One-piece Driveshaft Material Properties And Balance
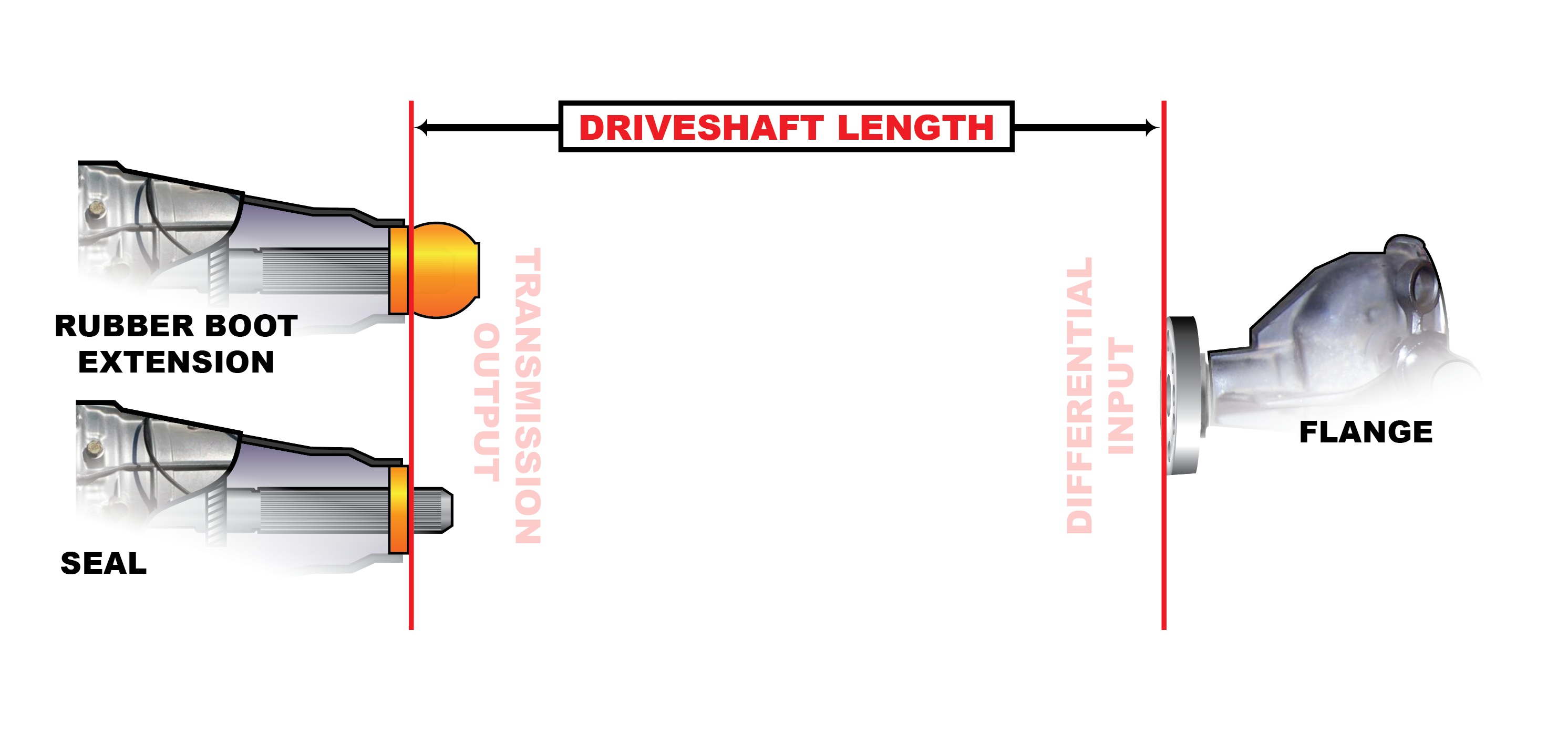
Hey folks, ever experienced a mysterious vibration creeping into your ride, especially at higher speeds? Or maybe a clunking sound during acceleration or deceleration? There’s a good chance your driveshaft might be the culprit. Today, we’re diving into the world of one-piece driveshafts, focusing on what they’re made of and why balance is absolutely critical. Think of me as your friendly neighborhood mechanic, here to help you diagnose and (hopefully) solve these frustrating issues.
Understanding One-Piece Driveshafts
Unlike multi-piece driveshafts that require center support bearings, a one-piece driveshaft connects the transmission directly to the differential. This design is simpler, potentially lighter, and reduces the number of potential failure points. However, it’s not without its challenges, and that's where material properties and balance become paramount.
Material Matters: Choosing the Right Metal
The material used in a one-piece driveshaft significantly impacts its strength, weight, and ability to handle rotational forces. The two most common materials are steel and aluminum, each with its own pros and cons:
- Steel: Steel driveshafts are generally more robust and can withstand higher torque loads. They’re a cost-effective solution, making them a common choice for trucks, SUVs, and high-performance applications. However, steel is heavier than aluminum, which can slightly impact fuel economy and acceleration. Think of a heavy-duty work truck – steel is usually the way to go.
- Aluminum: Aluminum driveshafts offer a significant weight reduction compared to steel. This lighter weight improves throttle response, acceleration, and even braking performance. They’re often found in performance cars and vehicles where weight savings are a priority. However, aluminum is less rigid than steel and can be more prone to bending or damage under extreme stress.
