How To Add A Skill To Alexa
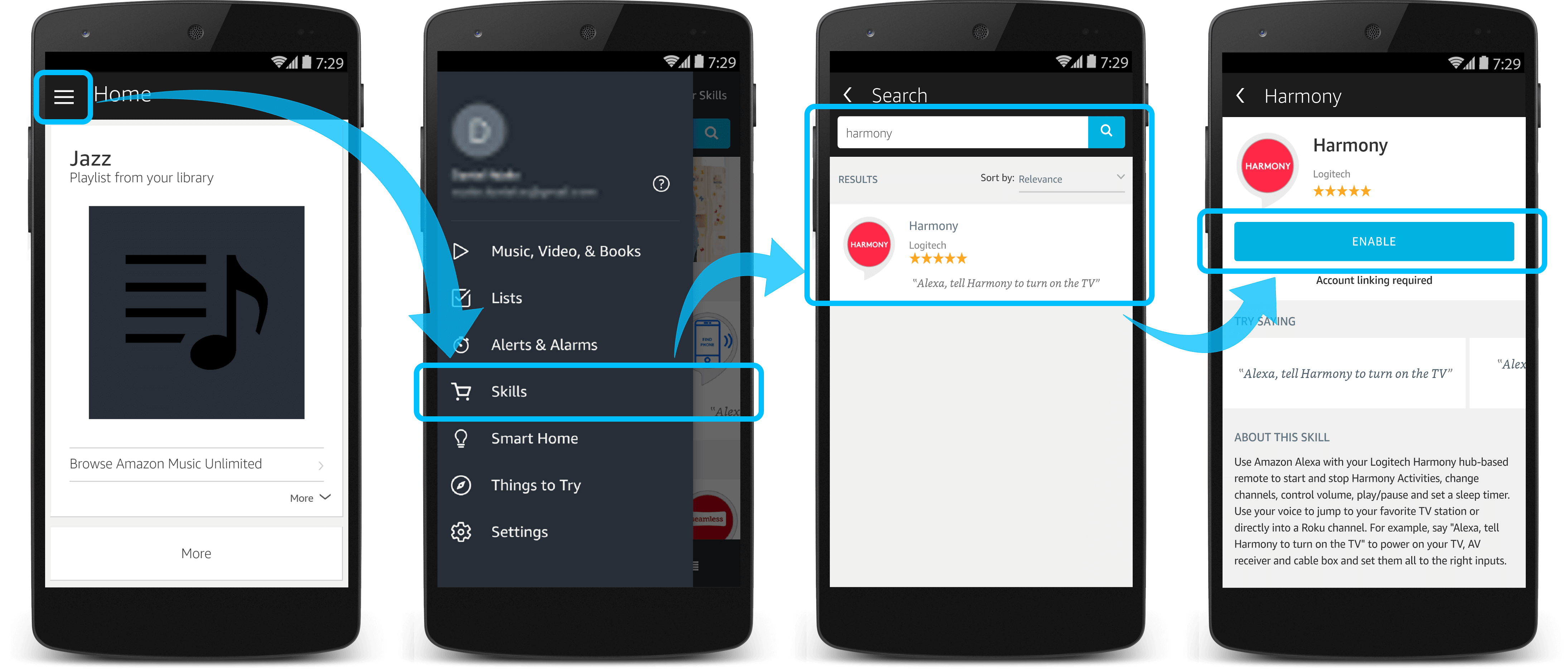
Alright, let's talk about getting down and dirty with Alexa and adding your own custom skills. You've probably used pre-built skills, but what if you want something tailored to your specific needs? Think of it like installing aftermarket parts on your ride – you're going beyond the factory setup and customizing things to your exact preferences.
Purpose: Why Bother Adding Custom Skills?
The pre-made skills on the Alexa store are great, but they are general purpose. Adding a custom skill, much like adding a turbocharger, allows you to fine-tune performance. You might want to control specific smart home devices in a way the default skills don't allow, automate complex routines, or even integrate Alexa with other services you use regularly. Maybe you want to control the lights in your garage based on the time of day *and* whether your car is parked inside. A custom skill lets you build that functionality. Furthermore, it's a fantastic learning experience. By building a skill from the ground up, you gain a deeper understanding of how Alexa, cloud services, and APIs work together.
Key Specs and Main Parts of Alexa Skill Development
Think of this like understanding the different parts of an engine. We've got a few key components to consider:
- Alexa Skills Kit (ASK): This is essentially your toolbox. It provides the APIs, documentation, and tools you need to build, test, and publish your skills.
- Amazon Developer Account: You'll need a free Amazon Developer account to access the ASK. This is like registering your shop.
- Interaction Model: This defines how users interact with your skill. It includes:
- Invocation Name: This is the name users say to start your skill (e.g., "Alexa, open my car skill"). Think of it as the key to start your car's engine.
- Intents: These represent actions users want to perform (e.g., "Turn on the garage lights," "Check the tire pressure"). These are like different gears in your car.
