How Many Electric Cars In Us
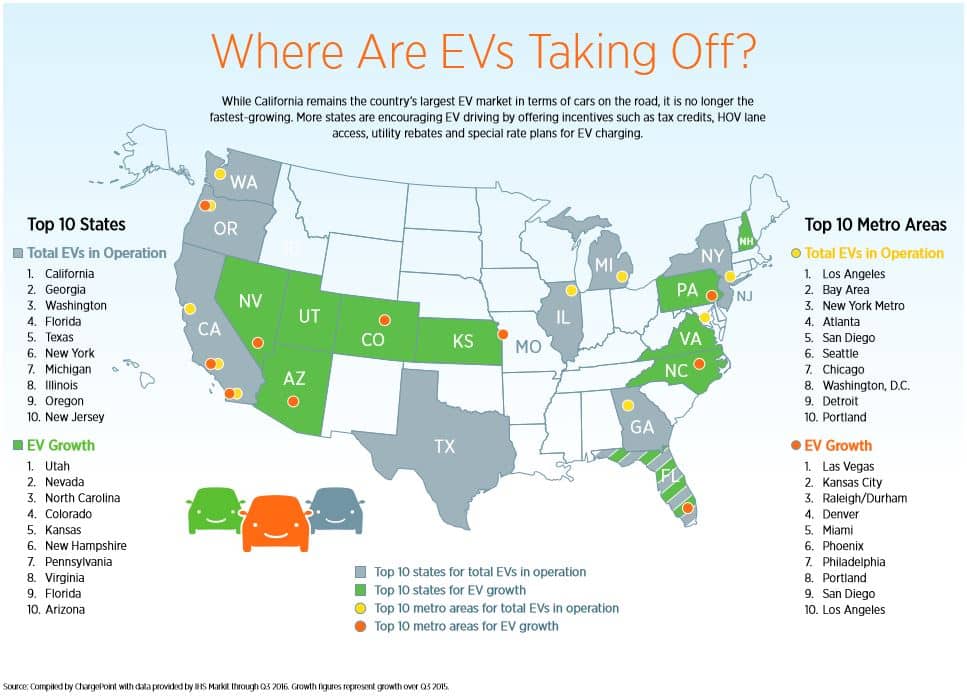
Alright, let's dive into the world of electric vehicle (EV) adoption in the US. Understanding the current landscape of EVs on American roads is crucial for several reasons. Whether you're planning on buying an EV, considering starting an EV repair business, or simply curious about the future of transportation, knowing the numbers and trends gives you a solid foundation.
How Many Electric Cars Are Actually in the US?
Pinpointing the exact number of EVs in the US is a moving target, but we can get a pretty good estimate. Various sources track EV sales and registrations. As of late 2024, estimates place the number of battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) on US roads at around 3.5 to 4 million vehicles. This figure represents a relatively small, but rapidly growing, percentage of the total vehicle fleet in the United States, which is somewhere north of 280 million vehicles. The percentage is small, but the growth rate is substantial.
Why This Matters to You
Purpose: Understanding EV adoption rates is essential for various reasons. For the DIY mechanic or modder, it means potentially expanding your skill set to include EV maintenance and repair. As the EV market grows, so does the demand for knowledgeable technicians. It also informs decisions about infrastructure investments, such as installing charging stations or modifying your home's electrical system. Finally, keeping abreast of these trends is valuable for anyone considering purchasing an EV.
Dissecting the Numbers: Key Specs and Main Parts Contributing to the Total
Breaking down the EV landscape requires considering a few key categories:
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs): These are purely electric vehicles, running solely on battery power. Examples include Tesla Model 3, Chevrolet Bolt, and Ford Mustang Mach-E. The number of BEVs is generally higher than PHEVs and constitutes the larger part of total EV count.
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs): These vehicles have both an electric motor and a gasoline engine. They can be plugged in to charge the battery, but can also run on gasoline when the battery is depleted. Examples include Toyota Prius Prime and Chrysler Pacifica Hybrid. PHEVs represent a significant but declining proportion of the total EV count as consumer preferences shift towards fully electric options.
Several factors influence the total number of EVs, including:
- Government Incentives: Federal and state tax credits, rebates, and other incentives play a significant role in making EVs more affordable.
- Battery Technology Advancements: Improvements in battery energy density (kWh/kg), range (miles per charge), and charging speed are driving increased EV adoption.
- Charging Infrastructure Availability: The expansion of public charging networks, particularly DC fast charging stations, is crucial for alleviating range anxiety and making EVs more practical for long-distance travel.
