How Does A Electric Car Work
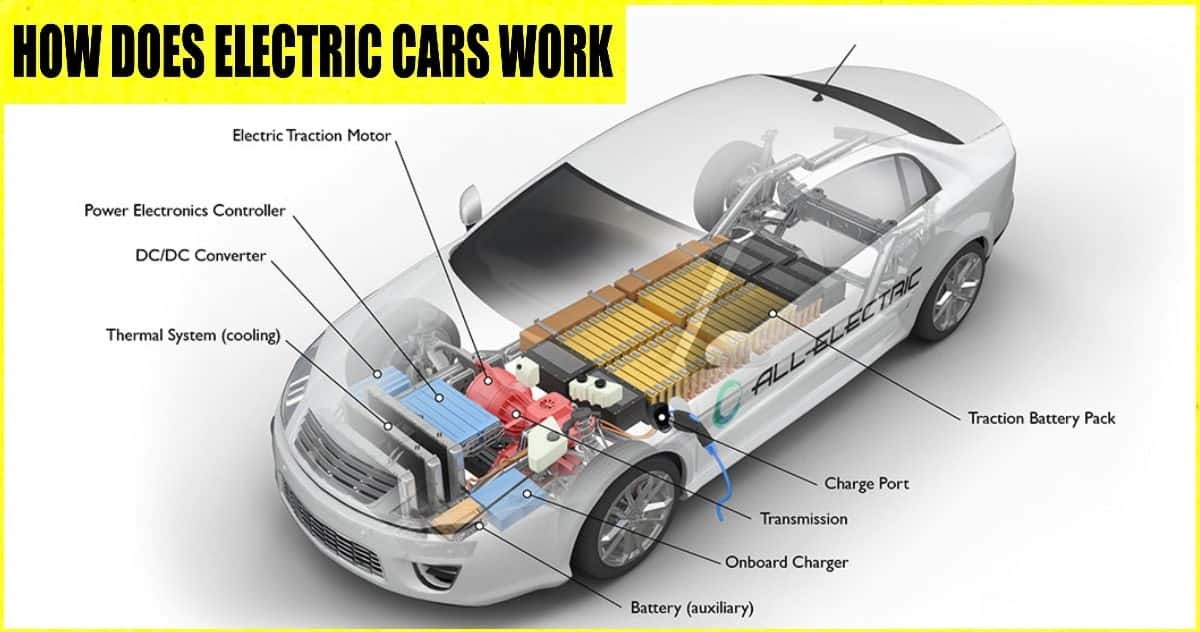
Alright, let's dive into the inner workings of an electric vehicle (EV). This isn’t just about knowing where the "go" pedal is; understanding the system-level operation is crucial for effective maintenance, troubleshooting, and even potential modifications. Whether you're thinking about converting a classic, diagnosing a fault, or just plain curious, grasping the interplay of components is key. Consider this your comprehensive guide – with an associated diagram (available for download, link provided at the end) – to the heart of electric mobility.
Key Specs and Main Parts
An EV, at its core, replaces the internal combustion engine (ICE) with an electric motor and a large battery pack. Instead of burning fuel, it draws power from the battery to drive the motor, which in turn spins the wheels. Here's a breakdown of the major components:
- Battery Pack: This is the energy reservoir of the EV. It's typically composed of hundreds or thousands of individual lithium-ion cells connected in series and parallel to achieve the desired voltage and capacity. Key specs include voltage (V), capacity (Ah or kWh), and C-rate (discharge rate).
- Inverter: The inverter converts the DC (Direct Current) power from the battery into AC (Alternating Current) power needed by the electric motor. It's essentially the electronic heart controlling the motor's speed and torque.
- Electric Motor: This is the prime mover, transforming electrical energy into mechanical energy. EVs commonly use either AC induction motors or permanent magnet synchronous motors. Key specs include power (kW or HP), torque (Nm or lb-ft), and maximum RPM.
- Onboard Charger (OBC): This handles AC to DC conversion when charging from standard wall outlets or public charging stations. The OBC's power rating (kW) dictates the charging speed.
- DC-DC Converter: This steps down the high-voltage DC from the battery pack to a lower voltage (typically 12V) to power auxiliary systems like lights, wipers, and infotainment.
- Thermal Management System: Maintaining the battery pack at its optimal operating temperature is crucial for performance and longevity. This system uses liquid cooling, air cooling, or a combination of both.
- Transmission (Single-Speed): Unlike ICE vehicles, EVs often use a single-speed transmission because electric motors produce high torque across a wide RPM range. This simplifies the drivetrain and improves efficiency.
