Spark Plug Wire Resistance And Emi Shielding Analysis
Alright, let's talk spark plug wires – a seemingly simple component that plays a crucial role in your engine's performance. We're going to dive into two key aspects: resistance and EMI shielding. Understanding these will not only help you diagnose potential problems but also inform your choices when upgrading or replacing your wires.
Spark Plug Wire Resistance: A Balancing Act
The primary function of a spark plug wire is to deliver the high-voltage pulse from the ignition coil to the spark plug, igniting the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber. However, wires aren't perfect conductors. They offer some resistance, which is the opposition to the flow of electrical current. This resistance is measured in ohms (Ω).
Why Resistance Matters
You might think zero resistance is ideal, but that's not entirely true. A small amount of resistance is actually beneficial. Here’s why:
- Reduced Radio Frequency Interference (RFI): Resistance helps dampen high-frequency oscillations that can generate RFI. We’ll cover EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) in more detail later, but understand that RFI is a type of EMI.
- Prevents Spark Plug Erosion: A little resistance helps to control the spark energy, which can extend the life of your spark plugs by preventing excessive erosion of the electrodes. Too much spark energy, delivered too quickly, can pit and wear down the spark plug electrode.
However, excessive resistance is a problem. It weakens the spark, leading to:
- Misfires: The spark may not be strong enough to ignite the fuel mixture consistently.
- Reduced Power: A weak spark results in incomplete combustion, reducing engine output.
- Poor Fuel Economy: Unburnt fuel is wasted, lowering your gas mileage.
- Rough Idle: Inconsistent firing can cause the engine to run unevenly at idle.
Types of Spark Plug Wires and Their Resistance
Spark plug wires are generally categorized based on their construction and the materials used, which directly affects their resistance:
- Solid Core Wires: These are the simplest type, typically made of a solid copper strand. They offer very low resistance, often less than 50 ohms per foot. However, they are a major source of RFI and are generally not recommended for modern vehicles with sensitive electronics. They were common on older cars.
- Carbon Core (Suppression Core) Wires: These wires use a fiberglass or Kevlar core coated with a carbon-impregnated latex. The carbon provides the resistance needed to suppress RFI. Resistance is typically much higher, ranging from 5,000 to 15,000 ohms per foot. These are a common and cost-effective option.
- Spiral-Wound Wires: These are considered the best compromise between performance and RFI suppression. They use a metallic (usually copper alloy) conductor wound in a spiral around a non-conductive core. This design provides a low-resistance path for the high-voltage current while still suppressing RFI. Resistance is usually in the range of 500 to 5,000 ohms per foot.
Testing Spark Plug Wire Resistance
You can easily test spark plug wire resistance using a digital multimeter (DMM). Here's how:
- Set the DMM to the Ohms (Ω) setting. Make sure it's set to a range high enough to read the expected resistance (e.g., 20kΩ).
- Disconnect the spark plug wire from both the spark plug and the distributor or coil pack. This isolates the wire for accurate testing.
- Touch one probe of the DMM to one end of the wire and the other probe to the other end.
- Read the resistance value displayed on the DMM.
- Compare the reading to the manufacturer's specifications. These specifications are usually provided in your vehicle's service manual or the spark plug wire manufacturer's documentation. As a general rule, if the resistance is significantly higher than the specification (e.g., more than 20% higher), the wire should be replaced.
Important Considerations:
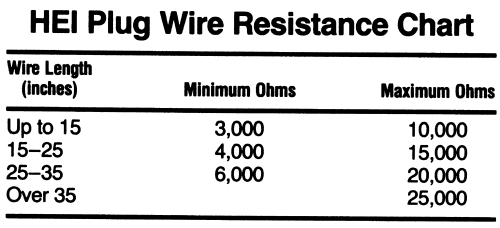
- Wire Length: Longer wires will naturally have higher resistance. The manufacturer's specifications will typically account for the wire length.
- Temperature: Resistance can change slightly with temperature. Test the wires at room temperature for the most accurate results.
- Damaged Wires: Visually inspect the wires for any signs of damage, such as cracks, cuts, or burns. Damaged wires should be replaced regardless of their resistance readings.
EMI Shielding: Protecting Your Electronics
Now let’s talk about Electromagnetic Interference (EMI). When a high-voltage pulse travels through a spark plug wire, it generates electromagnetic radiation. This radiation can interfere with sensitive electronic components in your vehicle, such as the engine control unit (ECU), sensors, and audio systems. This interference can manifest as anything from static in your radio to drivability problems caused by corrupted ECU signals.
How EMI Shielding Works
EMI shielding aims to contain this electromagnetic radiation and prevent it from interfering with other components. This is typically achieved through the use of a conductive layer, such as a braided metal shield or a conductive coating, around the spark plug wire. This shield acts as a Faraday cage, which is an enclosure that blocks electromagnetic fields.
The shielding works by intercepting the electromagnetic waves and conducting them to ground. This essentially short-circuits the radiation and prevents it from propagating into the surrounding environment.
Types of EMI Shielding
Here are some common methods used to shield spark plug wires:
- Braided Metal Shield: This is the most effective type of shielding, consisting of a tightly woven braid of metal (typically copper or stainless steel) surrounding the wire. The braid provides excellent coverage and conductivity.
- Conductive Coating: Some spark plug wires use a conductive coating, such as a carbon-impregnated polymer, to provide shielding. This is a less expensive option than a braided shield, but it may not be as effective.
- Resistor Spark Plugs: While not technically part of the spark plug wire, resistor spark plugs also play a crucial role in reducing EMI. They incorporate a resistor within the spark plug itself, which helps to dampen the high-frequency oscillations and reduce the amount of EMI generated at the spark plug gap. It's crucial to use resistor-type spark plugs with modern electronic ignitions.
Diagnosing EMI Issues
Diagnosing EMI issues can be tricky, as the symptoms can be varied and intermittent. Here are some things to look for:
- Radio Interference: Static or noise in your radio, especially when the engine is running.
- Sensor Problems: Erratic sensor readings or error codes related to sensors.
- ECU Malfunctions: Unexplained drivability issues, such as stalling, misfires, or poor performance.
If you suspect EMI issues, try these troubleshooting steps:
- Inspect Spark Plug Wires: Check for damaged or deteriorated shielding. Look for cracks, cuts, or loose connections.
- Ensure Proper Grounding: Make sure all engine and chassis grounds are clean and secure. Poor grounding can exacerbate EMI problems.
- Check Spark Plugs: Verify that you are using the correct resistor-type spark plugs for your vehicle.
- Shielded Wires: Consider upgrading to spark plug wires with better EMI shielding, such as those with a braided metal shield.
Upgrading Spark Plug Wires: Choosing Wisely
When upgrading your spark plug wires, consider both resistance and EMI shielding. Don't just focus on the lowest resistance possible. A low-resistance wire without proper shielding can create more problems than it solves. Here's a brief guideline:
- Modern Vehicles (with ECUs): Choose spiral-wound wires with good EMI shielding (braided shield is ideal) or high quality carbon core wires. Ensure you're using resistor-type spark plugs.
- Older Vehicles (without ECUs): Solid core wires are an option, but even then, shielded spiral wound wires are often a better choice for reducing radio interference.
Ultimately, the best spark plug wires for your vehicle will depend on your specific needs and driving conditions. Do your research, read reviews, and choose a reputable brand.
By understanding the principles of spark plug wire resistance and EMI shielding, you can make informed decisions about your ignition system and keep your engine running smoothly and reliably. Remember to always consult your vehicle's service manual for specific recommendations and specifications.
