How Much Is Gap Insurance In Nj
Alright gearheads, let's dive into a topic that's less about horsepower and more about financial security: Gap Insurance in New Jersey. It's not as sexy as a turbocharger, but understanding it can save you a ton of headache down the road. This isn't just for newbies; even experienced car owners often overlook the nuances of gap coverage. We're going to break down how gap insurance costs are determined in New Jersey, what affects those costs, and how to make informed decisions when purchasing it.
Purpose of Understanding Gap Insurance Costs
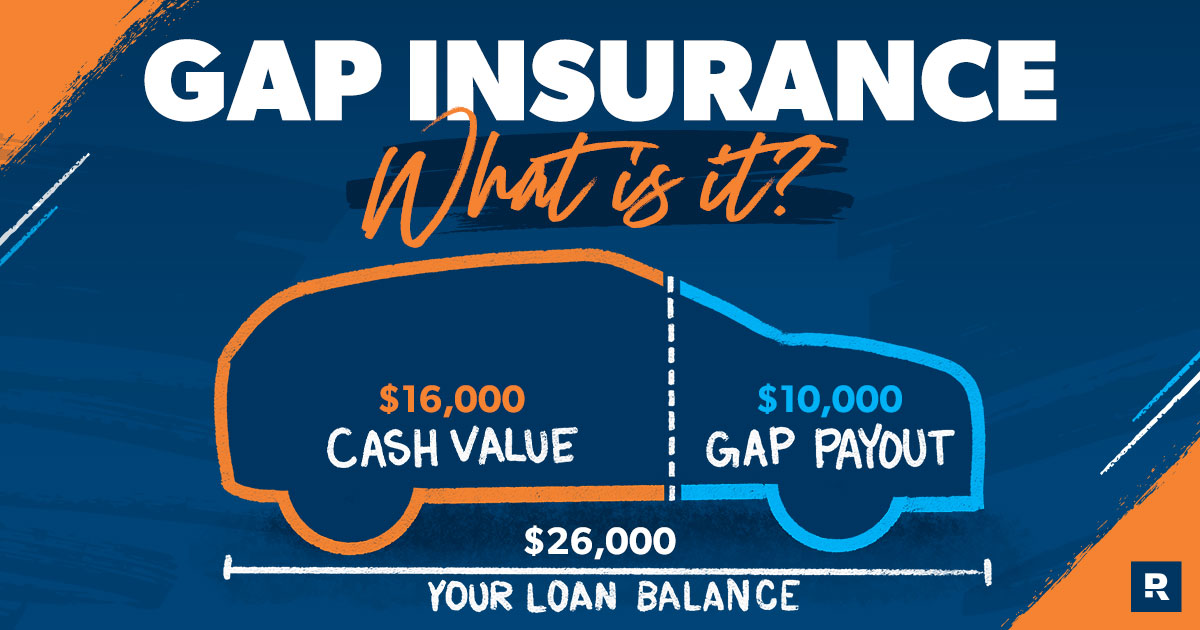
The purpose here is simple: avoid getting underwater on your car loan. "Underwater," in this context, means you owe more on your car than it's actually worth. This situation is particularly risky if your car is totaled or stolen. Without gap insurance, you're responsible for the difference between what your insurance pays out (the car's actual cash value or ACV) and the remaining loan balance. Understanding the cost factors empowers you to negotiate effectively and choose the right coverage level. Think of it as preventative maintenance for your wallet.
Key Specs and Main Parts of Gap Insurance Costs
The cost of gap insurance isn't a fixed number. It's a variable influenced by several factors, which we can consider the "main parts" that contribute to the final premium:
- Vehicle's Depreciation Rate: Some cars depreciate faster than others. Luxury vehicles and those with high mileage tend to lose value rapidly. This is a critical factor influencing gap insurance cost.
- Loan-to-Value (LTV) Ratio: This is the percentage of the vehicle's price you're financing. A higher LTV ratio (financing a large percentage of the car's value) generally means a higher risk for the insurer and thus, a higher gap insurance premium. LTV = (Loan Amount / Vehicle Value) * 100.
- Loan Term Length: Longer loan terms mean slower principal repayment, leading to a greater chance of being underwater for a longer period. Consequently, gap insurance tends to be more expensive for longer loans.
- Down Payment Amount: A larger down payment reduces the initial LTV ratio, lowering the risk and potentially the gap insurance cost.
- Interest Rate: While not directly part of the gap insurance calculation, a higher interest rate will slow down principal repayment, increasing the likelihood of needing gap coverage for a longer period. This indirectly affects the cost.
