How Many Cars Made In Usa
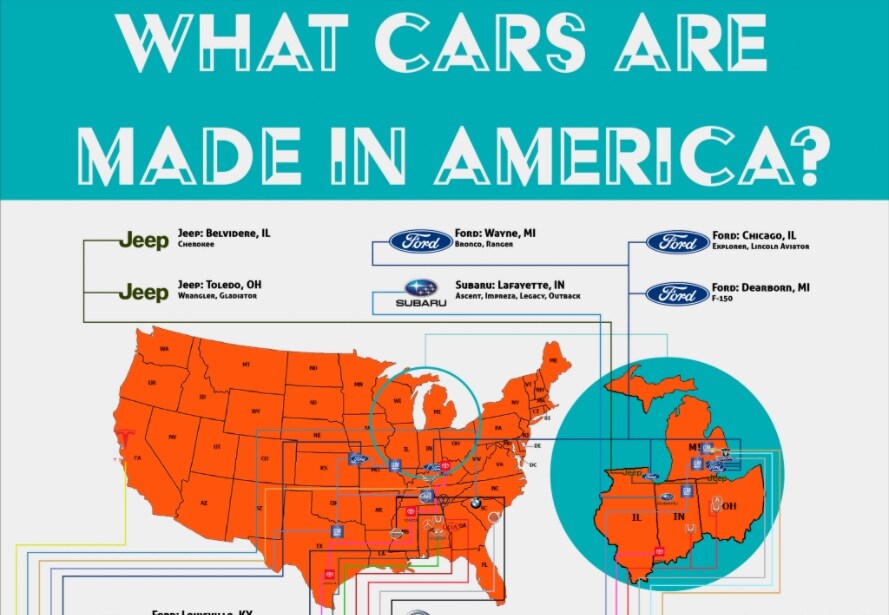
Estimating the precise number of cars manufactured in the USA is a surprisingly complex task. Unlike tracking smartphones or televisions, the automotive industry involves a multitude of manufacturers, constantly shifting production locations, and varying definitions of what constitutes a "made in USA" vehicle. This article aims to demystify the process and provide you with a comprehensive understanding of how we can approximate this figure and why it matters.
Why Understanding US Car Production Matters
For an experienced DIYer or car enthusiast, understanding US car production has several benefits:
- Parts Sourcing: Knowing where a car was primarily assembled can significantly impact the availability and cost of replacement parts. Vehicles assembled in the US often utilize US-sourced components, making replacements easier to find and potentially cheaper.
- Modding and Customization: Assembly location can influence subtle variations in vehicle specifications. Understanding these variations allows for more informed customization and modification decisions.
- Repair Strategies: Familiarity with the common manufacturing processes and potential weak points of US-assembled vehicles can inform your diagnostic and repair strategies.
- Informed Purchasing: You can make informed decisions about the origin and support of the vehicles you are buying, knowing if they will be supported by local manufacturers.
Furthermore, for those interested in the economic impact of the automotive industry, tracking US car production provides insights into employment trends, supply chain dynamics, and overall economic health.
Key Specs and Main Players
Instead of pinpointing a single, definitive number, it's more accurate to discuss annual production ranges and the key factors influencing them. We're talking in the millions. Here are some key players and their typical US production volume ranges:
- General Motors (GM): Operates multiple assembly plants across the US, producing a wide range of vehicles from trucks and SUVs to cars. Annual US production varies, but typically falls within the 1.5 to 2.5 million vehicle range.
- Ford Motor Company: Similar to GM, Ford maintains a significant US manufacturing footprint. Their US production generally ranges from 1.2 to 2 million vehicles annually.
- Stellantis (formerly Fiat Chrysler Automobiles): Stellantis has a substantial US manufacturing presence. Production varies widely depending on model popularity and market demand, but often falls within the 1 to 1.8 million vehicle range.
- Toyota Motor Manufacturing, North America (TMMNA): While a Japanese company, Toyota has significant US manufacturing operations. Their US production typically ranges from 1 to 1.5 million vehicles annually.
- Honda of America Mfg., Inc.: Similar to Toyota, Honda maintains a sizable US manufacturing presence. Production usually falls between 800,000 and 1.2 million vehicles annually.
- BMW Manufacturing Co. (South Carolina): BMW manufactures a significant number of SUVs in South Carolina. Their US production is typically between 400,000 and 500,000 vehicles annually.
- Mercedes-Benz US International, Inc. (Alabama): Mercedes-Benz also has a large US production facility. Their annual output usually falls between 300,000 and 400,000 vehicles.
