How To Charge A Nissan Leaf
So, you're looking to delve deeper into the charging system of your Nissan Leaf. Maybe you're planning some modifications, trying to diagnose a charging issue, or just want to understand how this vital part of your EV works. Understanding the charging process, from the wall socket to the battery pack, is essential for any serious EV enthusiast. This guide provides a technical overview of the Nissan Leaf's charging system, breaking down the key components, explaining the charging process, and offering practical troubleshooting tips.
Purpose of Understanding the Charging System
Why bother understanding the intricacies of your Leaf's charging system? There are several reasons:
- DIY Repairs: Diagnosing and potentially repairing charging issues yourself can save you significant money. While high-voltage work should always be approached with extreme caution (more on that later), understanding the system allows you to identify potential problems before taking it to a professional.
- Performance Tuning & Modifications: Some enthusiasts explore options like increasing charging speeds or modifying charging curves. This requires a deep understanding of the charging system's limitations and capabilities.
- General Knowledge: Understanding how your car works is empowering. Knowing how the electricity flows and what components are involved gives you a better appreciation for your vehicle and allows you to communicate more effectively with mechanics if needed.
- Preventative Maintenance: Understanding the system and recognizing early warning signs can help prevent catastrophic failures and extend the life of your Leaf's battery and charging components.
Key Specs and Main Parts
Before we dive into the details, let's review some key specifications and the main components involved in charging a Nissan Leaf.
Key Specs:
- Battery Voltage: The Nissan Leaf typically uses a high-voltage lithium-ion battery pack, with nominal voltages varying depending on the model year and battery size. Older Leafs (e.g., 24 kWh models) may have lower voltages than newer models (e.g., 62 kWh models). Expect values in the range of 360V to 400V DC.
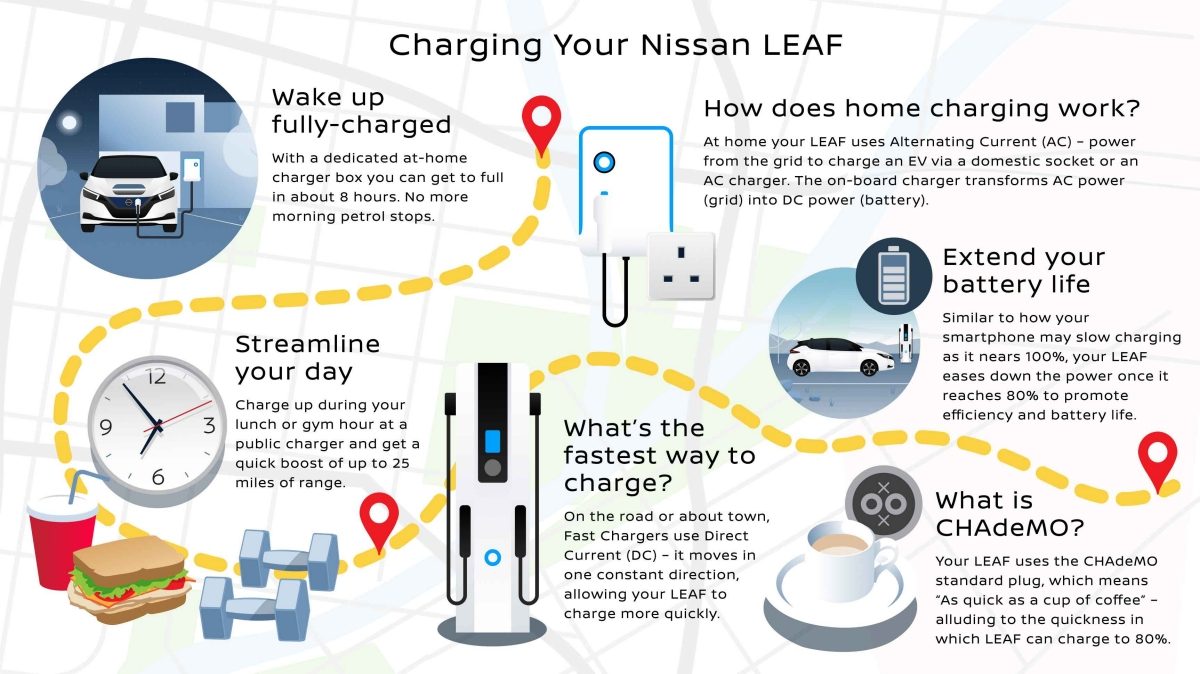
- Charging Power (AC): The Leaf supports Level 1 (120V AC) and Level 2 (240V AC) charging. Level 1 provides a trickle charge, adding only a few miles of range per hour. Level 2 offers significantly faster charging, typically adding 10-25 miles of range per hour. The onboard charger (OBC) converts AC power to DC power for battery charging.
- Charging Power (DC Fast Charging): The Leaf also supports DC fast charging using CHAdeMO (for older models) or CCS (for newer models). This allows for rapid charging, adding significant range in a relatively short time (e.g., 30-60 minutes to 80% charge).
