How Do I Charge A Nissan Leaf
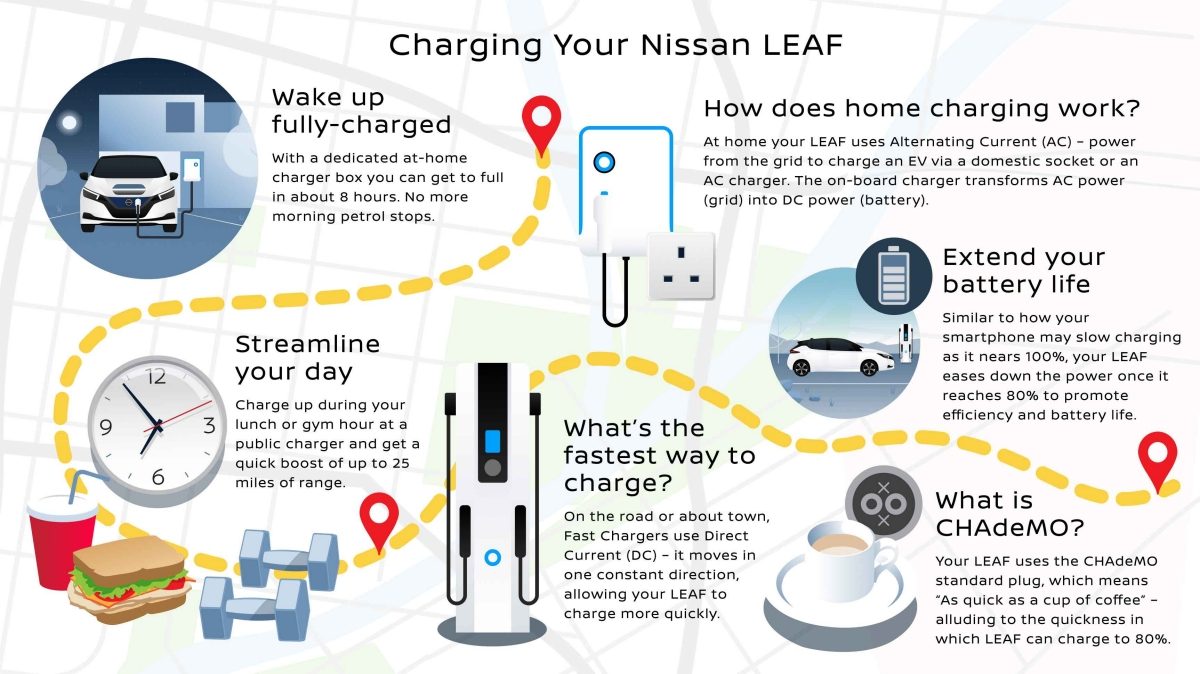
So, you're diving into the world of electric vehicles (EVs) and want to understand the ins and outs of charging your Nissan Leaf? Excellent! Knowing how your Leaf charges is crucial not just for everyday use, but also for performing your own maintenance, troubleshooting potential problems, and even exploring modifications down the road. Think of this guide as your deep dive into the Leaf's charging system, giving you the knowledge you need to keep your electric ride running smoothly.
Purpose of Understanding the Nissan Leaf Charging System
Why bother understanding the intricacies of the Leaf's charging system? Several reasons come to mind:
- Troubleshooting: When your Leaf refuses to charge, knowing the components and their functions allows you to pinpoint the problem, potentially saving you a trip to the dealership.
- Maintenance: Understanding the charging system can help you identify potential issues early, allowing for preventative maintenance.
- Modification: For the more adventurous DIYer, understanding the system opens doors to modifications, such as upgrading the charging port or exploring alternative charging methods (with the proper safety precautions, of course!).
- Education: Simply understanding how your car works is empowering.
Key Specs and Main Parts
Let's break down the core components of the Nissan Leaf's charging system and some key specifications:
Key Specifications (varies slightly by model year):
- Charging Voltage: Primarily 120V (Level 1) and 240V (Level 2). Some models support DC Fast Charging.
- Charging Current: Varies depending on the charger and your Leaf's onboard charger capabilities.
- Battery Capacity: Ranging from 24 kWh to 62 kWh, depending on the model year and trim.
- Charging Port: SAE J1772 (Level 1 & 2) and CHAdeMO (DC Fast Charging - on older models, newer models use CCS).
Main Parts:
- Charging Port (J1772/CHAdeMO/CCS): The physical interface where you connect the charging cable. The J1772 port handles Level 1 and Level 2 AC charging. CHAdeMO, found on earlier models, is a DC fast charging standard. CCS (Combined Charging System) is becoming the standard for DC fast charging on newer Leafs.
- Onboard Charger: This crucial component converts AC power from the charging station into DC power suitable for charging the battery. The onboard charger's kW rating determines the maximum AC charging speed.
