How Do I Use Android Auto
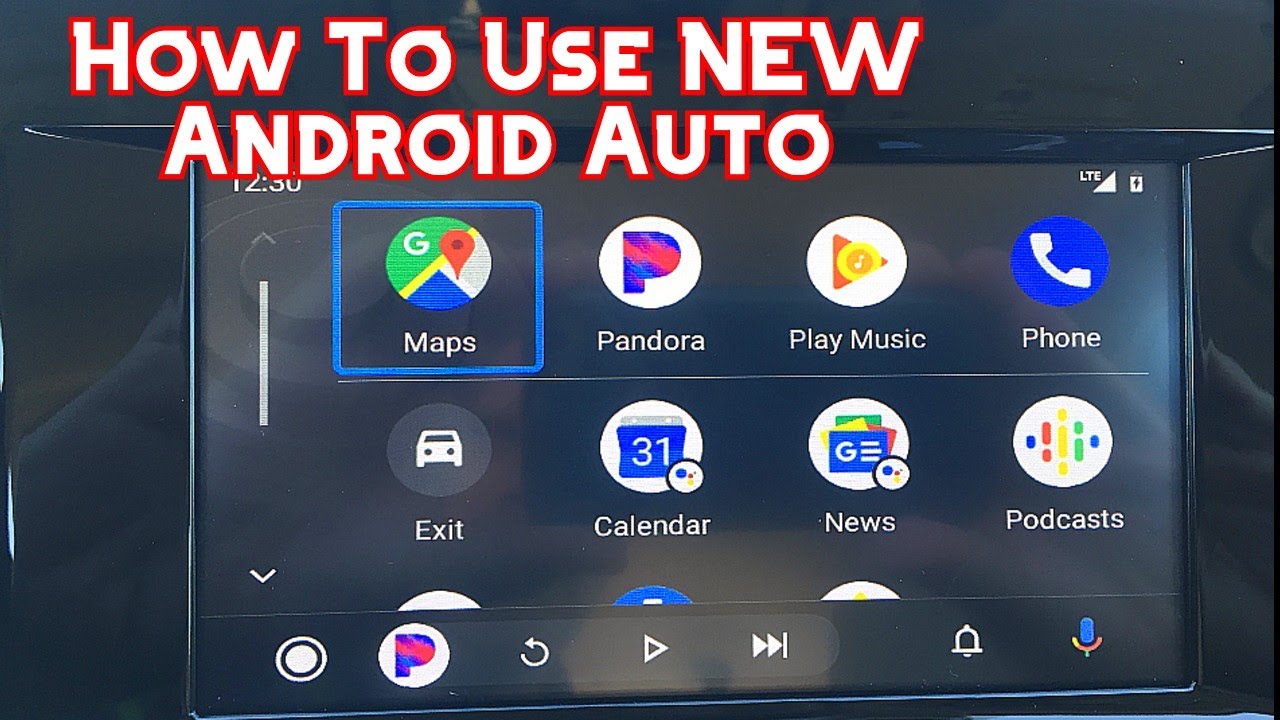
Alright, let's dive into the world of Android Auto. This isn't just about mirroring your phone on your car's display; it's about integrating your digital life into your driving experience. Think of this article as your comprehensive guide to understanding, troubleshooting, and even potentially extending the capabilities of Android Auto.
Purpose: Integrating Your Smartphone into Your Vehicle
Why bother learning about Android Auto? Simple: seamless integration. The purpose behind mastering Android Auto lies in leveraging your smartphone's power (navigation, music, communication) within your car's infotainment system. This not only enhances convenience but also promotes safer driving by minimizing distractions associated with handling your phone directly. Understanding the system allows for troubleshooting common problems, optimizing performance, and even exploring advanced features like custom app integrations (with appropriate caution and skill).
Key Specs and Main Parts
Android Auto isn't just a single piece of hardware; it's a software ecosystem interacting with various components. Here's a breakdown:
- Android Device (Smartphone): This is the brain of the operation. It runs the Android Auto app and houses all your data (maps, music, contacts). The minimum Android OS version is typically Android 8.0 (Oreo) or later, although some features might require a newer version.
- Car's Infotainment System: This is the interface through which you interact with Android Auto. It includes the display screen, touch controls (if applicable), and audio system. It needs to be Android Auto-compatible, meaning it possesses the necessary hardware and software to communicate with your Android device.
- USB Cable (for Wired Connections): High-quality USB cables are crucial for a stable connection. A cheap or damaged cable can cause connectivity issues, lag, or even data corruption. Look for a cable that supports data transfer (not just charging). USB-C is increasingly common for newer phones and cars.
- Wireless Connection (for Wireless Android Auto): Requires both your phone and car to support Wireless Android Auto. It uses Wi-Fi Direct for a direct connection between your phone and the infotainment system, bypassing your car's cellular data.
