How Long To Charge Ev At Station
So, you've taken the plunge and joined the electric vehicle (EV) revolution. Congratulations! Now, you're probably wondering about one of the most frequently asked questions: How long does it *actually* take to charge an EV at a charging station? It's a valid question, and the answer isn't always straightforward. It depends on a variety of factors, ranging from your car's battery capacity and state of charge to the charging station's power output and even the ambient temperature. This article will delve into the technical details behind EV charging times, providing you with the knowledge to estimate charging duration accurately and troubleshoot common issues. Consider this your guide to mastering the art of EV charging.
Purpose: Understanding the Charge Time Equation
Understanding EV charging times isn't just about knowing how long you'll be stuck at a charging station. It's crucial for:
- Trip Planning: Accurately estimate travel times and charging stops on long journeys.
- Charging Optimization: Choose the right charging station and charging strategy (e.g., partial vs. full charge) to suit your needs.
- Cost Management: Understand how charging costs vary based on charging speed and energy consumption.
- Troubleshooting: Diagnose charging problems and identify potential issues with your vehicle or the charging station.
- Repair and Modification: For those adventurous souls considering battery upgrades or custom charging solutions, understanding the underlying principles is essential.
Key Specs and Main Parts Influencing Charge Time
Several key specifications and components significantly impact how long it takes to charge your EV. Let's break them down:
Battery Capacity (kWh)
The battery capacity, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), represents the total amount of energy your battery can store. Think of it like the size of your fuel tank. A larger battery (e.g., 75 kWh) generally provides a longer driving range but takes longer to charge than a smaller battery (e.g., 40 kWh).
State of Charge (SoC)
The State of Charge (SoC) is the percentage representing how full your battery is. Charging from 20% to 80% will always take less time than charging from 0% to 100%. Charging slows down considerably as you approach 100% to protect the battery's long-term health.
Charging Power (kW)
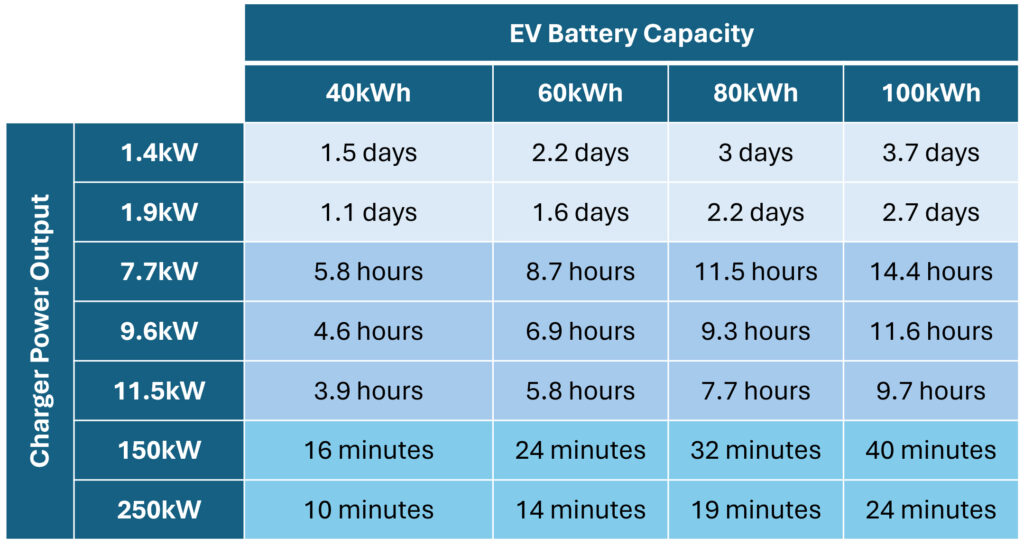
The charging power, measured in kilowatts (kW), indicates the rate at which energy is transferred to your battery. Different charging levels offer varying power outputs:
- Level 1 Charging (120V AC): Typically provides 1.4 kW to 1.8 kW. This is the slowest charging method and is generally used at home with a standard household outlet. Expect extremely slow charging times, adding only a few miles of range per hour.
