How Long To Charge Nissan Leaf
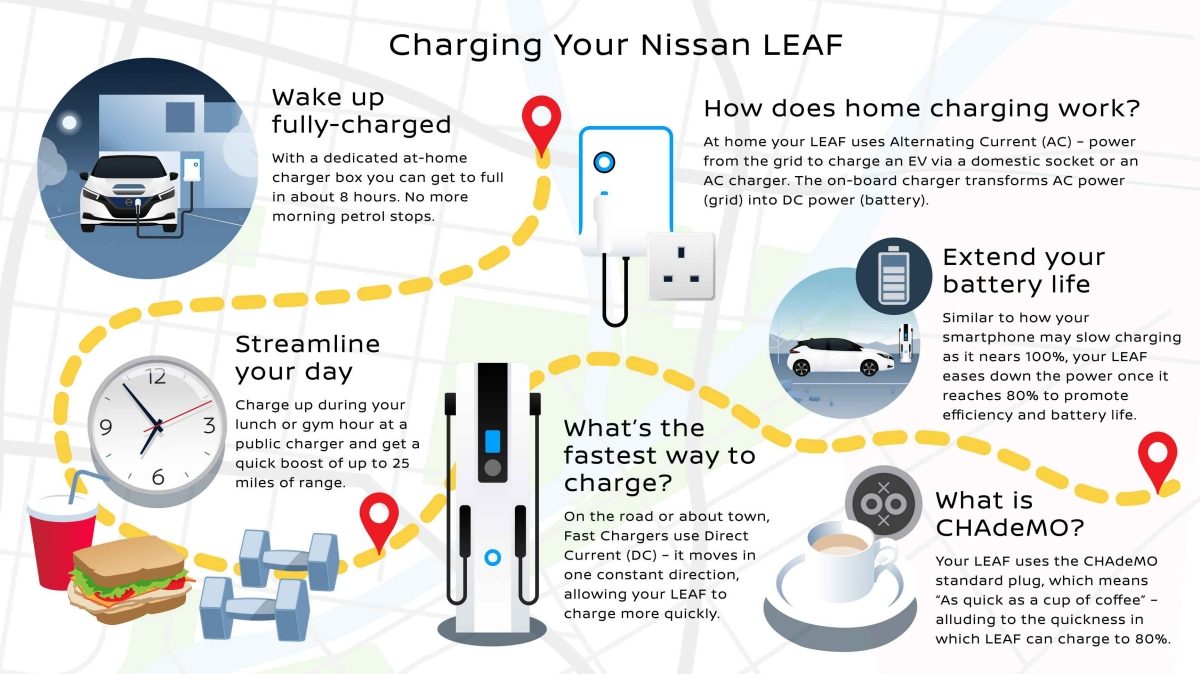
Understanding the charging process of your Nissan Leaf is crucial for maximizing battery life, optimizing charging times, and even diagnosing potential issues. This article will delve into the technical aspects of Leaf charging, providing you with the knowledge needed to troubleshoot common problems and make informed decisions about your charging routine. We'll be focusing on the factors influencing charging time and what you, as an experienced DIYer, can do to ensure efficient and safe charging. We even have a detailed charging system diagram available for download later in this article to assist with repairs or further learning.
Why Understanding Leaf Charging Matters
The information presented here empowers you to take control of your Leaf's charging. It's useful for understanding why charging takes longer than expected, diagnosing potential charging issues (like a failing onboard charger), optimizing your charging schedule to take advantage of off-peak electricity rates, and even performing minor repairs or modifications to your charging setup (within safe and legal limits, of course!).
This knowledge goes beyond simply plugging in your car. It allows you to anticipate potential problems and avoid costly repairs. It also empowers you to make informed decisions about charging infrastructure upgrades, like installing a faster home charger.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the Nissan Leaf Charging System
Before we dive into the charging process itself, let's familiarize ourselves with the main components:
- Onboard Charger (OBC): This converts AC power from the charging station or wall outlet into DC power that the battery can store. Leaf models have varying OBC capacities, typically 3.6 kW or 6.6 kW. The onboard charger capacity is a major limiting factor in AC charging speed.
- Battery Management System (BMS): The BMS constantly monitors the battery's voltage, current, temperature, and state of charge (SoC). It regulates the charging process to prevent overcharging, overheating, and other conditions that could damage the battery.
- Charging Port (J1772 or CHAdeMO): The J1772 port is used for Level 1 and Level 2 AC charging. The CHAdeMO port is used for DC fast charging.