- Consumer Awareness and Acceptance: Increased public awareness about the benefits of EVs, such as reduced emissions and lower running costs, is driving demand.
- Automaker Investment: The commitment of major automakers to developing and producing a wide range of EV models is expanding consumer choice.
Deciphering EV Market Share Diagrams
While we don't have a specific schematic diagram to dissect here, let's imagine one representing EV market share. Such a diagram would typically use visual elements to convey information about different aspects of the EV market.
Common Visual Elements and Their Meanings
- Pie Charts: These are commonly used to represent the market share of different EV manufacturers or vehicle types (BEV vs. PHEV). The size of each slice corresponds to its percentage of the total market.
- Bar Graphs: These can show the sales volume of different EV models or brands over time. Horizontal bars might represent different manufacturers, while the length of the bar indicates the number of vehicles sold.
- Line Graphs: These are useful for illustrating trends in EV adoption over time, such as the annual growth rate of EV sales. The X-axis would represent time, and the Y-axis would represent the number of EVs sold or the percentage of the total vehicle market.
- Color Coding: Different colors might be used to represent different EV brands or vehicle types. For example, blue might represent Tesla, green might represent Nissan, and so on.
- Icons: Small icons might be used to represent different EV models or charging station types. For example, a car icon with a plug symbol might represent a PHEV, while a lightning bolt icon might represent a DC fast charging station.
Analyzing such diagrams allows you to quickly grasp key trends in the EV market, such as which manufacturers are leading in sales, which vehicle types are most popular, and how quickly the EV market is growing.
How the EV Market Functions
The EV market works through the interplay of several key stakeholders:
- Automakers: These companies design, manufacture, and sell EVs. They invest heavily in research and development to improve battery technology, vehicle performance, and charging infrastructure.
- Battery Manufacturers: These companies produce the batteries that power EVs. They are constantly working to improve battery energy density, range, and charging speed.
- Charging Infrastructure Providers: These companies build and maintain public charging networks. They install and operate charging stations in various locations, such as shopping malls, parking garages, and highway rest stops.
- Utilities: These companies provide the electricity that powers EVs. They are working to ensure that the grid can handle the increased demand from EVs.
- Government Agencies: These agencies provide incentives and regulations to promote EV adoption. They also invest in research and development and work to develop charging infrastructure standards.
- Consumers: These are the people who buy and drive EVs. Their purchasing decisions influence the direction of the EV market.
Real-World Use: Understanding Market Fluctuations
Let's say you notice a sudden dip in the sales of a particular EV model on the diagram. Here are some basic troubleshooting steps to consider:
- Check for Recall Notices: Has there been a recent recall of the vehicle due to safety concerns or manufacturing defects?
- Review Recent News Articles: Have there been any negative news reports about the vehicle, such as poor reliability ratings or safety issues?
- Compare to Competitor Models: Have there been recent improvements or price reductions in competing EV models that might be drawing customers away?
- Investigate Production Issues: Is the manufacturer experiencing any production bottlenecks or supply chain disruptions that are limiting the availability of the vehicle?
By investigating these factors, you can gain a better understanding of why the sales of a particular EV model are fluctuating.
Safety Considerations
While we're talking about EVs, it's crucial to highlight the safety aspect, especially when dealing with high-voltage systems. Remember, these are not gasoline engines. Working on EVs requires specialized training and equipment.
- High-Voltage Batteries: These batteries contain a significant amount of energy and can deliver lethal shocks. Always disconnect the battery and follow proper lockout/tagout procedures before working on any electrical components. Never assume a system is de-energized; always verify with a calibrated multimeter.
- High-Voltage Cables: These cables carry high-voltage current and can also deliver lethal shocks. Handle them with extreme care and always use insulated tools.
- Capacitors: These components can store a charge even after the battery has been disconnected. Discharge capacitors before working on them.
- Regenerative Braking Systems: These systems can generate electricity when the vehicle is braking. Be aware of the potential for voltage to be present even when the vehicle is not running.
Always consult the vehicle's service manual for specific safety procedures and precautions. If you are not comfortable working on high-voltage systems, seek the assistance of a qualified EV technician.
The EV market is dynamic, influenced by technological advancements, government policies, and consumer preferences. Keeping abreast of these trends is crucial for anyone involved in the automotive industry or considering EV ownership.
We have access to detailed schematics and market analysis data. If you'd like to delve deeper into specific aspects of the EV market, feel free to reach out. We can provide you with relevant diagrams and information to support your research or project.