- Onboard Charger (OBC): This is the critical component that converts AC power from Level 1 or Level 2 charging stations into DC power for the battery. The OBC has a maximum power rating (e.g., 3.3 kW, 6.6 kW), which determines the maximum charging speed on Level 2.
Main Parts:
- Charging Port: The physical interface where you plug in the charging cable. Leafs typically have separate ports for AC and DC charging.
- Onboard Charger (OBC): As mentioned, this converts AC to DC.
- Battery Management System (BMS): The BMS is responsible for monitoring and managing the battery pack's health, temperature, voltage, and current. It controls the charging process to prevent overcharging, overheating, and other potential damage.
- DC-DC Converter: This converts the high-voltage DC power from the battery pack to lower voltages (e.g., 12V) to power the car's auxiliary systems (lights, infotainment, etc.). This is often used during charging to power the cooling systems.
- Cooling System: The battery pack and OBC generate heat during charging. The cooling system, which typically includes a pump, radiator, and coolant, is essential for maintaining optimal operating temperatures.
- Charging Cable: The physical cable that connects the car to the charging station. Level 1 and Level 2 cables use different connectors.
How It Works
Let's break down the charging process step-by-step:
- Plugging In: You connect the charging cable to the charging port on the Leaf and the charging station.
- Communication: The car and the charging station communicate to establish the charging parameters (voltage, current, etc.). This communication often uses the SAE J1772 standard for Level 1 and Level 2 charging and CHAdeMO or CCS standards for DC fast charging.
- AC to DC Conversion (Level 1 & 2): If using Level 1 or Level 2 charging, the AC power from the charging station enters the OBC. The OBC converts the AC power to DC power.
- DC Charging (DC Fast Charging): If using DC fast charging, the DC power flows directly from the charging station to the battery pack, bypassing the OBC.
- Battery Management System (BMS) Control: The BMS monitors the battery's voltage, current, temperature, and state of charge (SOC). It regulates the charging process to ensure the battery is charged safely and efficiently. The BMS adjusts the charging current and voltage to optimize charging speed while preventing overcharging or overheating.
- Cooling: The cooling system activates to dissipate heat generated during charging. The BMS often controls the cooling system's operation, adjusting the coolant flow based on the battery's temperature.
- Charging Completion: Once the battery reaches its target SOC (typically 80% or 100%), the BMS signals the charging station to stop charging.
Real-World Use - Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some basic troubleshooting tips if you encounter charging issues:
- Check the Charging Cable: Ensure the charging cable is properly connected to both the car and the charging station. Look for any signs of damage to the cable or connectors.
- Check the Charging Station: Verify that the charging station is powered on and functioning correctly. Try a different charging station if possible.
- Check the Car's Display: The car's display should indicate the charging status. Look for any error messages or warnings. Consult the owner's manual for explanations of error codes.
- Check the 12V Battery: A weak or dead 12V battery can sometimes prevent the car from charging properly. Check the 12V battery's voltage and condition.
- Check for Blocked Vents: Ensure the cooling system vents are not blocked by debris, snow, or ice.
- Reset the System: In some cases, a simple reset can resolve charging issues. Try turning the car off and on, unplugging and replugging the charging cable, or disconnecting the 12V battery for a few minutes.
Important Note: If you suspect a problem with the OBC, BMS, or high-voltage components, it's best to consult a qualified EV technician. Do not attempt to repair these components yourself unless you have the necessary training and experience.
Safety - Risky Components
Working on an EV's charging system involves dealing with high voltages, which can be extremely dangerous. Always exercise extreme caution and follow these safety guidelines:
- Disconnect the Power: Before working on any electrical components, disconnect the charging cable and turn off the car. If possible, disconnect the 12V battery as well.
- Use Insulated Tools: Use insulated tools designed for high-voltage work.
- Wear Safety Gear: Wear appropriate safety gear, including insulated gloves and safety glasses.
- Avoid Water: Never work on electrical components in wet or damp conditions.
- Consult a Professional: If you're not comfortable working with high-voltage systems, consult a qualified EV technician.
Specific components that pose a high risk:
- Battery Pack: The high-voltage battery pack contains a significant amount of energy. Mishandling the battery pack can result in serious injury or death.
- Onboard Charger (OBC): The OBC contains high-voltage circuits that can be lethal.
- DC-DC Converter: The DC-DC converter also operates at high voltages.
- High-Voltage Wiring: The orange cables indicate high-voltage wiring. Avoid cutting or damaging these cables.
Always remember that safety is paramount. If in doubt, consult a qualified professional.
Diagram and Further Learning
Understanding the charging system visually is incredibly helpful. We have a detailed diagram of the Nissan Leaf's charging system available for download. This diagram includes detailed component layouts, wiring schematics, and signal flow charts. This resource will be invaluable for deeper diagnostics or any modification planning.
This guide provides a foundation for understanding the Nissan Leaf's charging system. Remember to prioritize safety and consult a qualified technician if you're not comfortable working on high-voltage systems. By understanding the principles outlined here, you'll be better equipped to diagnose problems, perform basic maintenance, and appreciate the technology behind your EV.
