How Much Do New Cars Cost
So, you're looking to buy a new car, or perhaps you're just curious about the sticker shock at your local dealership. Understanding the cost of a new car isn't as simple as looking at the MSRP (Manufacturer's Suggested Retail Price). There's a complex interplay of factors at play, from manufacturing costs to market demand. This article will break down those factors, acting as your trusted mechanic explaining the engine of new car pricing.
Understanding the Components of a New Car's Price
Before we dive into the specifics, it's crucial to understand that a new car's price is a composite of several key elements. Think of it as a layered cake, each layer contributing to the final taste (or in this case, the final price).
Key Specs and Main Parts of the Price "Cake"
- Manufacturing Costs: This is the foundation of the cake. It encompasses everything from raw materials (steel, aluminum, plastics, etc.) to labor costs at the factory. Automation and supply chain efficiency play a huge role here.
- R&D (Research and Development): Automakers invest heavily in developing new technologies, safety features, and engine designs. This cost is spread across the vehicles they produce. Consider the cost of developing hybrid or electric powertrains – a significant investment.
- Marketing and Advertising: That slick TV commercial and glossy magazine ad? Someone has to pay for it. Marketing costs are a significant factor, especially for new models or brands trying to gain market share.
- Dealer Costs and Markup: Dealers aren't making money by simply holding cars on their lot. They have overhead costs (rent, utilities, salaries) and, of course, they need to make a profit. The difference between the invoice price (what the dealer pays the manufacturer) and the selling price is their markup.
- Taxes and Fees: These are the unavoidable government charges. Sales tax is the most obvious, but there might also be registration fees, title fees, and other local taxes depending on your location.
- Destination Charges: This covers the cost of transporting the vehicle from the factory to the dealership. It's usually a fixed amount and is non-negotiable.
- Options and Packages: The base price of a car is often just that – the base. Adding options like leather seats, a sunroof, a premium sound system, or advanced safety features can significantly increase the price.
How It Works: The Pricing Equation
The final price you see on the sticker is the result of a complex equation. Let's break it down further:
Manufacturing Cost + R&D + Marketing + Dealer Invoice Price + Dealer Markup + Destination Charge + Options/Packages + Taxes/Fees = Final Price
Understanding this equation is crucial for negotiating a fair price. You can't do much about the manufacturing cost, R&D, or marketing expenses, but you *can* influence the dealer markup and the price of options. Research is key. Know the invoice price (which you can often find online) and compare prices from different dealerships. Be prepared to walk away if you're not getting a fair deal.
Symbols and Terminology Explained
Let's clarify some common terms and concepts you'll encounter when researching car prices:
- MSRP (Manufacturer's Suggested Retail Price): This is the price the manufacturer suggests the dealer sell the car for. It's often higher than the actual selling price.
- Invoice Price: This is the price the dealer pays the manufacturer for the car. It's a good starting point for negotiations.
- Dealer Incentives: These are discounts or rebates offered by the manufacturer to the dealer to encourage them to sell more cars. Dealers may or may not pass these incentives on to the customer.
- Rebates: These are direct discounts offered by the manufacturer to the customer. They can be in the form of cash rebates, financing incentives, or lease deals.
- APR (Annual Percentage Rate): This is the annual interest rate you'll pay on a car loan. It's important to shop around for the best APR.
- Residual Value: This is the estimated value of the car at the end of a lease. It's used to calculate your monthly lease payments.
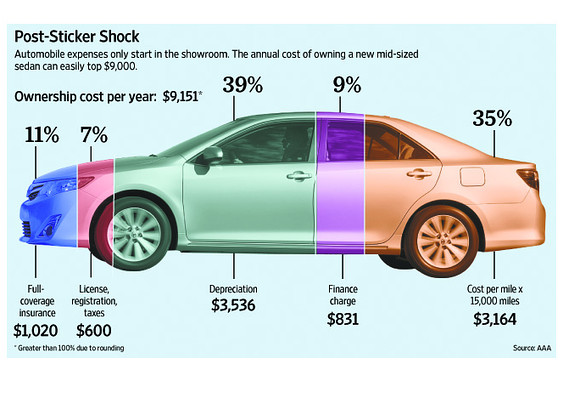
- Depreciation: The decline in value of a car over time. Some cars depreciate faster than others. Understanding depreciation is crucial for making a smart financial decision.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting for Price Negotiations
Here are some tips for navigating the price negotiation process:
- Do your research: Know the invoice price, available rebates, and the average selling price of the car in your area. Websites like Edmunds, Kelley Blue Book, and TrueCar can be helpful.
- Get multiple quotes: Contact several dealerships and get quotes in writing. This will give you leverage when negotiating.
- Negotiate the price, not the payment: Focus on the total price of the car, not just the monthly payment. Dealers can manipulate the payment by extending the loan term or increasing the interest rate.
- Be prepared to walk away: Don't be afraid to walk away if you're not getting a fair deal. There are plenty of other dealerships out there.
- Consider buying at the end of the month or year: Dealers are often under pressure to meet sales quotas at the end of the month or year, which can make them more willing to offer discounts.
- Look for dealer incentives: Ask the dealer about any available incentives that you might qualify for.
- Don't be afraid to haggle: The price on the sticker is just a suggestion. Be prepared to haggle for a lower price.
Safety: Avoiding Common Pricing Traps
There are a few common pricing traps to watch out for:
- "Lowball" offers: Be wary of dealers who offer suspiciously low prices. They may be trying to lure you in with a bait-and-switch tactic.
- Hidden fees: Make sure you understand all the fees that are included in the price. Some dealers may try to add on hidden fees like "dealer prep" or "documentation fees."
- "Add-ons" you don't need: Dealers may try to sell you add-ons like extended warranties, paint protection, or fabric protection. These are often overpriced and unnecessary.
- Financing scams: Be careful of dealers who try to trick you into accepting a higher interest rate than you qualify for. Shop around for financing from different lenders before you go to the dealership.
Important Note: Always read the fine print and understand all the terms and conditions before signing any paperwork. If you're unsure about anything, consult with a trusted advisor or attorney.
Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to buying a new car. By understanding the factors that influence the price, you can be a more informed and confident buyer.
We have a detailed diagram illustrating the price breakdown of a new car, including average markups and potential negotiation points. This visual aid can be incredibly helpful in understanding the complexities of new car pricing. If you'd like a copy, please contact us and we'll provide it to you.
