How Long Is A Car Under Warranty
Understanding your car's warranty is crucial for any vehicle owner, especially those who enjoy DIY maintenance or modifications. This article breaks down the intricacies of automotive warranties, covering their purpose, key components, and practical applications. We'll provide the information you need to confidently navigate warranty claims and make informed decisions about your vehicle.
Purpose of Understanding Your Car's Warranty
Why bother learning about your car's warranty? Simply put, it can save you a significant amount of money. A warranty is a contract between you (the car owner) and the manufacturer or dealer, guaranteeing certain repairs or replacements will be covered for a specific period or mileage. Knowing the specifics of your warranty allows you to:
- Identify Covered Repairs: Quickly determine if a specific issue is covered, avoiding unnecessary out-of-pocket expenses.
- Plan for Maintenance: Understand which maintenance tasks are required to maintain warranty validity.
- Negotiate Repairs: Armed with knowledge, you can confidently discuss repair options with dealerships or independent mechanics.
- Make Informed Modification Decisions: Determine if modifications void the warranty and weigh the risks accordingly.
Understanding warranty limitations is equally important. Knowing what's not covered can prevent frustration and unrealistic expectations.
Key Warranty Specs and Main Parts
Automotive warranties aren't one-size-fits-all. They typically comprise several key components:
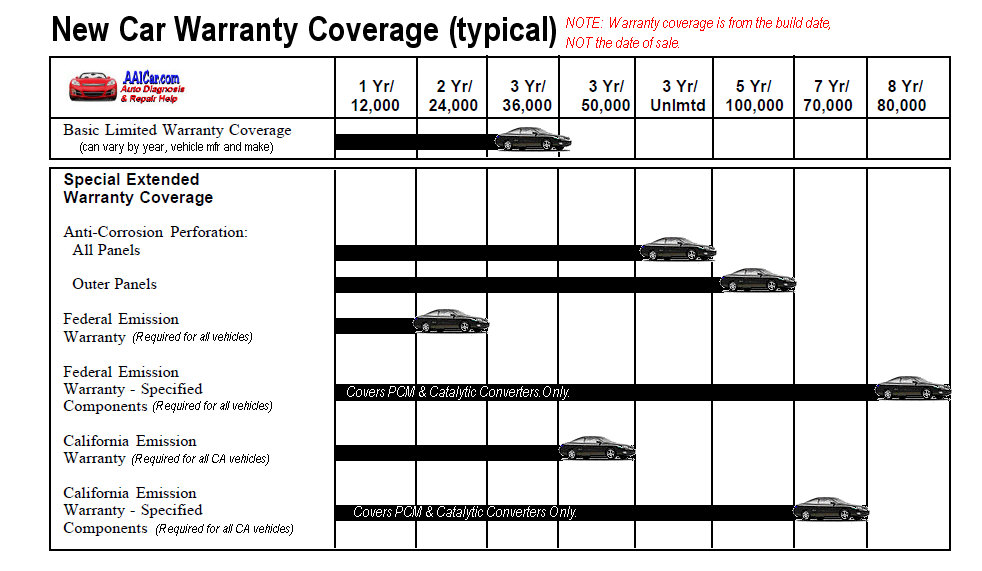
Basic/Bumper-to-Bumper Warranty
This is the most comprehensive coverage. It covers nearly everything between the bumpers, excluding wear-and-tear items like tires, brake pads, and fluids. The terms are usually expressed as a duration (e.g., 3 years) and mileage (e.g., 36,000 miles), whichever comes first. Understanding this "whichever comes first" clause is vital.
Powertrain Warranty
This warranty focuses on the engine, transmission, and drivetrain components. It's often longer than the bumper-to-bumper warranty, reflecting the high cost of repairing or replacing these critical systems. For example, a powertrain warranty might be 5 years/60,000 miles. Key components covered typically include:
- Engine: Engine block, cylinder heads, internal components (pistons, crankshaft, connecting rods, etc.), oil pump, water pump, and related seals and gaskets.
