulb might be advertised as a "55W equivalent" while only consuming 10W. This means it produces the same amount of light as a 55W halogen bulb but only draws 10W of power. This is the information you should prioritize.
It's also important to ensure that the LED bulb is compatible with your vehicle's electrical system. Some vehicles may require a CAN bus (Controller Area Network) compatible LED bulb to avoid error codes or flickering. These CAN bus LEDs have built-in resistors that mimic the electrical characteristics of a halogen bulb, preventing the vehicle's computer from detecting a fault.
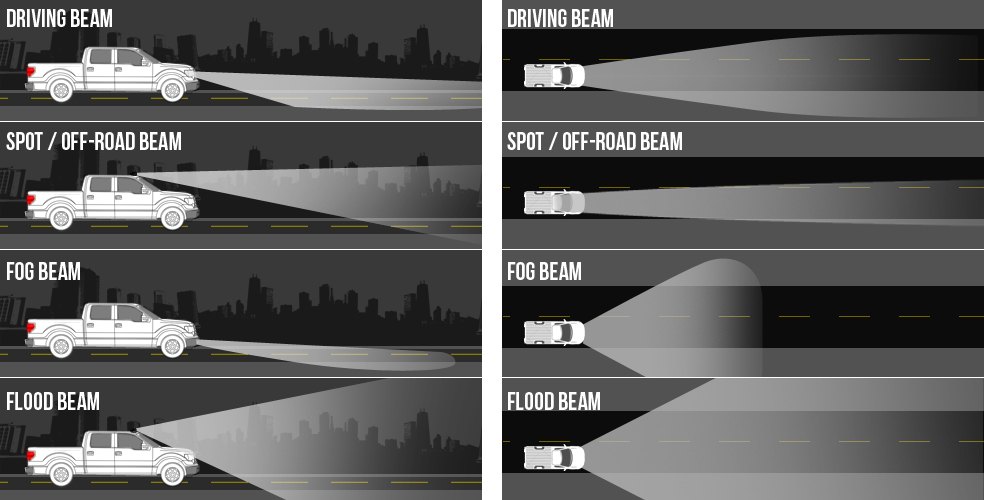
Beam Pattern Specifications: Directing the Light
The beam pattern refers to the shape and direction of the light emitted by the fog light. OEM fog lights are designed with a specific beam pattern to maximize visibility in foggy or adverse conditions without blinding other drivers. The ideal fog light beam pattern is wide and flat, projecting a low, broad beam of light that illuminates the road surface and the edges of the road.
Horizontal Spread and Vertical Cutoff
The horizontal spread refers to the width of the beam, while the vertical cutoff refers to the height of the beam. A wide horizontal spread is essential for illuminating the sides of the road, allowing you to see potential hazards like pedestrians, cyclists, or animals. A sharp vertical cutoff is crucial for preventing glare and blinding oncoming drivers.
OEM fog lights typically have a beam pattern that is significantly wider and lower than the beam pattern of headlights. This is because fog tends to hover close to the ground, and a low-mounted, wide beam can penetrate the fog more effectively.
SAE and ECE Standards
Fog light beam patterns are often regulated by standards set by organizations like the SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) in the United States and the ECE (Economic Commission for Europe) in Europe. These standards specify the minimum and maximum light intensity at various points within the beam pattern to ensure that the fog lights provide adequate visibility without causing excessive glare. Lights meeting these standards will often be marked with the SAE or ECE logo, indicating that they have been tested and certified to meet the requirements.
Types of Beam Patterns
While the ideal fog light beam pattern is generally wide and flat, there can be variations depending on the specific vehicle and the intended use. Some common types of beam patterns include:
- Driving beam: A driving beam is a long-range, focused beam designed for high-speed driving on open roads. While useful, it can create excessive glare in foggy conditions.
- Flood beam: A flood beam is a wide, diffused beam designed for illuminating a large area. It's ideal for off-road use or low-speed maneuvering but may not provide sufficient range for highway driving.
- Combination beam: A combination beam combines the characteristics of a driving beam and a flood beam, offering a balance of range and width.
When replacing OEM fog lights, it's essential to choose a beam pattern that is appropriate for your driving needs and the typical weather conditions in your area. If you frequently drive in foggy conditions, a wide, flat beam is the best choice. If you primarily drive on open roads, a combination beam may be more suitable.
Projector vs. Reflector Fog Lights
Fog lights come in two primary designs: projector and reflector. Reflector fog lights use a curved reflector to focus and direct the light from the bulb. Projector fog lights use a lens to focus the light, resulting in a more precise and controlled beam pattern. Projector fog lights generally offer better beam control and reduced glare compared to reflector fog lights, but reflector fog lights can be more affordable.
When upgrading fog lights, consider the type of lens design. Projector-style fog lights are often favored for their focused beam pattern, reducing glare and enhancing visibility. However, the best choice ultimately depends on individual preferences and budget.
Adjusting Fog Light Aim
Properly aiming fog lights is crucial for maximizing their effectiveness and preventing glare. Most fog lights have adjustable screws that allow you to adjust the vertical aim. To aim your fog lights, park your vehicle on a level surface about 25 feet away from a wall. Turn on your fog lights and observe the beam pattern on the wall. The top of the beam should be no higher than 4 inches below the height of the fog light itself. Adjust the aiming screws until the beam is properly positioned.
Conclusion
Understanding the wattage and beam pattern specifications of OEM fog lights is essential for maintaining optimal visibility and safety in adverse weather conditions. By adhering to OEM wattage recommendations, you can avoid overloading your vehicle's electrical system and ensure the longevity of your fog lights. Choosing a beam pattern that is appropriate for your driving needs and properly aiming your fog lights will maximize their effectiveness and minimize glare to other drivers. When selecting replacement or upgrade options, prioritizing SAE or ECE-certified lights ensures compliance with safety standards, giving you peace of mind and enhancing your driving experience.
