How Fast Is Level 2 Charging
So, you're looking to dive deeper into the world of Level 2 EV charging. Smart move. Understanding how fast your electric vehicle charges at home is crucial, whether you're planning upgrades, troubleshooting issues, or simply want to squeeze every last mile out of your battery. This guide breaks down the technical aspects of Level 2 charging speed, equipping you with the knowledge to optimize your charging experience.
Understanding Level 2 Charging Speed: It's More Than Just Volts
Forget everything you think you know about plugging in your phone. Level 2 charging is a different beast, operating on a much larger scale. The speed at which your EV juices up via Level 2 depends on several interconnected factors. We're not just talking about plugging into a 240V outlet; we're talking about power, current, onboard charger capabilities, and the vehicle's battery management system (BMS).
Key Specs and Main Parts: The Charging Ecosystem
Let's dissect the major players in the Level 2 charging game:
- EVSE (Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment): This is the "charging station" you see mounted on walls. It doesn't actually *charge* the car; it provides the power and communication needed for the car's onboard charger to do its job. Think of it as a smart extension cord.
- Onboard Charger: Located *inside* your EV, this converts the AC power from the EVSE into DC power that the battery can store. The onboard charger has a maximum power rating (e.g., 7.2 kW, 11.5 kW) that dictates the maximum charging speed. This is a critical limiting factor.
- Charging Cable (J1772 Connector): This cable physically connects the EVSE to your car's charging port. J1772 is the North American standard for Level 2 charging.
- Electrical Panel: Your home's electrical panel is the source of power. You need sufficient amperage available in the panel to support the Level 2 EVSE without overloading the circuit.
- Dedicated Circuit: Level 2 chargers require a dedicated circuit – a circuit breaker and wiring solely for the EVSE. This prevents overloading and ensures safe operation.
- Battery Management System (BMS): The BMS monitors and controls the charging process, preventing overcharging, overheating, and other potential issues. It also communicates with the EVSE and onboard charger to optimize charging speed and battery health.
Key Specifications to consider:
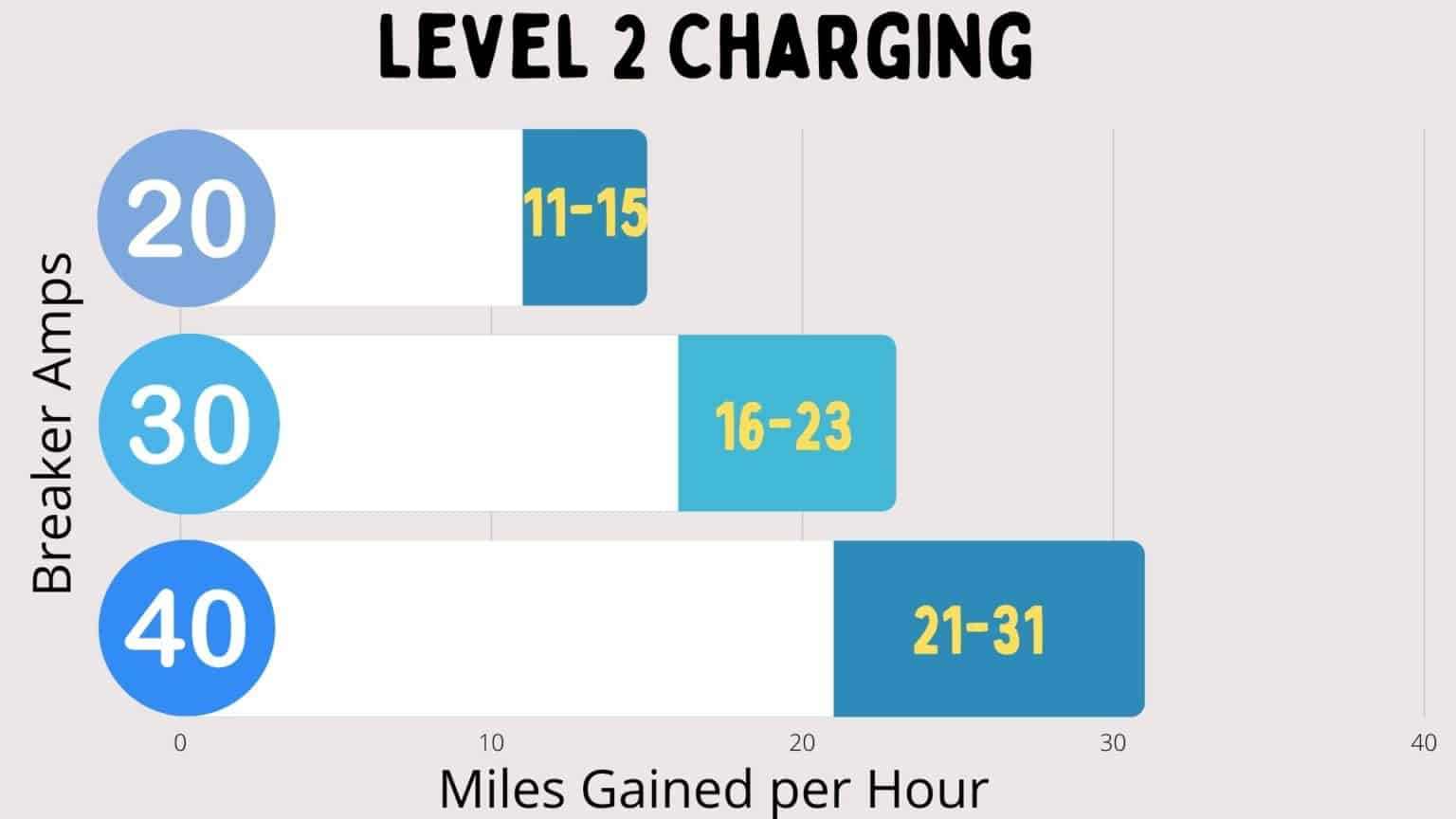
- Voltage: Level 2 charging typically operates at 208-240V AC.
