How Long Do Fast Chargers Take
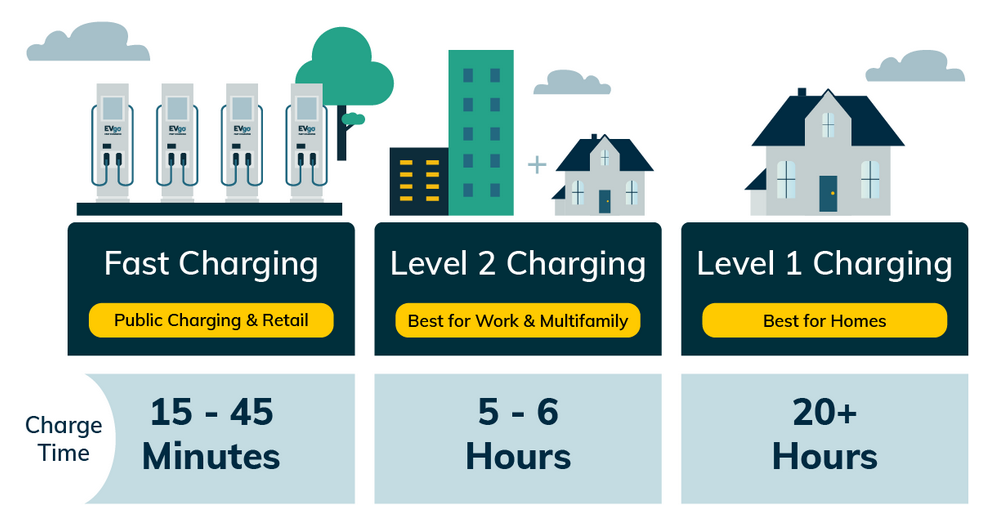
Alright folks, let's talk fast charging – specifically, how long it *actually* takes. We're not going to just throw around marketing buzzwords. We're diving into the nitty-gritty of voltage, current, battery chemistry, and thermal management. Whether you're considering upgrading your home charging setup, tinkering with an EV conversion, or just want to understand why your charging speeds seem inconsistent, this guide will give you the insights you need.
Purpose – Beyond the Plug: Why Understanding Fast Charging Matters
Knowing the ins and outs of fast charging is crucial for more than just topping up your battery quickly. Think of it like this: understanding your engine's timing allows you to diagnose performance issues and optimize fuel efficiency. Similarly, a grasp of fast charging principles equips you to:
- Diagnose Charging Problems: Is your charger delivering the power it should? Is your battery accepting it? Understanding the process helps you troubleshoot issues.
- Optimize Charging Strategy: Knowing the sweet spot for your battery's charging curve lets you minimize charging time and maximize battery life.
- Evaluate Charging Equipment: Is that bargain-bin charger safe and effective? Knowledge helps you make informed purchasing decisions.
- Plan Road Trips Effectively: Knowing your car's charging rate at different charging levels allows you to schedule charging stops accurately, which can be critical when traveling long distances.
Key Specs and Main Parts
Before we dive into the charging process, let's define some key specifications and components:
- Voltage (V): Think of voltage as the electrical "pressure." Higher voltage allows for more power delivery. Fast chargers typically operate at higher voltages than Level 1 or Level 2 chargers. Common voltages include 400V and 800V.
- Current (A): Current is the flow of electrical charge. Higher current, along with high voltage, delivers more power. This is often referred to as "Amperage".
- Power (kW): Power is the rate at which energy is transferred, calculated as Voltage x Current (V x A). This is what you see advertised for fast chargers (e.g., 50kW, 150kW, 350kW).
- Battery Capacity (kWh): Battery capacity represents the amount of energy the battery can store. A larger capacity means a longer range but also a longer charging time.
- State of Charge (SoC): SoC is the percentage of energy currently stored in the battery. Charging times vary significantly depending on the SoC.
- Battery Management System (BMS): The BMS is the brain of the battery pack. It monitors voltage, current, temperature, and other parameters, and it controls the charging and discharging process to protect the battery from damage. The BMS is the most important part of the charging equation.
- Charging Station (EVSE): This is the equipment providing the power to the car. It communicates with the car's onboard charger and regulates the charging process.