- Battery Management System (BMS): The BMS is the brain of the battery pack. It monitors cell voltage, temperature, and current, ensuring safe and efficient charging and discharging. It also prevents overcharging and deep discharging, which can damage the battery.
- High Voltage Battery Pack: The heart of the Leaf, storing the electrical energy that powers the motor.
- DC-DC Converter: Converts high-voltage DC power from the battery pack to the lower voltage (12V) needed to power the car's accessories, such as lights, radio, and control units.
- Charging Control Unit: Communicates with the charging station and manages the charging process. It receives information about available voltage and current, and tells the onboard charger how to charge the battery safely.
Understanding the Charging Diagram Symbols
A charging system diagram visually represents the flow of electricity and the interaction between different components. Here's a breakdown of common symbols you might encounter:
- Solid Lines: Typically represent high-voltage DC power circuits. Thicker lines may indicate higher current capacity.
- Dashed Lines: Usually represent communication or control signals.
- Colors: While color coding isn't standardized across all diagrams, common conventions include:
- Red: Positive (+) DC voltage.
- Black: Negative (-) DC voltage or ground.
- Blue or Green: Communication or control signals.
- Component Symbols: Each component has a specific symbol. You'll see rectangles for modules (like the BMS), coils for inductors, and specific symbols for diodes, resistors, and capacitors. Refer to an electrical engineering reference for detailed symbol definitions.
- Arrows: Indicate the direction of current flow or signal transmission.
Key takeaway is that understanding these symbols allows you to trace the path of electricity and identify potential fault locations within the charging circuit.
How the Nissan Leaf Charging System Works
Let's walk through the charging process step-by-step:
- Connection: You plug the charging cable into the J1772 (Level 1 or Level 2) or CCS/CHAdeMO (DC Fast Charging) port on your Leaf.
- Communication: The Leaf and the charging station establish communication. The charging station identifies its voltage and current capabilities. The Leaf's charging control unit requests power based on the battery's state of charge (SOC) and temperature.
- AC to DC Conversion (Level 1 & 2): For Level 1 and Level 2 charging, the AC power from the charging station enters the Leaf's onboard charger. The onboard charger converts this AC power into DC power at the appropriate voltage for the battery.
- DC Power Routing (DC Fast Charging): For DC Fast Charging, the charging station provides DC power directly to the battery, bypassing the onboard charger. This allows for much faster charging speeds.
- Battery Charging: The DC power flows into the high-voltage battery pack. The BMS monitors the charging process, ensuring that each cell charges safely and evenly. It adjusts the charging rate to prevent overcharging or overheating.
- Termination: Once the battery reaches its target state of charge (usually around 80-90% for DC Fast Charging to protect battery health), the BMS signals the charging station to stop delivering power.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are a few common charging issues and potential solutions:
- Leaf won't charge:
- Check the charging cable and port: Inspect for damage or debris.
- Verify the charging station is working: Try a different charging station if possible.
- Check the car's charging settings: Ensure scheduled charging isn't enabled unintentionally.
- Inspect the 12V battery: A weak 12V battery can sometimes prevent the car from entering charging mode.
- Slow charging:
- Check the charging station's output: Ensure it's providing the expected voltage and current.
- Verify the onboard charger's health: A failing onboard charger can reduce charging speed.
- Consider temperature: Extremely hot or cold temperatures can slow down charging.
- Charging stops unexpectedly:
- Check for error messages on the dashboard.
- Monitor battery temperature using an OBD-II scanner and app. Overheating can cause charging to stop.
Important: If you suspect a serious electrical issue, consult a qualified EV technician. Do not attempt repairs you're not comfortable with.
Safety Considerations
Working with high-voltage systems is inherently dangerous. Here are critical safety precautions:
- High Voltage: The Nissan Leaf's battery pack operates at hundreds of volts. This is enough to cause serious injury or death.
- Always Disconnect: Before working on any part of the charging system, disconnect the high-voltage battery pack according to the service manual.
- Insulated Tools: Use only insulated tools designed for high-voltage applications.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wear appropriate PPE, including insulated gloves and safety glasses.
- Knowledge is Key: Don't attempt repairs without a thorough understanding of the system and the proper procedures. Refer to the service manual for detailed instructions.
- Beware of Capacitors: High voltage circuits often contain capacitors that can store a dangerous charge even after the system is disconnected. Follow discharge procedures outlined in the service manual before working on these circuits.
Warning: The high-voltage battery pack, onboard charger, and DC-DC converter are particularly risky components. Exercise extreme caution when working near these areas.
By understanding the components, functions, and safety considerations outlined above, you're well on your way to mastering the Nissan Leaf's charging system. Remember to consult the service manual for specific details about your Leaf's model year and configuration. And always prioritize safety when working with electrical systems.
You now have a solid foundation for understanding your Leaf's charging system. With careful study, and a healthy respect for safety, you can perform basic troubleshooting and maintenance, and even explore more advanced modifications. Good luck, and happy driving!
We have the Nissan Leaf charging system diagram available for download. You can access it here.