- Charging Cable: The cable connects the car to the charging station. It carries both power and communication signals.
- Battery Pack: The Leaf's battery pack stores the electrical energy. Its capacity is measured in kWh (kilowatt-hours).
- Inverter: While not directly involved in the charging process, the inverter converts DC power from the battery to AC power to run the motor.
Important Specs to Consider:
- Battery Capacity (kWh): This determines the total amount of energy the battery can store.
- Onboard Charger Capacity (kW): This dictates the maximum AC charging rate.
- Charging Station Power (kW): This determines the maximum power the charging station can deliver.
- Voltage (V): The voltage of the charging station and the car's charging system must be compatible.
- Current (A): The maximum current the charging cable and the charging system can handle.
Understanding Charging System Symbols (Referencing the Downloadable Diagram)
The charging system diagram we offer uses standard electrical and automotive symbols. Here's a quick guide to some of the key symbols:
- Solid Lines: Represent power conductors (carrying electrical current).
- Dashed Lines: Represent communication signals (carrying data between components).
- Thick Lines: Indicate high-current circuits.
- Thin Lines: Indicate low-current circuits.
- Rectangles: Typically represent electronic components or modules (e.g., BMS, OBC).
- Circles: Often represent connectors or connection points.
- Ground Symbol: Indicates a connection to the vehicle's chassis ground.
- Specific Icons: Look for icons representing fuses, relays, and other components. These are usually standard electrical symbols.
The color coding in the diagram typically indicates the voltage level or function of the circuit (e.g., red for high-voltage DC, blue for communication signals). Consult the diagram's legend for specific color assignments.
How Leaf Charging Works: A Step-by-Step Explanation
The charging process varies depending on the charging level (Level 1, Level 2, or DC Fast Charging):
Level 1 Charging (120V AC)
- The charging cable is plugged into a standard 120V wall outlet.
- The OBC converts the 120V AC power to DC power.
- The BMS monitors the battery's condition and controls the charging process.
- The battery charges at a slow rate (typically 1.2-1.8 kW).
Level 2 Charging (240V AC)
- The charging cable is plugged into a 240V charging station.
- The OBC converts the 240V AC power to DC power.
- The BMS monitors the battery's condition and controls the charging process.
- The battery charges at a faster rate (up to the OBC's capacity, typically 3.6 kW or 6.6 kW).
DC Fast Charging (CHAdeMO)
- The charging cable is plugged into a CHAdeMO DC fast charging station.
- The DC fast charger bypasses the OBC and delivers DC power directly to the battery. This is a key difference!
- The BMS monitors the battery's condition and controls the charging process.
- The battery charges at a much faster rate (up to the charging station's capacity, typically 50 kW or more).
In all charging scenarios, the BMS plays a critical role in ensuring safe and efficient charging. It communicates with the charging station and the OBC (or the DC fast charger) to regulate the charging voltage and current. It also monitors the battery's temperature and can slow down or stop charging if the battery gets too hot or too cold.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some common charging issues and potential solutions:
- Charging is slow: Check the charging station's power output, the OBC capacity, and the charging cable's current rating. Also, consider battery temperature – charging slows significantly in extreme temperatures.
- Charging stops unexpectedly: This could be due to overheating, a faulty charging station, or a problem with the BMS. Check the charging station's display for error messages.
- Car won't charge: Inspect the charging cable for damage. Try a different charging station. If the problem persists, it could be a problem with the OBC or the charging port.
- Error messages on the dashboard: Consult the owner's manual or a qualified technician.
Remember: Always disconnect the power source before performing any repairs or inspections on the charging system.
Safety: Highlighting Risky Components
The charging system involves high voltages and currents, which can be dangerous. Exercise extreme caution when working with these components.
- High-Voltage Battery Pack: This contains a significant amount of energy and can deliver a lethal shock. Do not attempt to open or repair the battery pack yourself.
- Onboard Charger: This converts AC power to DC power and contains high-voltage components. Avoid opening or tampering with the OBC unless you are a qualified technician.
- Charging Cables: Inspect charging cables for damage before each use. Do not use damaged cables.
- DC Fast Charging Stations: These deliver very high power levels. Follow all safety instructions provided by the charging station operator.
Always disconnect the power source before working on any electrical components. Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as insulated gloves and eye protection. If you are unsure about any aspect of the charging system, consult a qualified technician.
We have prepared a detailed charging system diagram of the Nissan Leaf, which you can download here. This diagram can assist you in understanding the intricate details of the charging system, aiding in troubleshooting and repair endeavors.