- Amperage: Common amperage ratings for Level 2 EVSEs are 16A, 32A, 40A, and 48A.
- Power (kW): Power is calculated as Voltage x Amperage / 1000. This determines the rate at which energy is transferred to the battery. For example, a 240V, 32A charger delivers 7.68 kW.
- Charging Rate (miles per hour): This is the estimated range added to your vehicle per hour of charging. It varies based on the vehicle's efficiency (miles per kWh).
How It Works: The Charging Process Unveiled
The Level 2 charging process involves a carefully orchestrated sequence of events:
- Connection: You plug the J1772 connector into your EV's charging port.
- Communication: The EVSE and the car communicate to verify the connection and safety. The EVSE checks for ground faults and other potential hazards.
- Pilot Signal: The EVSE sends a pilot signal to the car indicating the maximum available current.
- Onboard Charger Activation: The car's onboard charger receives the pilot signal and, if compatible, begins converting AC power to DC power.
- Charging: The onboard charger regulates the DC power flow to the battery, based on the battery's state of charge and temperature, as determined by the BMS.
- Monitoring and Control: The BMS continuously monitors the battery's condition and communicates with the onboard charger to adjust the charging rate as needed. This prevents overcharging and ensures optimal battery health.
- Termination: Once the battery reaches its desired state of charge (typically 80% or 100%), the BMS signals the onboard charger to stop charging. The EVSE then de-energizes the circuit.
The speed of this process is dictated by the lowest common denominator. If your EVSE can deliver 48A (11.5 kW), but your car's onboard charger is limited to 32A (7.7 kW), you'll only charge at 7.7 kW. Similarly, if your home wiring can't handle the amperage draw, the EVSE might throttle back the charging rate to prevent overloading the circuit.
Real-World Use: Troubleshooting and Optimizing
Here are some common scenarios and basic troubleshooting tips:
- Slow Charging: If your charging speed is slower than expected, check the onboard charger's maximum rating. Consult your vehicle's owner's manual. Also, verify the amperage setting on your EVSE (if adjustable). Weather conditions can also impact charging speeds, as cold temperatures can slow down the charging process.
- Charging Interruption: If charging suddenly stops, check the circuit breaker for the EVSE. If it has tripped, reset it. If it trips repeatedly, there may be an overload or a wiring issue. Consult a qualified electrician. Also, check the EVSE for any error codes or indicator lights, and consult its manual.
- "Reduced Charging Rate" Message: This message often indicates that the vehicle is limiting the charging rate due to battery temperature or other factors. It's usually not a cause for concern, but if it persists, consult your vehicle's service center.
Safety: Respect the High Voltage
Working with electricity is inherently dangerous. Never attempt to repair or modify your EVSE or home wiring unless you are a qualified electrician.
Key Safety Considerations:
- High Voltage: Level 2 charging involves high voltage (240V), which can be lethal.
- Proper Grounding: Ensure that the EVSE is properly grounded to prevent electric shock.
- Overcurrent Protection: The dedicated circuit for the EVSE must be protected by a properly sized circuit breaker.
- Weather Resistance: If the EVSE is installed outdoors, it must be rated for outdoor use and protected from the elements.
- Regular Inspection: Periodically inspect the EVSE and charging cable for any signs of damage.
Components like the high-voltage terminals in the EVSE and the wiring in your electrical panel are particularly risky. Do not tamper with these components unless you have the necessary training and experience.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of Level 2 charging empowers you to optimize your charging setup, troubleshoot issues effectively, and ensure safe operation. By grasping the key components, the charging process, and the potential pitfalls, you can take control of your EV charging experience.
We have a detailed diagram illustrating the Level 2 charging process. It includes circuit schematics, component layouts, and troubleshooting flowcharts. You can download the diagram [link to diagram]. This resource will provide you with a visual aid to further enhance your understanding.