- Insurance Provider: Different insurance companies use different algorithms to calculate risk. Some providers might be more competitive than others for gap insurance.
- Credit Score: While not always a direct factor, a poor credit score can lead to higher loan interest rates, as mentioned above, indirectly affecting the gap insurance need and perceived risk.
- New Jersey Regulations: While New Jersey doesn't have specific laws regulating gap insurance costs, general insurance regulations apply, ensuring fair pricing practices.
Think of these factors as the variables in a complex equation. Changing one will affect the outcome, which in this case is your gap insurance premium.
"Symbols" – Understanding Cost Drivers
Let's break down how these factors (the "symbols") influence cost:
- Fast Depreciation Rate: Consider a line trending steeply downward on a graph. This represents a car losing value quickly. The steeper the decline, the greater the potential gap between the loan balance and the car's ACV.
- High LTV Ratio: Imagine two buckets – one representing the loan amount and the other the vehicle value. If the "loan" bucket is almost full compared to the "value" bucket, you have a high LTV, indicating greater risk.
- Long Loan Term: Picture a timeline representing the loan duration. A longer timeline implies a prolonged period where you might be underwater, necessitating longer coverage.
- Small Down Payment: Visualize a lever. A small down payment provides less "leverage" to quickly reduce the loan principal compared to a large down payment.
- High Interest Rate: Think of it as a friction force acting against your principal repayment. Higher friction means slower progress, keeping you underwater longer.
These "symbols" are mental models to visualize the impact of each factor on your potential financial exposure.
How It Works: Gap Insurance Cost Calculation
The exact formula insurers use is proprietary, but the underlying principles are relatively straightforward. They are essentially estimating the difference between the car's projected ACV (Actual Cash Value) and the outstanding loan balance over the life of the loan, taking into account depreciation and repayment schedules. They then factor in the probability of a total loss occurring. This "expected value" of the potential loss is then used to determine the premium.
Essentially, the calculation looks like this (simplified):
Gap Insurance Premium ≈ (Projected Gap Amount * Probability of Total Loss) + Profit Margin + Administrative Costs
The "Projected Gap Amount" is where the depreciation rate, loan term, LTV, and down payment all come into play. The "Probability of Total Loss" depends on factors like driving history and the vehicle's safety rating.
It's crucial to note that this is a simplified view. Insurers use sophisticated statistical models to refine these calculations. The goal is to accurately assess the risk and price the coverage accordingly.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some practical tips to minimize your gap insurance costs and ensure you have adequate coverage:
- Shop Around: Get quotes from multiple insurance providers. Prices can vary significantly.
- Negotiate the Vehicle Price: A lower purchase price means a lower loan amount and a lower LTV.
- Make a Larger Down Payment: This immediately reduces the LTV and the potential gap.
- Consider a Shorter Loan Term: While it means higher monthly payments, it reduces the overall interest paid and the duration you need gap coverage.
- Review Your Existing Insurance Policy: Some comprehensive car insurance policies may already include limited gap coverage. Always confirm the extent of this coverage.
- Understand the Fine Print: Ensure you know what's covered and what's excluded by your gap insurance policy. For example, some policies may not cover negative equity rolled over from a previous loan.
Troubleshooting Tip: If your gap insurance quote seems excessively high, double-check your LTV ratio and explore making a larger down payment or opting for a shorter loan term. Also, challenge the dealer or insurer to explain the factors contributing to the high cost.
Safety: High-Risk Components and Considerations
The "risky component" in this context isn't a physical part of your car, but rather your *financial exposure*. Failing to understand gap insurance can put you at significant financial risk if your car is totaled or stolen. Here's what to be mindful of:
- High Depreciation Vehicles: Be extra cautious with vehicles known for rapid depreciation. These cars are more likely to create a gap between the loan balance and the ACV.
- Rolled-Over Negative Equity: If you rolled negative equity from a previous car loan into your new loan, the gap between the loan balance and the vehicle's value is already significant. Gap insurance is *essential* in this scenario.
- Leases vs. Purchases: Leases often include gap insurance as part of the agreement. Verify this with your leasing company.
- Cancellation Policies: Understand the cancellation policy for your gap insurance. If you pay off your loan early, you may be entitled to a refund of the unused premium.
Important Safety Note: Don't assume that all gap insurance policies are created equal. Read the terms and conditions carefully. Know what's covered and what's not. A poorly understood gap insurance policy is as dangerous as a faulty brake line.
By understanding these key aspects of gap insurance costs in New Jersey, you can make informed decisions to protect yourself from financial loss. It's not just about saving money on the premium; it's about securing your financial future.