- Transmission: Transmission case, internal components (gears, shafts, bearings, etc.), torque converter (automatic transmissions), and related seals and gaskets.
- Drivetrain: Drive shafts, axles, differentials, transfer case (4WD/AWD vehicles), and related seals and gaskets.
Corrosion/Rust Warranty
This warranty covers perforation due to rust. It typically has a longer duration than the bumper-to-bumper warranty, often ranging from 5 to 10 years or more. It usually only covers rust that penetrates through the metal, not surface rust or cosmetic issues.
Emissions Warranty
Federally mandated, this warranty covers specific emissions control components for a defined period. This is typically 2 years/24,000 miles, but certain components, like the catalytic converter, are covered for a longer period (usually 8 years/80,000 miles). This warranty ensures the vehicle meets EPA emission standards.
Hybrid/Electric Vehicle (EV) Component Warranty
Hybrid and EV vehicles often have separate warranties specifically covering high-voltage batteries, electric motors, and related components. These warranties are usually quite long, often exceeding 8 years/100,000 miles, to address concerns about the longevity of these expensive components. The exact components covered and the length of the warranty can vary significantly between manufacturers and models.
Extended Warranty
These are optional warranties purchased separately, either from the manufacturer or a third-party provider. They extend the coverage beyond the original factory warranty. The terms, coverage, and cost of extended warranties can vary widely, so it's crucial to read the fine print carefully before purchasing one.
How It Works: The Warranty Process
The warranty process generally involves these steps:
- Identify the Issue: Determine the problem and whether it's covered under your warranty. Refer to your warranty booklet for specific coverage details.
- Contact the Dealership or Authorized Repair Facility: Schedule an appointment to have the issue diagnosed and repaired.
- Diagnosis: The service technician will diagnose the problem to determine if it's a warrantable defect.
- Authorization: The dealership will contact the manufacturer to obtain authorization for the warranty repair.
- Repair: Once authorized, the repair will be performed using original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts or approved equivalents.
- Payment: If the repair is covered under warranty, you typically won't have to pay for the repair (except for any deductible, if applicable).
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some troubleshooting tips for navigating warranty issues:
- Keep Detailed Records: Maintain records of all maintenance and repairs performed on your vehicle. This documentation is crucial for proving that you've properly maintained the vehicle and haven't voided the warranty.
- Follow Maintenance Schedule: Adhere to the manufacturer's recommended maintenance schedule. Failure to do so can void the warranty.
- Document Modifications: Keep records of any modifications you've made to the vehicle. Some modifications can void the warranty, particularly if they directly cause the failure.
- Know Your Rights: Familiarize yourself with your rights under the Magnuson-Moss Warranty Act, which protects consumers from unfair warranty practices.
- Be Persistent: If you believe a repair should be covered under warranty but the dealership is refusing, don't give up. Contact the manufacturer directly and escalate the issue.
Safety: Potential Warranty-Related Risks
Improper maintenance or modifications can create safety hazards and potentially void the warranty. Consider these risks:
- DIY Repairs: While DIY repairs can save money, incorrect repairs can damage the vehicle and void the warranty. Be cautious and only perform repairs you're qualified to handle. Incorrectly installed aftermarket parts can also cause damage.
- Using Non-OEM Parts: While using aftermarket parts doesn't automatically void the warranty, using substandard or incompatible parts can cause damage and lead to warranty denials. Some warranties require the use of OEM parts for certain repairs. Check your specific warranty for these details.
- Ignoring Warning Signs: Ignoring warning lights or unusual noises can lead to more significant and costly repairs. Address issues promptly to prevent further damage.
- Engine Tuning: Remapping the engine control unit (ECU) or using performance chips can significantly alter engine parameters and potentially void the powertrain warranty. These modifications can increase stress on engine components and lead to premature failure.
Remember, safety is paramount. When in doubt, consult a qualified mechanic.
We have compiled an easy-to-read, technical document with common warranty terms and coverages to serve as a helpful guide to navigating your vehicle's warranty. You can download it here.