- Brake System (Regenerative Braking): EVs utilize regenerative braking, which uses the motor as a generator to recapture kinetic energy during deceleration, charging the battery and reducing wear on the conventional friction brakes.
- Battery Management System (BMS): This is the brain of the battery pack, monitoring cell voltage, temperature, and current to ensure safe and efficient operation. The BMS prevents overcharging, over-discharging, and thermal runaway.
Symbols and Diagram Conventions
Understanding the diagram is crucial. Expect to see the following:
- Solid Lines: Indicate high-voltage DC power flow (typically orange or red).
- Dashed Lines: Indicate low-voltage DC power flow (typically black or gray).
- Thin Lines: Indicate communication signals or control circuits.
- Arrows: Show the direction of current or energy flow.
- Color Coding: Orange/Red generally denotes high-voltage circuits, while black/gray is for low-voltage. However, always refer to the specific diagram legend.
- Standard Electrical Symbols: Resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits are represented using their standard electrical symbols.
How It Works
The operation of an EV can be broken down into a few key stages:
- Power Source (Battery): When the accelerator pedal is pressed, the BMS signals the inverter to draw power from the battery pack.
- DC-to-AC Conversion (Inverter): The inverter takes the DC voltage from the battery and converts it into AC voltage with varying frequency and amplitude, controlled by the driver's input.
- Motor Control (Electric Motor): The AC power feeds the electric motor, creating a rotating magnetic field that drives the rotor and spins the wheels. The inverter controls the motor's speed and torque by adjusting the frequency and amplitude of the AC voltage.
- Regenerative Braking: When the driver releases the accelerator or applies the brakes, the motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy and charging the battery. The BMS manages the regenerative braking process to optimize energy recovery and prevent overcharging.
- Auxiliary Systems: The DC-DC converter provides a stable 12V supply to power auxiliary systems like lights, wipers, and infotainment, ensuring they function reliably regardless of the battery pack voltage.
- Charging: During charging, either the OBC (for AC charging) or an external DC fast charger converts AC power from the grid to DC power, which is then fed to the battery pack. The BMS monitors the charging process to ensure safe and efficient charging.
Real-World Use - Basic Troubleshooting Tips
So, your EV is acting up? Here are a few common issues and basic troubleshooting steps:
- Reduced Range: Check tire pressure, driving habits (aggressive acceleration and braking), and battery health. External temperature affects battery performance. If the range is significantly reduced and other factors are ruled out, consider a battery health check by a qualified technician.
- Charging Issues: Verify the charging cable is properly connected and that the charging station is functioning correctly. Check the onboard charger's fault indicators. If charging is slow, it could be due to a low charging current setting or a problem with the charging station.
- Warning Lights: Pay attention to warning lights on the dashboard. Consult the owner's manual to understand the meaning of each light and take appropriate action. Some warning lights may require professional diagnosis.
- Motor Malfunctions: Unusual noises or vibrations from the motor area are red flags. Reduced performance could indicate issues with the motor, inverter, or related components. These issues typically require expert diagnosis and repair.
Note: Always consult your vehicle's service manual before attempting any repairs. EVs contain high-voltage components, and improper handling can be dangerous.
Safety – Highlighting Risky Components
Working on EVs involves significant risks due to the high-voltage battery pack. Treat all orange cables and connectors as live, high-voltage circuits. NEVER attempt to disconnect or repair high-voltage components without proper training, personal protective equipment (PPE), and isolation procedures.
- Battery Pack: The battery pack contains a large amount of stored energy and can deliver a lethal electric shock.
- Inverter: The inverter converts DC to AC at high voltages and currents, posing a significant electrocution hazard.
- High-Voltage Cables: These cables carry high-voltage DC power throughout the vehicle and must be handled with extreme care.
Before working on any electrical components, follow these safety precautions:
- Disconnect the High-Voltage Battery: Follow the manufacturer's instructions for disconnecting the high-voltage battery pack. Verify that the system is de-energized using a high-voltage meter.
- Wear Appropriate PPE: Wear high-voltage insulated gloves, safety glasses, and appropriate clothing.
- Work in a Safe Environment: Ensure the work area is clean, dry, and well-lit.
- Use Insulated Tools: Use only insulated tools rated for high-voltage applications.
- Never Work Alone: Always have a second person present in case of emergency.
Remember, safety is paramount. If you are not comfortable working with high-voltage systems, seek assistance from a qualified EV technician.
Now that you've got a good grasp of how an EV works, you can use this knowledge for informed maintenance, troubleshooting, and even for more advanced projects. As promised, we have a detailed schematic diagram illustrating all the components and their connections. You can download it here: [Insert Download Link Here - Replace with Actual Link]. Happy wrenching, but always prioritize safety!
