How Fast Is Level 1 Charging
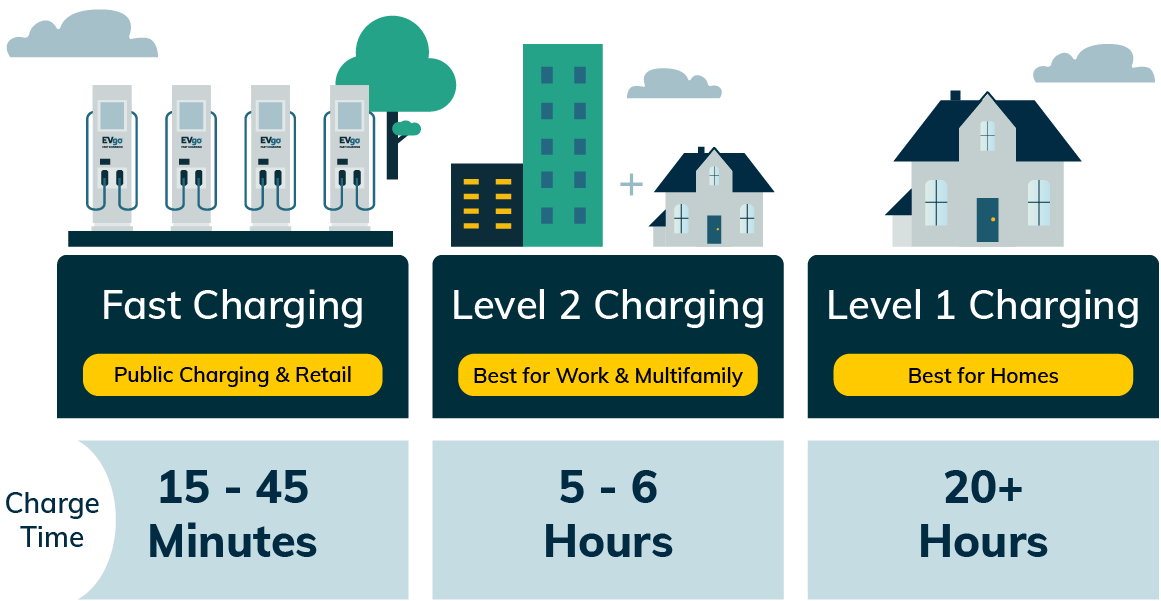
So, you're diving into the world of electric vehicles (EVs) and want to understand the ins and outs of charging at home? Excellent! Let's break down Level 1 charging. It's the simplest and most accessible charging method, but also the slowest. Understanding its capabilities and limitations is crucial for managing your EV ownership experience. This article will give you a solid understanding of Level 1 charging, from the electrical basics to practical troubleshooting.
Purpose of Understanding Level 1 Charging
Why bother learning about Level 1 charging? Because it's often the first charging method new EV owners use. You plug your car into a standard wall outlet, and voila, it charges! But there's more to it than that. Understanding Level 1 charging allows you to:
- Estimate Charging Times: Know how long it takes to add a certain amount of range.
- Identify Charging Problems: Recognize when something isn't working correctly.
- Optimize Charging: Make the most of the limited charging speed.
- Inform Future Upgrades: Decide if you need to upgrade to Level 2 charging.
- Understand its limitations: Level 1 charging often requires 12+ hours for a full charge, or may not be sufficient for those with long commutes.
Essentially, this knowledge empowers you to be a more informed and proactive EV owner.
Key Specs and Main Parts of Level 1 Charging
Let's dive into the specifics. Level 1 charging utilizes a standard 120-volt AC outlet, the same one you use for your toaster or lamp. Here are the key specifications:
- Voltage: 120V AC (in North America; 230V in many other regions)
- Amperage: Typically 12 amps (after continuous load derating from a 15-amp circuit), or sometimes 8 amps (user selectable in the car or charging adapter).
- Power Output: Around 1.4 kW (kilowatts) at 12 amps or 0.96kW at 8 amps (120V x Amperage).
The main components involved in Level 1 charging are:
- Standard Wall Outlet (NEMA 5-15): The common three-prong outlet you find everywhere.
- Charging Cable (EVSE - Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment): This cable connects the outlet to the car and contains safety features and communication electronics. It's often referred to as a "portable charger," though it's technically the EVSE.
- Onboard Charger (Inside the EV): This converts the AC power from the outlet into DC power that the battery can store. Every EV has one of these.
How Level 1 Charging Works
The charging process is relatively straightforward, but here's a breakdown:
- Plug In: You plug the Level 1 charging cable into a standard wall outlet.
- Connect to Vehicle: The other end of the cable goes into the charging port on your EV.
- Communication: The EVSE and the car communicate to ensure a safe connection and verify charging parameters. This communication uses a control pilot signal, which is a PWM (pulse width modulation) signal that indicates the maximum current available to the car.
- AC to DC Conversion: The onboard charger inside the EV converts the 120V AC power from the outlet into DC power suitable for charging the battery.
- Battery Charging: The DC power is then used to charge the EV's battery.
The charging rate is determined by the voltage and amperage, resulting in the power output mentioned earlier. This power output translates to a certain amount of range added per hour of charging. Typically, Level 1 charging adds about 3-5 miles of range per hour.
Real-World Use and Basic Troubleshooting
Level 1 charging is convenient for topping off the battery or for those who drive very short distances daily. However, it's generally too slow for regular use with larger batteries or longer commutes.
Here are some common problems and troubleshooting tips:
- Slow Charging: Make sure the outlet is not shared with other appliances. A dedicated circuit is best. Also, check your car's settings to ensure it's not limited to a lower amperage.
- Charging Cable Not Working: Inspect the cable for damage. Try a different outlet. If the problem persists, the EVSE may be faulty.
- GFCI Outlet Tripping: Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) outlets are designed to protect against electrical shock. If one trips frequently, it could indicate a ground fault in the charging cable or the EV. Consult an electrician or EV technician.
- Car Not Recognizing Charger: Ensure the charging port on the car is clean and free of debris. Try restarting the car. If the problem persists, there may be an issue with the car's onboard charger or the EVSE communication.
Important Note: If you're experiencing electrical issues, always consult a qualified electrician. Don't attempt to repair electrical components yourself unless you have the necessary knowledge and experience.
Safety Considerations
Safety is paramount when dealing with electricity. Here are some crucial safety points:
- Proper Outlet: Always use a properly grounded and functioning outlet. Never use an extension cord for Level 1 charging, as they can be a fire hazard due to the continuous current draw.
- Circuit Overload: Ensure the circuit you're using is not overloaded with other appliances. A dedicated 15-amp or 20-amp circuit is recommended.
- Weather Protection: If charging outdoors, use a weather-resistant outlet cover and ensure the charging cable is designed for outdoor use.
- Cable Inspection: Regularly inspect the charging cable for damage, such as cuts, frayed wires, or loose connections. If you find any damage, replace the cable immediately.
- Avoid Water: Never use the charging cable in wet conditions.
The onboard charger within the vehicle can be a potential source of issues if it malfunctions. It's a complex electronic component and requires specialized knowledge for troubleshooting. Similarly, the EVSE contains electronics that communicate with the vehicle, so repairs to it should be completed by qualified personnel.
Conclusion
Level 1 charging is a simple but essential aspect of EV ownership. Understanding its workings, limitations, and safety considerations will empower you to use it effectively and troubleshoot common problems. While it may not be the fastest charging method, it's a valuable tool for topping off your battery and ensuring you have enough range for your daily needs. Remember to prioritize safety and consult qualified professionals for any electrical issues you can't resolve yourself.