- Tesla:Tesla's production volume is highly variable depending on factory ramp ups and demand, but is a significant player in the total US numbers.
Key Specs to Consider:
- Assembly Location: This is the primary factor. A vehicle "made in USA" typically means final assembly occurred within the US.
- Domestic Parts Content: The percentage of parts sourced from the US or Canada. The higher the percentage, the more "domestic" the vehicle. The American Automobile Labeling Act (AALA) requires manufacturers to disclose this percentage.
- Engine and Transmission Origin: While the vehicle may be assembled in the US, the engine and transmission might be imported. This affects the overall "domestic content."
How US Car Production Works
The car production process is a complex, highly orchestrated operation involving several stages:
- Stamping: Large presses stamp metal sheets into body panels.
- Body Assembly: Robots and skilled workers weld the stamped panels together to form the vehicle's body.
- Painting: The assembled body undergoes multiple layers of paint and coating for protection and aesthetics.
- Powertrain Installation: The engine, transmission, and drivetrain components are installed into the vehicle's chassis.
- Interior Assembly: Seats, dashboard, trim, and electronics are installed.
- Final Assembly: Wheels, tires, and other final components are added.
- Quality Control: The vehicle undergoes rigorous testing and inspection to ensure it meets quality standards.
Modern car factories rely heavily on automation, especially in welding and painting. However, skilled workers are still essential for many tasks, including quality control, complex assembly operations, and maintenance of the automated systems.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting and Parts Identification
Understanding the general production process can aid in troubleshooting:
- Rust Issues: Knowing the stamping and painting processes can help you identify potential rust-prone areas. For instance, seams and welds are often susceptible to corrosion.
- Electrical Problems: Understanding the wiring harness routing during assembly can aid in tracing electrical faults.
- Parts Identification: Knowing the model year and assembly location can help you identify the correct replacement parts. Vehicle Identification Numbers (VINs) contain information about the assembly plant.
For example, if you are experiencing rust issues on a vehicle that was assembled in a region with harsh winters and uses a significant amount of road salt, you might focus your inspection on areas where water and salt are likely to accumulate, such as wheel wells, rocker panels, and undercarriage seams.
Safety: Highlighting Risky Components
Working on vehicles involves inherent risks. Here are some components that require extra caution:
- High-Voltage Systems (Electric and Hybrid Vehicles): Electric and hybrid vehicles contain high-voltage systems that can be lethal. Always disconnect the high-voltage battery and follow proper safety procedures before working on these systems.
- Airbag Systems: Airbags can deploy unexpectedly if mishandled. Disconnect the battery and wait several minutes before working near airbags.
- Fuel Systems: Fuel is highly flammable. Work in a well-ventilated area and avoid open flames or sparks when working on fuel systems.
- Suspension Systems: Compressed springs can release with tremendous force. Use proper spring compressors when disassembling suspension components.
Always consult the vehicle's service manual for specific safety procedures and precautions before performing any repairs or modifications.
Disclaimer: Automotive repair and modification can be dangerous. Always prioritize safety and consult with a qualified professional if you are unsure about any procedure.
The Challenge of "Made in USA"
The definition of "made in USA" is increasingly blurred in the automotive industry due to globalization. While a vehicle might be assembled in the US, many of its components could be sourced from other countries. The AALA mandates that automakers disclose the percentage of US and Canadian content, but this number can be misleading, as it doesn't account for the origin of all parts. For example, parts made in Mexico but assembled in the US count towards the domestic parts total. This makes it nearly impossible to be perfectly certain where every single component came from.
The domestic parts content label is only an indicator of US/Canadian parts, not all domestically produced parts.
Accessing Detailed Production Information
Detailed production data, broken down by manufacturer, model, and assembly location, is often considered proprietary information and isn't readily available to the general public. However, several resources can provide valuable insights:
- Automotive Industry Associations: Organizations like the Alliance for Automotive Innovation and the United Auto Workers (UAW) often publish reports and data on US automotive production.
- Market Research Firms: Companies like IHS Markit and LMC Automotive provide comprehensive data and analysis on the automotive industry, but their reports are typically subscription-based.
- Government Agencies: The US Department of Commerce and the US International Trade Commission collect and publish data on automotive trade and production.
- VIN Decoding Services: Online VIN decoding services can provide information about the vehicle's assembly plant.
By cross-referencing information from these sources, you can gain a more accurate understanding of US car production trends and the origin of specific vehicles.