- Onboard Charger: This is the circuitry within the car that converts the AC power from the charging station to DC power suitable for charging the battery. In fast charging (DC Fast Charging or DCFC), this is bypassed, and the DC power goes directly to the battery.
- Cooling System: A vital component, especially during fast charging. Batteries generate heat, and excessive heat can damage them. Liquid cooling systems are common in EVs to manage battery temperature.
How It Works – The Dance of Electrons
Here's a simplified explanation of how fast charging works:
- Connection and Communication: You plug the charging cable into your car. The charging station and the car's BMS communicate to establish a charging protocol (e.g., CCS, CHAdeMO, Tesla Supercharger). They negotiate the voltage and current limits.
- Direct DC Power Delivery: Unlike Level 1 and 2 charging where the AC power is converted to DC within the car, fast charging (DCFC) supplies DC power directly to the battery pack, bypassing the onboard charger. This allows for significantly higher power delivery.
- Constant Current (CC) Phase: Initially, the charger delivers a constant current to the battery. This is the fastest part of the charging process, and the battery voltage gradually increases.
- Constant Voltage (CV) Phase: As the battery approaches full charge, the charger switches to a constant voltage. The current gradually decreases as the battery fills up. This phase is slower than the CC phase.
- BMS Control: Throughout the entire process, the BMS monitors the battery's voltage, current, and temperature. It adjusts the charging parameters to protect the battery from overcharging, overheating, or other damage.
- Tapering: Near the end of the charging cycle, the charging rate tapers down. This is due to the internal resistance of the battery increasing as it becomes full and the BMS intentionally reducing the current to protect the battery and extend its lifespan. Going from 80% to 100% will always take significantly longer than going from 20% to 40%.
It’s also important to remember that the charging station's maximum output doesn't guarantee that's what your car will receive. The car's BMS and its ability to dissipate heat play a critical role in determining the actual charging rate. Also, many charging stations throttle their output when multiple cars are charging simultaneously to manage grid load.
Real-World Use – Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are a few common scenarios and basic troubleshooting steps:
- Slow Charging:
- Check the Charger's Output: Verify that the charger is actually delivering the advertised power. Many charging networks have apps or displays that show the charging rate.
- Battery Temperature: If the battery is too hot or too cold, the charging rate will be reduced. Preconditioning (warming up the battery before charging) can help in cold weather.
- State of Charge: As mentioned earlier, charging slows down significantly as the battery approaches full charge. Don't expect to charge from 80% to 100% as quickly as you charged from 20% to 40%.
- BMS Restrictions: The BMS might be limiting the charging rate due to a cell imbalance or other internal issues. In this case, consult a qualified EV technician.
- Charging Interruption:
- Charging Station Error: Check the charging station's display for error messages. Try a different charging station if possible.
- Cable Connection: Ensure the charging cable is securely plugged into both the car and the charging station.
- Communication Error: Sometimes, there can be a communication glitch between the car and the charging station. Unplugging and replugging the cable can sometimes resolve the issue.
Safety – Respecting the High Voltage
High voltage is extremely dangerous. Never attempt to disassemble or repair a fast charger or EV battery pack unless you are a qualified technician with the proper training and equipment. Here are a few key safety considerations:
- High Voltage Components: Fast chargers and EV batteries contain high-voltage components that can deliver a lethal shock. Always disconnect the power source and follow proper lockout/tagout procedures before working on any electrical components.
- Battery Acid: EV batteries contain corrosive electrolyte that can cause severe burns. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) if you need to handle a damaged battery.
- Thermal Runaway: Damaged or improperly charged batteries can experience thermal runaway, which can lead to fire or explosion. Store and handle batteries carefully, and follow all manufacturer's instructions.
- Never tamper with the BMS: This is the battery's primary safety system. Bypassing or modifying the BMS can have catastrophic consequences.
If you are not comfortable working with high-voltage systems, leave it to the professionals. Your safety is paramount.
Diagram Download
To help you visualize the charging process and its components, we've created a detailed fast-charging system diagram. The diagram illustrates the power flow, communication protocols, and key safety features. This will provide a better understanding of the different parts of fast charging. To obtain access to this comprehensive visual guide, simply contact us, and we'll provide you with the diagram file.
