How Many Electric Cars In Usa
Alright folks, let's dive into the electrifying world of EVs and take a look at the current landscape: How many electric cars are actually cruising around in the USA? This isn't just a trivia question; understanding the scale of EV adoption is crucial for anyone involved in automotive repair, modification, or even just informed ownership. Knowing the numbers helps predict future trends, understand the growing demand for specialized tools and knowledge, and potentially even influence policy decisions.
Current Electric Car Numbers in the USA
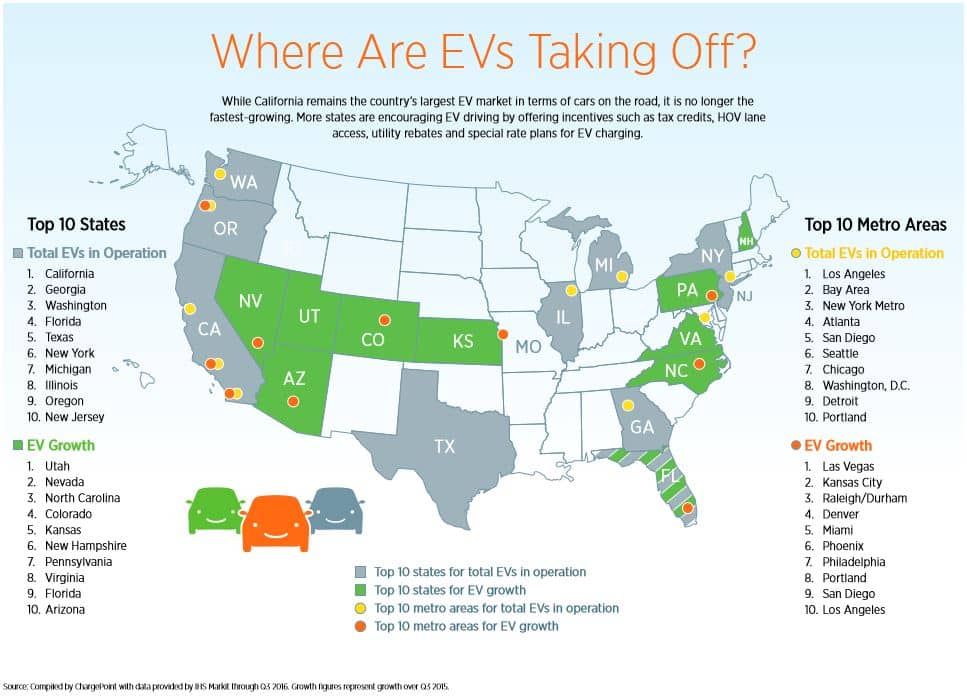
Pinpointing the exact, real-time number of electric vehicles (EVs), including Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) and Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs), on US roads is a constantly moving target. Data is gathered from various sources like vehicle registrations, sales figures from manufacturers, and independent research institutions. However, a fairly accurate snapshot is achievable. As of late 2024, estimates suggest that there are well over 3 million EVs registered in the United States. This represents a significant increase over the past few years, and the trend is expected to continue upwards. Keep in mind that the rate of adoption varies considerably by state, with California leading the charge, followed by other states offering incentives and robust charging infrastructure.
Now, let's break that down a bit. This 3 million+ number includes both BEVs (pure electric vehicles like Teslas, Chevy Bolts, and Nissan Leafs) and PHEVs (hybrids like the Toyota Prius Prime or Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV, which have both a battery and a gasoline engine). It's important to distinguish between these because their maintenance and repair needs differ significantly.
Why This Matters to You
As an intermediate car owner, modder, or DIY mechanic, this information has several practical implications:
- Growing Market: The increasing number of EVs means a growing market for specialized tools, diagnostic equipment, and training. If you're thinking of expanding your skills, EV maintenance and repair are areas with high potential.
- Parts Availability: As more EVs hit the road, the demand for replacement parts – batteries, inverters, motors, and charging components – will rise. Understanding where to source these parts and how to diagnose common EV issues will become increasingly valuable.
- Infrastructure: The expansion of the charging infrastructure directly impacts EV ownership. Knowing the density of charging stations in your area or areas you plan to travel to is crucial for planning and range anxiety mitigation.
- Safety Considerations: Working on EVs presents unique safety challenges. Understanding high-voltage systems and proper safety procedures is essential to avoid serious injury.
