How Long To Charge An Ev
So, you've taken the plunge and joined the electric vehicle (EV) revolution. Congratulations! One of the biggest adjustments for new EV owners is understanding the charging process. Forget filling up at the pump – now it's all about kilowatt-hours (kWh) and charge rates. This article aims to demystify the process, providing you with the knowledge to optimize your charging strategy and keep your EV running smoothly. We'll dive into the factors that affect charging time, explore different charging levels, and offer practical advice for troubleshooting common charging issues.
Understanding EV Charging: A Deep Dive
Before we get into specific charging times, let’s establish some foundational concepts. The charging time of an EV isn't fixed; it's influenced by several factors. Understanding these allows you to anticipate charging needs and optimize for efficiency.
Key Specs and Main Parts
Let's break down the main components and specifications that dictate EV charging:
- Battery Capacity (kWh): This is the "fuel tank" of your EV, measured in kilowatt-hours. It represents the amount of energy the battery can store. A larger kWh battery means longer range, but also potentially longer charging times.
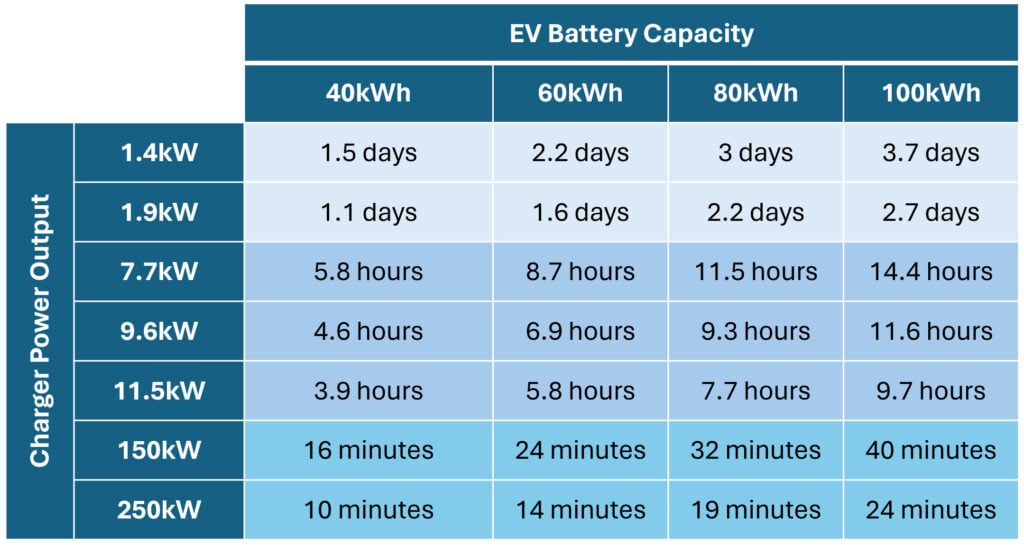
- Charging Level: Refers to the voltage and current of the power source. There are three main levels:
- Level 1: Uses a standard 120V household outlet. Slowest charging speed, typically adding 3-5 miles of range per hour.
- Level 2: Uses a 240V outlet (like those used for dryers or ovens). Significantly faster than Level 1, adding 12-30 miles of range per hour. Requires a dedicated Level 2 charger.
- DC Fast Charging (Level 3): Uses high-voltage DC power (400V or higher). The fastest charging method, adding 50-200+ miles of range per hour. Found at public charging stations.
- Onboard Charger (kW): This component within the vehicle converts AC power from the charging station into DC power that the battery can store. It has a maximum power rating (e.g., 7.2 kW, 11 kW). The lower of the charger output or charging station output determines the charging speed.
- Charging Cable/Connector: The physical connection between the charging station and the vehicle. Common connector types in North America include:
- J1772: Standard connector for Level 1 and Level 2 charging.
- CCS (Combined Charging System): Adds DC fast charging capability to the J1772 connector.
- CHAdeMO: Another DC fast charging standard, primarily used by older Nissan and Mitsubishi EVs. Increasingly being phased out in favor of CCS.
- NACS (North American Charging Standard): Developed by Tesla, it combines AC and DC charging into one connector. It is rapidly becoming an industry standard.
- Charging Station Output (kW): The power that the charging station can deliver. It's crucial to ensure the charging station's output is compatible with your vehicle's onboard charger.
- State of Charge (SoC): The percentage of battery capacity that is currently charged. Charging from 20% to 80% is generally faster than charging from 80% to 100%.