- Utterances: These are the actual phrases users say to invoke intents (e.g., "Turn on the garage lights," "I want to turn on the garage lights," "Garage lights on"). These are the words spoken by the driver to change gears.
- Slots: These are variables within an utterance that provide additional information (e.g., "Set the thermostat to 72 degrees"). The '72' here would be a slot. These are like the dials on your dashboard.
- Skill Logic (Backend): This is the code that handles the requests from Alexa and performs the desired actions. This typically involves:
- AWS Lambda: A serverless compute service where you can run your skill's code. This is like the engine itself that does the work.
- Programming Languages: You can use languages like Node.js (JavaScript) or Python to write your skill's code. These are the fuel and oil for your engine.
- APIs: Your skill may need to interact with external services or databases. You'll use APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) to do this. Think of these as the specialized tools in your garage.
A Simplified Flow Diagram (Imagine it's Downloadable Here!)
We have a diagram available for download that visually represents the flow of an Alexa skill. But let's describe the general flow here. The user speaks an utterance that is received by the Alexa service in the cloud. The Alexa service interprets the utterance based on your skill's interaction model, determining which intent the user is trying to trigger. The Alexa service then packages the intent data into a JSON payload (data format) and sends it to your skill's backend, typically hosted on AWS Lambda. The Lambda function executes the code you've written, interacts with any necessary external services or databases, and then formulates a response. This response is sent back to the Alexa service, which then converts it into speech that Alexa says back to the user.
How It Works: The Inner Workings
The process, in a nutshell, is as follows:
- User Speaks: The user says an invocation name followed by an utterance related to the desired intent (e.g., "Alexa, ask my car skill to check the tire pressure").
- Alexa Interprets: Alexa's natural language processing (NLP) engine analyzes the utterance and determines the intent and any slot values.
- JSON Payload Sent: Alexa sends a JSON payload containing the intent and slot values to your AWS Lambda function.
- Lambda Function Executes: Your Lambda function receives the JSON payload, parses it, and executes the appropriate code. This code might involve querying a database, controlling a smart home device, or making an API call to an external service.
- Response Generated: Your Lambda function generates a JSON response containing the text you want Alexa to say back to the user.
- Alexa Speaks: Alexa receives the JSON response and converts the text into speech.
Think of the JSON payload as a finely tuned carburetor, delivering the right fuel mixture to your engine (Lambda Function). A poorly formatted JSON payload can cause your skill to malfunction, just like a poorly tuned carburetor can cause your car to stall.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting
Like any complex system, things can go wrong. Here are a few common issues and how to troubleshoot them:
- Skill Doesn't Respond:
- Check your invocation name. Did you say it correctly? It's case insensitive but must match exactly.
- Test your skill in the Alexa Developer Console. This allows you to directly send requests to your Lambda function and see the responses.
- Check your AWS Lambda logs (CloudWatch Logs) for errors. This is like checking your car's diagnostic codes.
- Skill Gives Unexpected Responses:
- Review your interaction model. Are your intents and utterances defined correctly?
- Debug your Lambda function code. Use logging statements to track the flow of execution and identify any errors.
- Validate that the data being returned from external APIs is in the expected format.
- Lambda Function Errors:
- Ensure your Lambda function has the necessary permissions to access other AWS services or external APIs.
- Check the Lambda function's memory allocation. Insufficient memory can cause the function to crash.
- Ensure the Lambda function's execution role has the necessary permissions.
If your skill isn't working, take a systematic approach. Start with the basics (invocation name) and work your way through the more complex components (Lambda function code). Use the Alexa Developer Console and AWS Lambda logs to diagnose the issue.
Safety: Risky Components and Considerations
Working with cloud services and APIs introduces potential security risks, much like working with high-voltage systems in your car. Here are a few important safety considerations:
- API Keys and Secrets: Never hardcode API keys or other sensitive information directly into your Lambda function code. This is like leaving your keys in the ignition. Use environment variables or a secure secrets manager to store these values.
- Input Validation: Always validate user input to prevent security vulnerabilities such as injection attacks. This is like making sure your tires are properly inflated before a long trip.
- Permissions: Grant your Lambda function only the necessary permissions to access the resources it needs. This is like only giving someone the keys to the garage, not the entire house.
- Data Security: If your skill handles sensitive data, implement appropriate security measures to protect that data. This may involve encryption, access controls, and regular security audits.
- Rate Limiting: Implement rate limiting to prevent abuse of your skill. This is like a rev limiter on your engine, preventing it from over-revving.
Remember, security is paramount. A compromised skill can expose sensitive data or allow unauthorized access to your systems. Take the time to implement proper security measures to protect yourself and your users. Also, remember to remove test accounts or testing code you may have included in development before deploying the skill.
Conclusion
Adding custom skills to Alexa is a powerful way to extend its capabilities and tailor it to your specific needs. It requires a bit of technical know-how, but with the right tools and a systematic approach, you can create some truly amazing skills. Remember to take your time, follow the best practices, and always prioritize security.
As mentioned earlier, we have a flow diagram which visually represents the skill creation process. It's available for download at [link to download]. It will certainly help you create your own, unique skill!