- Carbon Fiber: While less common, carbon fiber driveshafts offer the ultimate in weight savings and strength. They are significantly lighter than both steel and aluminum and can handle incredible amounts of torque. However, they are also considerably more expensive and primarily used in high-end performance vehicles and racing applications. The cost is usually a significant barrier for most daily drivers.
The choice of material often depends on your vehicle's intended use and your budget. If you're towing heavy loads, steel is likely the better option. If you're looking for performance gains, aluminum or carbon fiber might be worth considering. But remember, with performance upgrades, you might need to upgrade other components as well, such as the U-joints.
The Importance of Driveshaft Balance
Now, let's talk about balance. Balance is absolutely critical for a smooth-running driveshaft. An imbalanced driveshaft can cause vibrations, noise, premature wear on other drivetrain components (like your transmission and differential), and even structural damage. Imagine a washing machine with clothes all bunched up on one side – that’s essentially what an imbalanced driveshaft feels like to your vehicle, only much faster!
Why does a driveshaft become imbalanced? Several factors can contribute, including:
- Manufacturing defects: Even with modern manufacturing processes, slight imperfections can exist.
- Damage from road debris: Hitting a pothole or running over something can bend or dent the driveshaft.
- Worn U-joints: Excessive play in the U-joints can throw off the balance.
- Improper installation: Not aligning the driveshaft correctly during installation can lead to imbalance.
Diagnosing Driveshaft Problems
So, how do you know if your driveshaft is causing problems? Here are some common symptoms:
- Vibration: This is the most common symptom. The vibration usually increases with speed and can be felt through the floorboards, seats, or steering wheel.
- Noise: Clunking, squeaking, or grinding noises, especially during acceleration or deceleration, can indicate a driveshaft issue. A rhythmic thumping can also point to balance issues.
- Shaking: A more severe vibration can manifest as a noticeable shaking of the entire vehicle.
- Difficulty steering: In some cases, a severely imbalanced driveshaft can affect steering stability.
Before you jump to conclusions and blame the driveshaft, it’s wise to rule out other potential causes of vibrations, such as:
- Tire imbalance: This is a very common cause of vibration and should be checked first.
- Wheel bearing issues: Worn wheel bearings can create noise and vibration.
- Suspension problems: Worn shocks, struts, or bushings can contribute to vibrations.
- Engine misfires: Misfires can cause a rough running engine that translates into vibrations.
Tools and Techniques for Inspection
If you suspect a driveshaft problem, here's how you can perform a basic inspection (always prioritize safety and use proper precautions when working under a vehicle):
- Visual inspection: Look for any signs of damage, such as dents, bends, or cracks. Check the U-joints for excessive play. A small pry bar can help you check for movement in the U-joints.
- Runout test: With the vehicle safely supported on jack stands, use a dial indicator to measure the driveshaft's runout (how much it deviates from a straight line) while rotating it by hand. Excessive runout indicates a bent or damaged driveshaft.
- Listening test: Have a friend slowly drive the vehicle while you listen for noises coming from the driveshaft area. A mechanic's stethoscope can be helpful.
Tools you might need:
- Jack and jack stands
- Safety glasses
- Gloves
- Pry bar
- Dial indicator (optional, but highly recommended for runout testing)
- Mechanic's stethoscope (optional)
Solutions: Repair or Replace?
Once you've identified a driveshaft problem, you have a few options:
- Driveshaft Balancing: If the driveshaft is simply out of balance (but not damaged), a professional balancing shop can correct it. They'll use specialized equipment to spin the driveshaft and add weights to specific locations to achieve perfect balance. This is often the most cost-effective solution for minor imbalance issues. Expect to pay around $100-$300 for balancing.
- U-Joint Replacement: If the U-joints are worn or damaged, they can be replaced. This is a relatively straightforward repair, although it can be a bit messy. U-joint replacement typically costs between $50 and $200 per U-joint, depending on the vehicle and the shop's labor rates.
- Driveshaft Repair: Minor dents or bends can sometimes be repaired, but this is best left to professionals. Welding repairs on a driveshaft require specialized equipment and expertise to ensure proper balance and strength.
- Driveshaft Replacement: If the driveshaft is severely damaged (e.g., bent, cracked, or significantly out of balance), replacement is usually the best option. A new driveshaft can range in price from $300 to $1500 or more, depending on the material and vehicle. Installation costs can add another $100 to $500, depending on the complexity of the job.
Practical Tips and Considerations
Before making a decision, consider these points:
- Get a professional opinion: If you're not comfortable diagnosing or repairing the driveshaft yourself, take it to a qualified mechanic. They can accurately assess the problem and recommend the best solution.
- Choose quality parts: When replacing U-joints or the entire driveshaft, opt for reputable brands. Cheap parts may fail prematurely, leading to further problems.
- Consider the long-term costs: While repairing a driveshaft may seem cheaper in the short term, replacing it might be a better investment if it's severely damaged or has a history of problems.
- Proper Installation: Ensure the driveshaft is installed correctly and that all bolts are torqued to the manufacturer's specifications. This is crucial for preventing future problems.
Finally, remember preventative maintenance! Regularly inspect your driveshaft for signs of wear and tear. Lubricate the U-joints (if they have grease fittings) according to the manufacturer's recommendations. Avoid driving aggressively over potholes or other road hazards, which can damage the driveshaft.
By understanding the material properties and balance requirements of your one-piece driveshaft, you can better diagnose and address any issues that arise, keeping your ride smooth and enjoyable. Drive safe!