- Level 2 Charging (240V AC): Offers a charging power of 3 kW to 19.2 kW, depending on the charger and your car's onboard charger's capabilities. Most home charging stations and public charging stations utilize Level 2 charging. This is significantly faster than Level 1.
- DC Fast Charging (DCFC): Provides the highest charging power, ranging from 50 kW to 350 kW or even higher. DCFC stations are typically found along highways and at dedicated charging plazas. They can add a significant amount of range in a short period (e.g., 20 minutes to 80% SoC).
Onboard Charger
The onboard charger is located inside your EV and converts AC power from Level 1 or Level 2 chargers into DC power that the battery can store. The onboard charger has a maximum power rating. For example, if your car has a 7.2 kW onboard charger, it cannot accept more than 7.2 kW even if connected to a Level 2 charger that provides 11 kW. DC Fast Charging bypasses the onboard charger, delivering DC power directly to the battery.
Charging Cable
The charging cable connects your car to the charging station. While most DC Fast Charging stations have integrated cables, Level 1 and Level 2 charging often require you to use your own cable or one provided by the station.
Battery Management System (BMS)
The Battery Management System (BMS) is a crucial component that monitors and controls the charging process. It ensures that the battery is charged safely and efficiently, preventing overcharging, overheating, and other potential issues. The BMS can also reduce the charging rate towards the end of the charging cycle to protect battery health.
How It Works: The Charging Process
The charging process can be simplified into a few key steps:
- Connection: You connect the charging cable to your car and the charging station.
- Authentication: The charging station verifies your identity and payment method (if applicable).
- Communication: The car and the charging station communicate to determine the optimal charging parameters (voltage, current, power).
- Conversion (Level 1 & 2): The onboard charger converts AC power to DC power. DC Fast Charging bypasses this step.
- Charging: The battery receives DC power, increasing its SoC.
- Monitoring: The BMS constantly monitors the charging process, adjusting the charging rate as needed.
- Termination: Once the battery reaches the desired SoC or charging is complete, the charging process is terminated.
Real-World Use: Estimating and Troubleshooting
To estimate charging time, use this formula:
Charging Time (hours) ≈ (Battery Capacity (kWh) * (Desired SoC % - Initial SoC %)) / Charging Power (kW)
Remember to account for charging inefficiencies (typically 10-20%) by increasing the estimated time accordingly. For example, if you want to charge a 60 kWh battery from 20% to 80% using a 7 kW Level 2 charger:
Charging Time ≈ (60 kWh * (80% - 20%)) / 7 kW = (60 kWh * 0.6) / 7 kW = 5.14 hours. Adding 15% for inefficiencies results in approximately 5.9 hours.
Troubleshooting Basic Charging Problems
- Car Won't Charge: Check the charging cable for damage. Verify that the charging station is functioning correctly (try a different station if possible). Ensure the car is properly plugged in and the charging port is clean. Also, check your car's settings to make sure that charging is enabled (some EVs allow you to schedule charging or limit the charging current).
- Slow Charging: Make sure you're using the appropriate charging level for your needs. Level 1 charging will always be slow. If you are using Level 2 or DCFC, confirm that the charging station is providing the expected power output and that your car's onboard charger can handle that power. Also, extreme temperatures can affect charging speeds.
- Charging Errors: Consult your car's owner's manual for specific error codes. Common causes include communication errors between the car and the charging station, or issues with the charging cable.
Safety: Handling High Voltage
EV charging systems operate at high voltages and currents. Never attempt to repair or modify charging equipment unless you are a qualified electrician with experience working on EV charging systems. The battery pack itself contains a significant amount of energy and can be extremely dangerous if mishandled. Always disconnect the power supply before working on any electrical components. Exercise extreme caution when handling charging cables, especially in wet conditions. Incorrectly handled, these components can result in severe electric shock or even death.
Remember, while this article provides a good overview, it's always best to consult your car's owner's manual and manufacturer's specifications for the most accurate information. Drive safe, and happy charging!