- Android Auto App: This app acts as the intermediary, translating your phone's data and commands into a format understandable by the car's infotainment system. Older versions of Android OS might require downloading the app from the Play Store; newer versions often have it pre-installed or integrated into the system settings.
How It Works: A Technical Overview
At its core, Android Auto works by essentially projecting a simplified version of your Android phone's interface onto the car's infotainment screen. Here's a more detailed breakdown:
- Connection Establishment:
- Wired: When you plug your phone into the car via USB, the Android Auto app detects the connection and initiates a handshake. The car's infotainment system identifies the phone as an Android Auto device.
- Wireless: The phone and infotainment system establish a Wi-Fi Direct connection. This often involves an initial pairing process where you select your phone from a list of available devices on the car's screen.
- Data Transfer and Processing: Once connected, the Android phone sends data to the car's infotainment system. This data includes map information from Google Maps, music playlists from Spotify, and contact details. The car's system then renders this data into a car-friendly interface.
- Input and Output: Your interactions with the car's touchscreen, steering wheel controls, or voice commands are relayed back to the phone. The phone processes these commands and sends updated data back to the car. For example, if you use voice commands to navigate to a destination, the phone's voice assistant (usually Google Assistant) handles the speech recognition and route calculation, and the updated map data is sent to the car.
- Audio Routing: Android Auto seamlessly integrates with your car's audio system. Audio output from your phone (music, navigation directions, phone calls) is routed through the car's speakers. The system usually prioritizes audio based on importance (e.g., navigation directions will interrupt music playback).
Symbols, Icons and their Significance
Android Auto uses a consistent set of symbols and icons to represent different functions and statuses. Understanding these symbols is crucial for effective use and troubleshooting:
- Microphone Icon: Activates voice control. Tapping this allows you to use Google Assistant to make calls, send messages, play music, or navigate.
- Navigation Icon (Arrow or Compass): Indicates access to navigation apps like Google Maps or Waze.
- Phone Icon: Displays recent calls, contacts, and dial pad.
- Music Note Icon: Opens your preferred music app (e.g., Spotify, YouTube Music).
- Google Assistant Icon (Colored dots or a stylized "G"): Indicates Google Assistant is active and listening.
- Notifications Icon (Bell or Numbered Circle): Alerts you to new messages, missed calls, or other notifications.
- Battery Icon: Shows your phone's battery level.
- Signal Strength Icon: Indicates your phone's cellular signal strength. A weak signal can impact navigation and data-intensive apps.
- Wi-Fi Icon: Appears if you are using Wireless Android Auto.
- Settings Icon (Gear or Cogwheel): Allows you to access Android Auto settings, such as customization options and connection preferences.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting
Even with a solid understanding of Android Auto, you might encounter issues. Here's a troubleshooting guide:
- Connection Problems:
- Check the USB cable: Try a different, high-quality cable. Inspect the cable for damage.
- Restart your phone and car: A simple reboot can often resolve connectivity glitches.
- Update the Android Auto app: Ensure you have the latest version of the app installed.
- Check car's infotainment system firmware: Outdated firmware can cause compatibility issues. Check with your car manufacturer for updates.
- Wireless Connection issues: Make sure Bluetooth is on and Wi-Fi is enabled on your phone. Ensure your phone is discoverable.
- Lag or Slowness:
- Close unnecessary apps on your phone: Running too many apps simultaneously can strain your phone's resources.
- Clear the cache and data for the Android Auto app: This can resolve performance issues.
- Check your phone's storage: A full storage can slow down your phone and impact Android Auto performance.
- App Compatibility Issues:
- Ensure the app is compatible with Android Auto: Not all apps are designed to work with Android Auto.
- Update the app: Developers often release updates to fix compatibility issues.
- Audio Problems:
- Check that your car's audio is set to the correct source (e.g., USB or Bluetooth).
- Verify the volume level on your phone and car.
- Try disconnecting and reconnecting your phone.
Safety: Minimizing Distractions
While Android Auto aims to enhance safety by minimizing phone handling, it's crucial to use it responsibly. Avoid the following:
- Excessive interaction with the touchscreen while driving: Use voice commands whenever possible.
- Typing or reading lengthy messages while driving: Pull over to a safe location if you need to engage with text.
- Using apps that are not designed for driving: Stick to navigation, music, and communication apps.
- Ignoring the road and your surroundings: Android Auto should augment your awareness, not replace it. Always prioritize safe driving.
Remember, safe driving is paramount. Android Auto is a tool to enhance your driving experience, but it should never compromise your safety or the safety of others.
We have the diagram file that compliments this article with visual aids. You can request to download it.
