How Long To Charge Ev Car
So, you've got yourself an electric vehicle (EV), or you're seriously considering the leap. Excellent! But beyond the silent ride and zero tailpipe emissions, a crucial question lingers: how long does it take to charge the darn thing? It's not as simple as filling up a gas tank; it's a multifaceted process governed by various factors. Understanding these factors allows you to optimize your charging routine, plan road trips effectively, and even diagnose charging issues should they arise.
Purpose: Understanding EV Charging Times
Why dive into the nitty-gritty of EV charging times? Well, there are several compelling reasons:
- Trip Planning: Knowing how long it takes to replenish your battery allows you to accurately plan journeys, including charging stops along the way. No more range anxiety!
- Home Charging Optimization: Understanding the capabilities of your home charging setup enables you to choose the right equipment and configure it for optimal charging speed.
- Troubleshooting: When things go wrong (and sometimes they do), a solid understanding of the charging process helps you identify potential issues, whether it's a faulty charger, a damaged cable, or a problem with the car's onboard charging system.
- Battery Health: While modern EV batteries are quite robust, charging habits can impact their longevity. Understanding charging rates and voltage levels allows you to minimize any potential long-term degradation.
In this article, we'll dissect the key elements that influence EV charging times, essentially reverse engineering the process. We'll explore the different charging levels, battery capacity, charging infrastructure, and even address some common troubleshooting scenarios. And, because visuals often speak louder than words, we have a detailed diagram (available for download) that illustrates the key components and data flow involved in EV charging.
Key Specs and Main Parts
Let's break down the critical components and specifications that affect EV charging speed:
1. Battery Capacity (kWh)
This is the energy your battery can store, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Think of it like the size of your gas tank. A larger battery (e.g., 100 kWh) provides a longer range but also takes longer to charge than a smaller battery (e.g., 40 kWh).
2. Charging Level
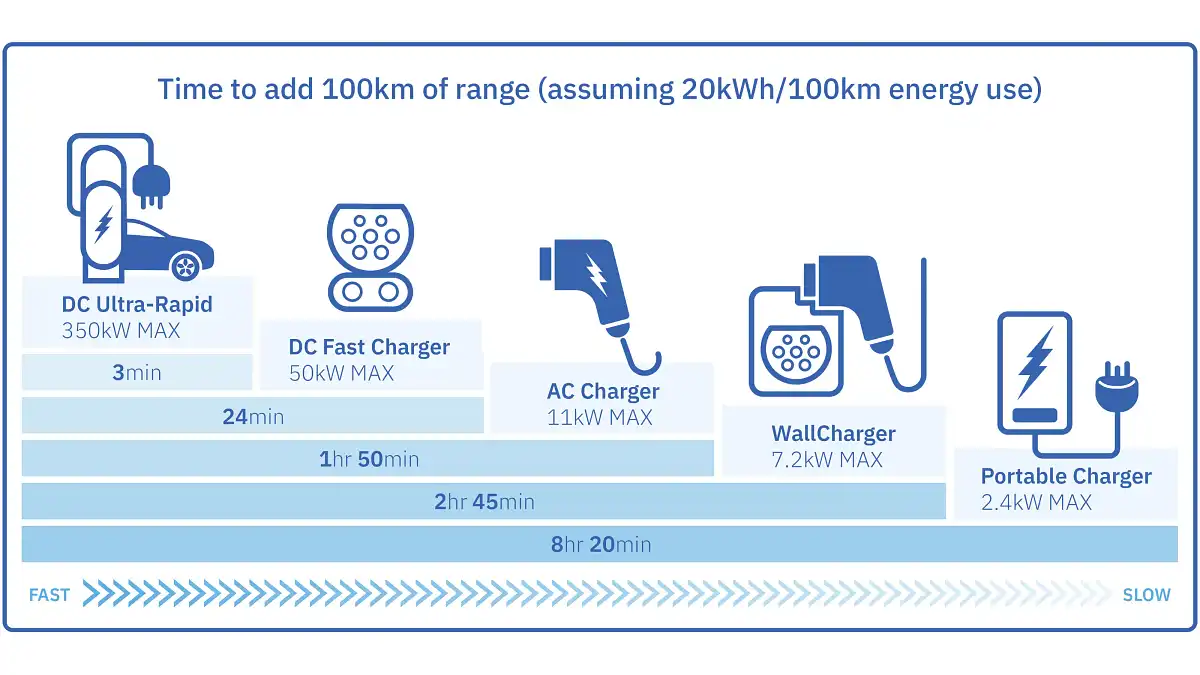
This refers to the power available from the charging source, impacting how quickly the battery fills. There are three main levels:
Level 1 Charging (120V AC):
This is your standard household outlet. It's the slowest option, adding only about 3-5 miles of range per hour. Good for topping off, but impractical for a full charge.