Key Specs and Main Parts of an Electric Vehicle
Let's briefly touch on the key components that differentiate EVs from traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles:
- Battery Pack: This is the heart of the EV, storing the electrical energy that powers the motor. Batteries are typically Lithium-ion, but other chemistries are being explored. The capacity of the battery pack, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), determines the vehicle's range.
- Electric Motor: This converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, driving the wheels. EVs typically use AC (Alternating Current) motors, which are known for their efficiency and reliability.
- Inverter: This converts DC (Direct Current) power from the battery into AC power for the motor. It also regulates the motor's speed and torque.
- Onboard Charger (OBC): This converts AC power from the grid into DC power to charge the battery. The charging rate, measured in kilowatts (kW), determines how quickly the battery can be charged.
- Thermal Management System: This system regulates the temperature of the battery pack, motor, and other components. Maintaining optimal temperature is crucial for battery life and performance.
- Brake Regenerative System: This system captures kinetic energy during braking and converts it back into electrical energy, which is then stored in the battery. This improves the vehicle's efficiency and range.
- DC-DC Converter: Converts the high voltage DC from the traction battery to 12V DC for the car's auxiliary systems (lights, radio, etc.).
These components are interconnected and controlled by a complex electronic control system. Diagnosing problems in an EV often requires specialized diagnostic tools and software.
How It Works: The Basics
The fundamental principle is relatively straightforward: when you press the accelerator pedal, the vehicle's computer sends a signal to the inverter. The inverter then converts DC power from the battery pack into AC power and sends it to the electric motor. The motor spins, turning the wheels and propelling the vehicle forward. The brake regenerative system captures energy during braking and sends it back to the battery, increasing efficiency. Charging the battery involves plugging the vehicle into an external power source, which feeds AC power into the onboard charger. The charger converts the AC power into DC power and charges the battery. The battery pack voltage is extremely dangerous and can be lethal!
Real-World Use – Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Even with their advanced technology, EVs can experience problems. Here are a few basic troubleshooting tips:
- Charging Issues: If your EV isn't charging, check the charging cable, the charging port on the vehicle, and the charging station itself. Make sure the charging station is properly powered and that the cable is securely connected. Check the vehicle's display for any error messages.
- Range Reduction: If your EV's range has decreased significantly, check the tire pressure, driving habits, and battery health. Aggressive driving, low tire pressure, and extreme temperatures can all reduce range. A degraded battery will naturally hold less charge.
- Warning Lights: Pay attention to any warning lights on the dashboard. Consult the vehicle's owner's manual to understand the meaning of the lights and take appropriate action.
- Diagnostic Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner (some are EV-specific) to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). These codes can provide valuable clues about the nature of the problem. Note that while standard OBD-II is used, some codes are manufacturer-specific and require specialized software to interpret.
Important: Many EV issues require specialized diagnostic tools and expertise. If you're not comfortable working with high-voltage systems, it's best to take your vehicle to a qualified EV technician.
Safety – Highlighting Risky Components
Working on EVs can be extremely dangerous due to the high-voltage systems. The battery pack typically operates at voltages ranging from 200V to 800V, which can be lethal. Always disconnect the high-voltage battery before working on any electrical components. This involves following specific procedures outlined in the vehicle's service manual. Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including insulated gloves and safety glasses. Never touch any exposed wires or connectors. Be aware of the potential for arc flash, which can cause severe burns. De-energizing the high voltage system is a MUST. Always double check with a multimeter before touching any components.
Here are some specific areas to be cautious of:
- Battery Pack: Handle with extreme care. Do not puncture, crush, or expose to extreme temperatures.
- High-Voltage Cables: These cables are typically orange or yellow. Never cut or damage them.
- Inverter: This component contains high-voltage capacitors that can store energy even after the battery is disconnected.
- Electric Motor: Be aware of the potential for back EMF (electromotive force), which can generate high voltages.
Always consult the vehicle's service manual and follow proper safety procedures when working on EVs. If you are unsure about any aspect of the repair, seek professional assistance.
Downloadable Diagram
To aid in your understanding and potential future work, we have a simplified block diagram of a typical EV powertrain system available for download. This diagram outlines the major components and their interconnections. While not a substitute for a vehicle-specific service manual, it provides a valuable overview of the system.
Feel free to reach out if you have any further questions. Remember to prioritize safety when working with any automotive system, especially the high-voltage components of an electric vehicle.
