How Long Does It Take To Charge
Alright, let's talk about EV charging times – a question I get asked constantly. Understanding how long it takes to charge your electric vehicle isn't just about convenience; it's crucial for planning trips, understanding your vehicle's capabilities, and even troubleshooting charging issues. Whether you're a seasoned EV owner or just considering making the switch, knowing the factors that influence charging time will put you in the driver's seat (pun intended!). We're going to dive into the nuts and bolts, so buckle up.
Understanding the EV Charging Diagram: Why it Matters
Before we get into the nitty-gritty of charging times, let's consider why a charging system diagram is vital. Forget abstract concepts; think real-world applications. If your EV suddenly refuses to charge, or charging is suspiciously slow, a diagram allows you to trace the power flow, pinpoint potential bottlenecks, and understand the interplay between different components. This isn’t just for certified mechanics; even a reasonably skilled DIYer can use a diagram to perform basic diagnostics and potentially avoid costly repairs. The diagram also aids in understanding the overall architecture of the charging system. Perhaps you want to upgrade to a faster onboard charger or install a more powerful home charging station. Knowing the system's limits and capabilities is essential. Finally, understanding the diagram equips you to discuss issues intelligently with your mechanic, ensuring you get the right repairs at the right price. We have a detailed charging system diagram available for download at the end of this article, so you can refer to it as we go.
Key Specifications and Main Parts
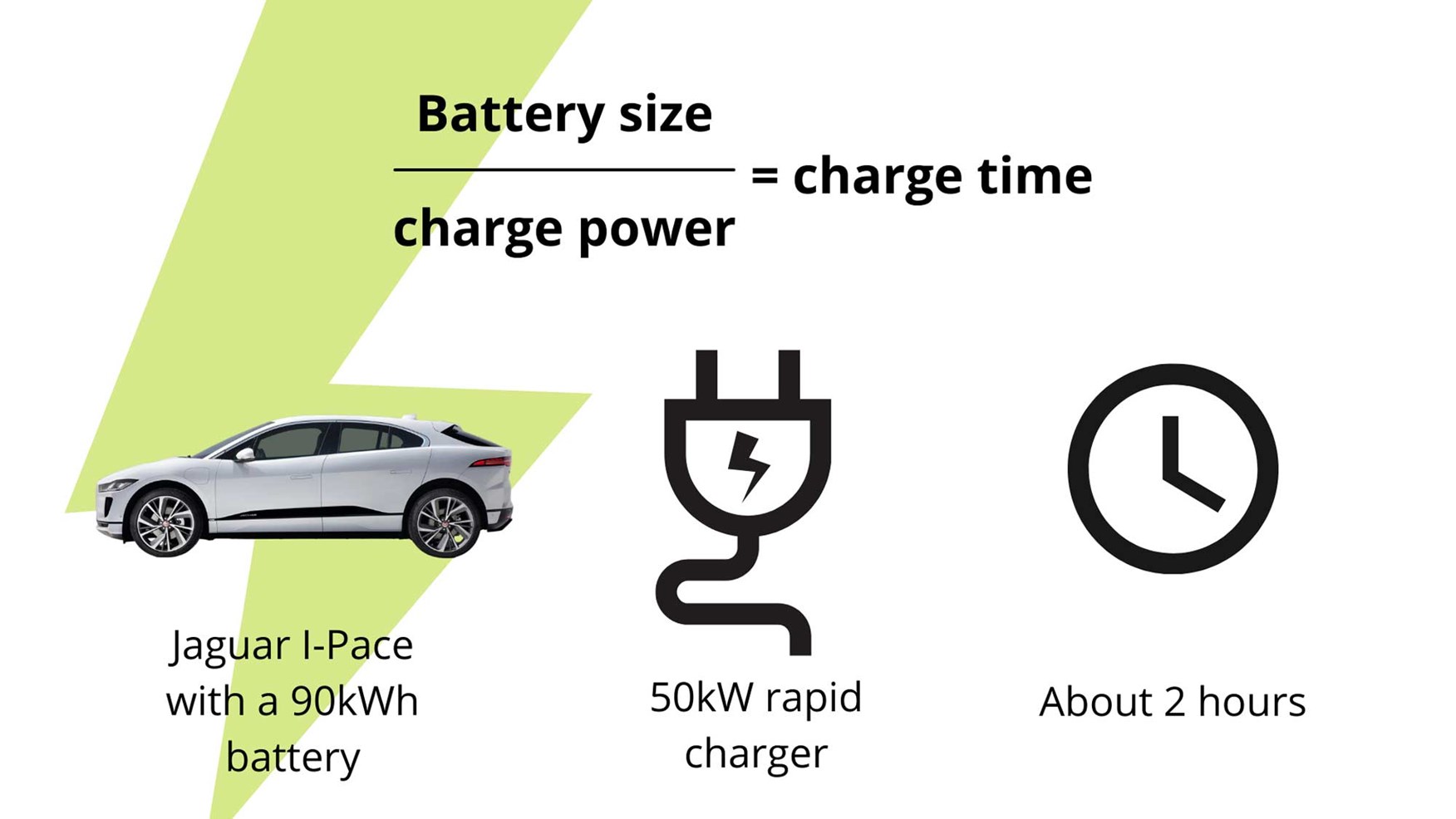
Let's break down the key specs and components involved in the EV charging process. This is essential for understanding the diagram and deciphering the information it provides.
