How Does The Electric Car Work
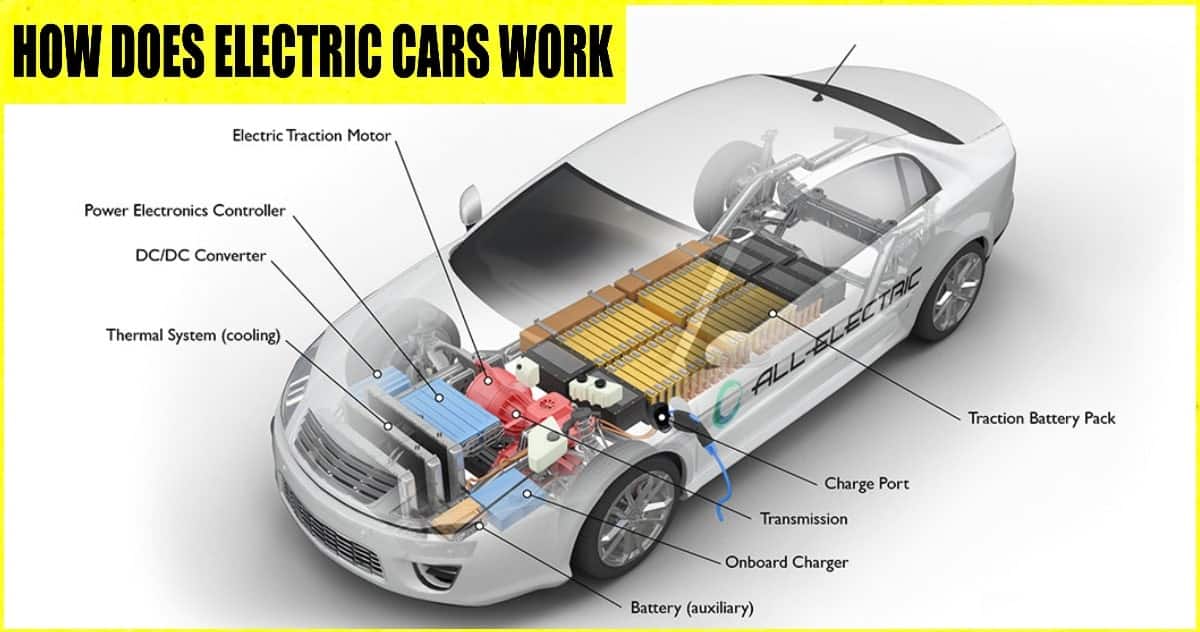
Alright, let's dive into the inner workings of an electric car. Forget the magic – we're going to get down and dirty with the components and how they all play together. Think of this as your advanced electric vehicle (EV) 101 course, designed for those of you who are comfortable getting your hands greasy (or, in this case, maybe getting shocked if you’re not careful – more on that later!).
Purpose: Understanding the EV architecture is crucial for several reasons. First, if you’re thinking about modifying or converting a vehicle to electric, this knowledge is non-negotiable. Second, even for basic maintenance or troubleshooting, knowing the system layout helps you pinpoint issues and potentially save money by avoiding unnecessary trips to the dealership. And finally, it’s just plain cool to understand how these machines function!
Key Specs and Main Parts
An EV, at its core, is relatively simple compared to an internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicle. Fewer moving parts mean fewer potential points of failure. Let's break down the main players:
1. Battery Pack
This is the heart of the EV. Usually composed of hundreds or even thousands of individual lithium-ion cells (similar to those in your laptop or phone, but much larger and more powerful), the battery pack stores the electrical energy needed to power the motor. Key specs include:
- Voltage: Measured in volts (V), this determines the electrical potential available. Common EV battery pack voltages range from 200V to over 800V.
- Capacity: Measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), this indicates the amount of energy the battery can store. A higher kWh rating means a longer driving range.
- Chemistry: The specific chemical composition of the cells (e.g., Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide - NMC, Lithium Iron Phosphate - LFP) affects performance, lifespan, and safety.
2. Electric Motor(s)
The motor converts electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy to drive the wheels. Key specs include:
- Power: Measured in kilowatts (kW) or horsepower (hp), this indicates the motor's maximum output.
- Torque: Measured in Newton-meters (Nm) or pound-feet (lb-ft), this determines the motor's rotational force, affecting acceleration.
- Type: Permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM) and induction motors are the most common types. PMSMs are generally more efficient, while induction motors are often more robust.
