Which Of The Following Process Map Symbols Signifies A Delay
Understanding process maps is crucial for anyone involved in business process improvement, project management, or even just trying to understand how things work within an organization. These visual representations break down complex processes into simple, easy-to-follow steps. However, interpreting the symbols used in process maps correctly is essential for accurate analysis and process optimization. One important symbol to understand is the one that signifies a delay.
What is a Process Map?
Before diving into the specific symbol for a delay, let's quickly recap what a process map is. A process map, also known as a flowchart, is a diagram that illustrates the sequence of activities in a process. It uses standardized symbols to represent different types of actions, decisions, and events. The goal of a process map is to:
- Visually represent a process from start to finish.
- Identify potential bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
- Improve communication and collaboration among team members.
- Standardize processes and ensure consistency.
- Analyze and optimize processes for better performance.
By creating a clear visual representation of a process, organizations can gain valuable insights into how work is performed and identify opportunities for improvement. Different variations of process maps exist, each suited for specific needs and levels of detail. Some common types include:
- Basic Flowchart: A simple representation of the process sequence.
- Deployment Flowchart (Swimlane Diagram): Shows the responsibilities of different individuals or departments involved in the process.
- Value Stream Map: Focuses on identifying value-added and non-value-added activities in a process.
- SIPOC Diagram: A high-level overview of a process, including Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, and Customers.
Common Process Map Symbols
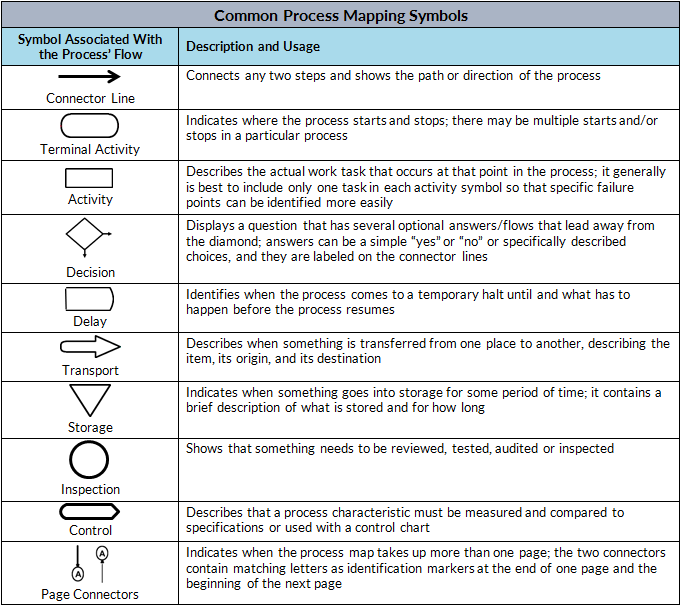
Process maps use a variety of symbols, each with a specific meaning. Understanding these symbols is crucial for correctly interpreting and analyzing a process map. Here are some of the most common symbols you'll encounter:
- Oval (Terminator): Represents the start or end of a process.
- Rectangle (Process): Represents a specific task or activity within the process.
- Diamond (Decision): Represents a point where a decision needs to be made, often leading to different paths.
- Arrow (Flow Line): Indicates the direction of flow and the sequence of activities.
- Circle (Connector): Used to connect different parts of a process map, especially when the flow is interrupted or spans multiple pages.
- Parallelogram (Input/Output): Represents data or materials entering or leaving the process.
Which Symbol Signifies a Delay?
The process map symbol that signifies a delay is typically represented by a D-shape, sometimes resembling a capital 'D' lying on its side or a curved line. This symbol indicates a period of waiting or inactivity within the process. It highlights a point where the process is held up, often due to a lack of resources, approval delays, or other waiting periods.
Identifying delays is crucial for process improvement because these periods of inactivity often represent wasted time and resources. By pinpointing the sources of delays, organizations can implement strategies to reduce or eliminate them, ultimately improving process efficiency and reducing cycle time.
Examples of Delays in a Process Map
To illustrate how the delay symbol is used in practice, here are a few examples:
- Waiting for Approval: In a procurement process, a delay might occur while waiting for a manager to approve a purchase order. The D-shape symbol would be placed after the 'Submit Purchase Order' activity and before the 'Order Approved' activity.
- Queue Time: In a manufacturing process, a delay could represent the time materials spend waiting in a queue before being processed. The D-shape symbol would be placed before the 'Process Material' activity.
- Information Lag: In a customer service process, a delay might occur while waiting for information from another department. The D-shape symbol would be placed before the 'Respond to Customer' activity.
When using the delay symbol, it's important to include a descriptive label that explains the reason for the delay and its potential impact on the process. For example, the label might read "Waiting for Management Approval (Estimated Delay: 2 days)" or "Materials Waiting in Queue (Average Delay: 4 hours)."
Why are Delays Important to Identify?
Identifying and analyzing delays is a critical step in process improvement for several reasons:
- Reduced Cycle Time: Delays directly contribute to longer cycle times, which is the total time it takes to complete a process. By eliminating or reducing delays, organizations can significantly shorten cycle times and deliver faster results.
- Improved Efficiency: Delays often indicate inefficiencies in the process. By identifying the root causes of delays, organizations can implement solutions to streamline the process and improve overall efficiency.
- Reduced Costs: Delays can lead to increased costs, such as inventory holding costs, labor costs, and opportunity costs. By minimizing delays, organizations can reduce these costs and improve profitability.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Delays can negatively impact customer satisfaction. By reducing delays, organizations can deliver faster and more responsive service, leading to happier customers.
- Better Resource Utilization: Delays can tie up resources, preventing them from being used for other productive activities. By eliminating delays, organizations can free up resources and improve resource utilization.
How to Address Delays Identified in a Process Map
Once you've identified delays in your process map, the next step is to develop strategies to address them. Here are some common approaches:
- Process Redesign: Consider redesigning the process to eliminate the need for the activity that causes the delay. Can steps be combined, automated, or eliminated altogether?
- Resource Allocation: Ensure that adequate resources are available to prevent bottlenecks. This may involve increasing staffing levels, investing in new equipment, or improving resource scheduling.
- Process Automation: Automate manual tasks to reduce human error and speed up the process. This can involve using software, robotics, or other technologies.
- Improved Communication: Improve communication and collaboration among team members to reduce delays caused by miscommunication or lack of information.
- Standardization: Standardize processes and procedures to ensure consistency and reduce variability.
- Bottleneck Analysis: Conduct a thorough bottleneck analysis to identify the most significant constraints in the process and develop targeted solutions.
- Prioritization: Implement a system for prioritizing tasks and projects to ensure that the most important activities are completed first.
For example, if the delay is caused by waiting for management approval, you might implement a faster approval process, delegate approval authority to lower-level employees, or automate the approval process using a workflow management system.
Conclusion
Understanding process map symbols is essential for effective process analysis and improvement. The D-shape symbol specifically represents a delay within a process, highlighting areas where time is being wasted. By identifying and addressing delays, organizations can improve efficiency, reduce costs, enhance customer satisfaction, and achieve better overall performance. Remember to clearly label the delay symbol with a description of the reason for the delay and its potential impact on the process. Regularly review and update your process maps to ensure they accurately reflect your current processes and to identify new opportunities for improvement. Using process maps correctly and addressing delays proactively will lead to significant improvements in your organization's efficiency and productivity.