- Onboard Charger (OBC): This is the heart of the charging system, converting AC power from the charging station to DC power suitable for storing in the battery pack. It's rated in kilowatts (kW), determining the maximum AC charging speed. Think of it like a power adapter for a laptop – it dictates how quickly electricity can be converted.
- Battery Pack: Measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), it represents the energy storage capacity of the battery. A larger battery pack means a longer range, but also a longer charging time.
- Charging Port (Inlet): The physical connection point on your vehicle. Different EVs use different connector types like J1772 (Level 1 and Level 2 AC charging), CCS (Combined Charging System, adding DC fast charging to J1772), and CHAdeMO (another DC fast charging standard, primarily used by older Japanese EVs).
- Charging Cable: The physical cable connecting the vehicle to the charging station. Amperage rating is critical – using a cable with a lower amperage rating than the charger can handle can lead to overheating and damage.
- Charging Station (EVSE – Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment): This is the "outlet" for your EV. It provides the necessary safety features and communication protocols. Charging stations are categorized into Level 1, Level 2, and DC Fast Charging (Level 3).
- BMS (Battery Management System): This critical system monitors the battery's voltage, current, temperature, and state of charge (SOC). It protects the battery from overcharging, over-discharging, and thermal runaway. Think of it as the brain of the battery pack, ensuring its safety and longevity.
Diagram Symbols Explained
Understanding the symbols in the EV charging diagram is essential for interpreting its information. Here’s a breakdown of common symbols:
- Solid Lines: Generally represent the main power flow path. Thicker lines usually indicate higher current capacity.
- Dashed Lines: Typically signify control or communication signals between components. These are lower voltage signals used to regulate the charging process.
- Colors: Colors often indicate voltage levels or function. For example, red might represent high voltage DC, blue might represent neutral, and green might represent ground. Check the diagram's legend for specific color coding.
- Icons: Standard electronic symbols represent components like resistors, capacitors, diodes, and switches. If you're not familiar with these, a quick online search will provide a visual guide.
- Arrows: Indicate the direction of current flow or signal flow.
- Ground Symbol: Crucial for safety, indicating the grounding point of the system.
How EV Charging Works: A Simplified View
The basic principle is simple: AC power from the grid is converted into DC power and stored in the battery. However, the specifics vary depending on the charging level:
- Level 1 Charging: Uses a standard 120V household outlet. The OBC converts the AC to DC. Slowest charging method, adding only a few miles of range per hour.
- Level 2 Charging: Uses a 240V outlet (similar to what your clothes dryer uses). The OBC again converts AC to DC, but at a much faster rate than Level 1.
- DC Fast Charging (Level 3): Bypasses the OBC entirely. The charging station directly delivers DC power to the battery pack, allowing for very rapid charging. This requires specialized and high-power equipment.
The BMS constantly monitors the battery's state and communicates with the charger (either the OBC or the DC fast charger) to regulate the charging process. It's a closed-loop system, ensuring that the battery charges safely and efficiently.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
So, what happens when things go wrong? Here are a few basic troubleshooting tips, informed by your understanding of the charging diagram:
- Charging is slow: First, verify that your charging station is working correctly. Check the voltage and amperage output. Then, make sure your vehicle's OBC is functioning correctly. A faulty OBC will severely limit charging speed. Also, outside temperature can impact charging speeds, especially in extremely cold temperatures.
- Charging stops prematurely: This could be a BMS issue. The BMS might be detecting a fault (e.g., overheating) and interrupting the charging process. Also check the charging station for any error codes.
- Vehicle won't charge at all: Check the charging cable for damage. A broken wire can prevent charging. Also, inspect the charging port on your vehicle for debris or corrosion. Finally, a blown fuse in the charging circuit can also prevent charging.
Important: Before attempting any electrical repairs, disconnect the vehicle from the charging station and consult a qualified electrician.
Safety Considerations
EV charging systems involve high voltages and currents. Here are some key safety considerations:
- Battery Pack: The battery pack contains a substantial amount of energy and is potentially lethal. Never attempt to disassemble or tamper with the battery pack unless you are specifically trained and equipped to do so.
- High-Voltage Cables: Marked with orange insulation, these cables carry high-voltage DC power. Avoid touching them, even when the vehicle is turned off.
- Charging Station: Ensure the charging station is properly grounded and that the wiring is in good condition. Damaged wiring can create a fire hazard.
- Water and Electricity: Never operate a charging station in wet conditions. Water can conduct electricity and create a shock hazard.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): When working with electrical systems, always wear appropriate PPE, including insulated gloves and safety glasses.
Working on any part of the high-voltage system should be left to qualified technicians who have the correct tools and training. The risks are simply too great for untrained individuals.
Remember that an EV charging system is a complex interaction between the vehicle and the charging station. Understanding the function of each component and the flow of electricity can greatly aid in troubleshooting problems and ensuring the safety and longevity of your EV. Always err on the side of caution and consult a qualified professional when in doubt. We hope this overview has been helpful in demystifying the EV charging process.
As promised, you can download a detailed EV charging system diagram here.