Symbols and Interpretation
While we don't have a physical diagram to dissect in this text-based article, understanding common symbols and indicators related to EV charging is essential:
- Battery Icon: Typically indicates the battery level on the vehicle's instrument panel. May be segmented to show charge percentage.
- Lightning Bolt: Universally used to denote charging. Often seen on charging ports and charging station displays.
- AC/DC: Indicate alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC), respectively. Essential for identifying the type of charging being used.
- kW/kWh: Kilowatt (power) and kilowatt-hour (energy). Understanding these units is crucial for understanding charging speed and energy consumption.
- LED Indicators on Charger: Charging stations often have LED indicators to show the charging status (e.g., ready, charging, completed, error). Colors often indicate different states.
How It Works: The Charging Process
Let's walk through the charging process:
- Connection: You plug the charging cable into the charging station and then into your EV's charging port.
- Communication: The vehicle and charging station communicate to establish the charging parameters (voltage, current, and maximum power).
- AC to DC Conversion (Level 1 & Level 2): For Level 1 and Level 2 charging, the onboard charger in your EV converts the AC power from the outlet into DC power that the battery can store. The charging station only provides AC power.
- DC Charging (Level 3): For DC fast charging, the charging station provides DC power directly to the battery, bypassing the onboard charger. This allows for much faster charging speeds.
- Battery Management System (BMS): The BMS monitors the battery's voltage, current, and temperature during charging to ensure safe and efficient operation. It controls the charging rate to prevent overcharging or overheating.
- Charging Termination: The charging process stops when the battery reaches the desired state of charge, as determined by the BMS.
Real-World Use and Troubleshooting
Here's how to apply this knowledge in real-world scenarios and some basic troubleshooting tips:
- Calculating Charging Time: Estimate charging time using this formula: `Charging Time (hours) = Battery Capacity (kWh) / Charging Power (kW)`. For example, charging a 60 kWh battery with a 7.2 kW charger would theoretically take about 8.3 hours. Remember this is an *ideal* time, and losses exist.
- Slow Charging: If your EV is charging slower than expected, consider these factors:
- Low Voltage: Ensure your 240V outlet is providing the correct voltage. Use a multimeter to check.
- Shared Circuit: If other appliances are using the same circuit, the charging power may be reduced.
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures can affect charging speed. The BMS may reduce the charging rate to protect the battery.
- Faulty Cable: Inspect the charging cable for damage. Try a different cable if possible.
- Onboard Charger Issue: In rare cases, the onboard charger itself might be faulty. This requires professional diagnosis.
- Charging Interruption: If charging stops unexpectedly:
- Power Outage: Check for power outages in your area.
- Circuit Breaker Trip: Reset the circuit breaker for the charging outlet.
- Charging Station Error: Check the charging station display for error messages.
- Overheating: The BMS may interrupt charging if the battery overheats.
- Optimizing Charging: To maximize battery life and charging efficiency:
- Avoid Frequent Full Charges: Charging to 100% regularly can degrade battery health over time. Aim to charge to 80% for daily use.
- Avoid Depleting the Battery Completely: Letting the battery drain to near zero can also be detrimental.
- Charge During Off-Peak Hours: Take advantage of lower electricity rates during off-peak hours (usually at night).
- Use a Timer: Set a timer on your charging station or use your EV's charging schedule feature to stop charging at the desired state of charge.
Safety Considerations
Working with electricity is inherently dangerous. Exercise extreme caution when dealing with EV charging systems. Here are some crucial safety points:
- High Voltage: DC fast charging stations operate at very high voltages (400V or higher). Never attempt to disassemble or repair a DC fast charging station. These are jobs for certified technicians.
- Proper Grounding: Ensure your 240V outlet is properly grounded. A faulty ground can create a shock hazard.
- Qualified Electrician: Always hire a qualified electrician for installing a Level 2 charging station.
- Water and Electricity: Never use a charging cable or station that is wet or damaged. Water and electricity are a deadly combination.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect your charging cables and outlets for any signs of damage (cracks, frayed wires, etc.).
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): When working with electrical components, wear appropriate PPE, including insulated gloves and safety glasses.
Remember, EV charging is a complex topic, but with a solid understanding of the fundamentals, you can optimize your charging strategy and keep your EV running efficiently. While this article provides a comprehensive overview, always consult your vehicle's owner's manual for specific charging instructions and recommendations.
For detailed schematics and technical diagrams specific to your EV model, it's best to consult the manufacturer's service manual or reputable online resources. We have access to a large library of these and can provide a relevant diagram. Please provide us the Make, Model, and Year of your EV and we'll provide the schematic. You can download these for your reference.