3. Power Electronics
This is where the magic (and complexity) happens. The power electronics manage the flow of electricity between the battery, motor, and other components. Key components include:
- Inverter: Converts direct current (DC) from the battery into alternating current (AC) for the motor. It also controls the motor's speed and torque by adjusting the frequency and voltage of the AC signal.
- DC-DC Converter: Steps down the high voltage from the battery pack to a lower voltage (typically 12V) to power auxiliary systems like lights, infotainment, and power windows.
- Onboard Charger: Converts AC power from the charging port into DC power to charge the battery.
4. Thermal Management System
Batteries and power electronics generate heat, especially during high-performance driving or rapid charging. The thermal management system, which typically includes a liquid coolant loop, keeps these components within their optimal temperature range to ensure performance and longevity.
5. Charging Port
This is where you plug in the car to recharge the battery. Different charging standards exist, including:
- Level 1: Standard household outlet (120V in North America). Very slow charging.
- Level 2: Dedicated 240V circuit. Much faster than Level 1.
- DC Fast Charging (DCFC): High-power chargers that can add significant range in a short amount of time.
Symbols - Understanding the Diagram
When looking at an EV schematic, here's a quick guide to interpreting common symbols:
- Solid lines: Typically represent high-voltage DC wiring.
- Dashed lines: Usually indicate low-voltage DC wiring or communication signals (e.g., CAN bus).
- Thick lines: Often represent high-current paths.
- Different colors: Can denote different voltage levels or specific circuit functions (e.g., orange for high-voltage, blue for cooling). Refer to the diagram's key for specific color coding.
- Icons: Standard electrical symbols represent components like resistors, capacitors, diodes, and transistors.
Pay close attention to the grounding symbols. Proper grounding is crucial for safety and to prevent electrical noise from interfering with the vehicle's electronics.
How It Works
Here’s the basic flow of energy in an EV:
- Charging: When you plug the car into a charging station, AC power enters the onboard charger. The onboard charger converts this AC power into DC power and feeds it to the battery pack, replenishing its charge.
- Driving: When you press the accelerator pedal, the vehicle control unit (VCU) signals the inverter to draw power from the battery pack. The inverter converts the DC power into AC power at the appropriate voltage and frequency to control the electric motor's speed and torque.
- Motor Operation: The AC power energizes the motor's windings, creating a magnetic field that interacts with the motor's rotor (the rotating part). This interaction generates torque, which is then transmitted to the wheels through a gearbox (typically a single-speed reduction gear).
- Regenerative Braking: When you decelerate, the motor can act as a generator, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy. This energy is then fed back into the battery pack, helping to slow the vehicle and improve efficiency.
Real-World Use – Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Let's say your EV isn't charging correctly. Here are some basic troubleshooting steps you can take:
- Check the Charging Cable: Ensure the charging cable is properly connected to both the car and the charging station. Look for any signs of damage to the cable or connectors.
- Inspect the Charging Port: Check the charging port on the car for any debris or corrosion.
- Test the Charging Station: If possible, try charging your car at a different charging station to rule out a problem with the station itself.
- Consult the Vehicle's Manual: The owner's manual contains valuable information about troubleshooting charging issues and other common problems.
- Check the 12V Battery: A dead or weak 12V battery can sometimes prevent the car from charging, even if the main battery pack is healthy. This is because the 12V system powers the control circuits.
Warning lights on the dashboard are your friend. They’re trying to tell you something. Use an OBD-II scanner (if compatible with EVs – some require specialized tools) to read the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and research their meaning. Remember, safety first!
Safety – Risky Components
High Voltage is Lethal! This cannot be stressed enough. EV battery packs operate at voltages that can easily cause serious injury or death. Never attempt to work on the high-voltage system without proper training and the correct safety equipment, including:
- High-Voltage Gloves: Insulated gloves rated for the voltage of the system you're working on.
- Insulated Tools: Tools specifically designed for working with high-voltage systems.
- Voltage Tester: A reliable voltage tester to verify that the system is de-energized before you start working.
- Lockout/Tagout Procedures: Procedures to ensure that the system cannot be accidentally re-energized while you're working on it.
Always disconnect the high-voltage battery pack before working on any electrical components. Follow the manufacturer's instructions for safe disconnection procedures. If you're not comfortable working with high-voltage systems, leave it to a qualified technician.
This is just an overview, of course. Each EV model has its own nuances and specific design. Remember to consult the service manual for your particular vehicle for detailed information.
Now that you have a solid understanding of the basics, you're well on your way to becoming an EV expert. Good luck with your projects, and remember: safety first!
We have a detailed schematic diagram to complement this article. It contains a breakdown of EV's electronic components. Feel free to download it from our website to aid your learning.