Level 2 Charging (240V AC):
This is what you typically find at home or in public charging stations. It provides significantly faster charging, adding approximately 12-80 miles of range per hour. This requires a dedicated 240V circuit, similar to what you'd use for a clothes dryer.
DC Fast Charging (DCFC):
These are high-powered chargers found along highways and at dedicated charging stations. They can deliver significant power, adding 60-200+ miles of range in just 30 minutes. However, not all EVs are compatible with DCFC, and excessive use can potentially impact battery life.
3. Onboard Charger (kW)
This is a crucial component inside your EV. It converts AC power from Level 1 or Level 2 chargers into DC power that the battery can use. The onboard charger's power rating (kW) limits the maximum charging rate, even if the charging station provides more power. For example, if your car has a 7.2 kW onboard charger, it will only draw 7.2 kW even if plugged into a 10 kW Level 2 charger.
4. Charging Cable (Amperage and Voltage)
The charging cable, also known as an EVSE (Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment), needs to be rated for the voltage and amperage of the charging source. Using a cable that's not adequately rated poses a serious safety hazard. Level 1 cables will come with your car. Level 2 charging will require an additional, appropriately rated EVSE.
5. Battery Management System (BMS)
The BMS is the "brain" of your EV battery. It monitors the battery's voltage, current, temperature, and state of charge. The BMS protects the battery from overcharging, over-discharging, and overheating. It also controls the charging rate to optimize battery health.
How It Works
The charging process can be simplified as follows:
- The driver connects the charging cable to the EV.
- The EVSE communicates with the car to establish a safe connection and determines the available power.
- For Level 1 and Level 2 charging, the AC power from the grid flows through the EVSE and into the car's onboard charger.
- The onboard charger converts the AC power to DC power.
- The BMS monitors the battery's condition and controls the charging rate to optimize battery health and prevent damage.
- For DC Fast Charging, the DC power flows directly from the charging station to the battery, bypassing the onboard charger. This allows for much faster charging rates.
The charging time depends on the factors mentioned above: battery capacity, charging level, onboard charger power, and BMS settings.
Real-World Use: Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some basic troubleshooting steps you can take if you encounter charging issues:
- Check the Charging Cable: Inspect the cable for any damage, such as frayed wires, cracks, or bent pins. A damaged cable can prevent charging or pose a safety hazard.
- Verify the Connection: Make sure the charging cable is securely plugged into both the charging station and the car. A loose connection can interrupt the charging process.
- Check the Charging Station: Ensure the charging station is powered on and functioning correctly. Look for any error messages or indicators on the station's display.
- Check the Car's Display: Look for any error messages or warnings on the car's display. The car might be indicating a problem with the charging process.
- Reset the Charger: Some charging stations have a reset button. Try pressing the reset button to see if it resolves the issue.
- Try a Different Charging Station: If possible, try charging at a different charging station to rule out a problem with the station itself.
If none of these steps resolve the issue, it's best to consult a qualified EV technician.
Safety: Risky Components
Working with electricity is inherently dangerous. Here are some critical safety considerations:
- High Voltage: EV batteries and charging systems operate at high voltage. Never attempt to disassemble or modify any high-voltage components unless you are a qualified technician with the proper training and equipment.
- Damaged Cables: Never use a damaged charging cable. A damaged cable can expose live wires and pose a serious electrocution hazard.
- Water: Never operate charging equipment in wet conditions. Water can conduct electricity and create a dangerous shock hazard.
- Grounding: Ensure that the charging station and electrical system are properly grounded. Grounding provides a path for fault current to flow, preventing electrical shock.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): When working with electrical systems, always wear appropriate PPE, such as insulated gloves and safety glasses.
If you are not comfortable working with electricity, it is always best to consult a qualified electrician or EV technician.
By understanding the intricacies of EV charging, you'll be well-equipped to maximize your charging efficiency, troubleshoot potential problems, and enjoy the benefits of electric vehicle ownership. Remember safety first! We hope that the knowledge here, and the detailed diagram, will help you on your EV journey.
We have the complete high-resolution charging diagram available for download. It includes detailed schematics and component breakdowns to further assist you in understanding EV charging systems. Contact us for the file, happy charging!
