How To Check A Tps Sensor
The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) is a critical component in your vehicle's engine management system. It's responsible for relaying the throttle's position to the engine control unit (ECU), allowing it to determine how much fuel to inject and when to adjust ignition timing. Understanding how to check a TPS sensor is vital for maintaining optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency.
Why Checking Your TPS Sensor Matters
A malfunctioning TPS sensor can lead to a variety of frustrating and potentially damaging problems. These include:
- Poor fuel economy: An inaccurate TPS signal can cause the engine to run too rich (too much fuel) or too lean (not enough fuel), both of which negatively impact fuel consumption.
- Rough idling: The ECU relies on the TPS to maintain a smooth idle. A faulty sensor can cause the engine to idle erratically, stall, or surge.
- Hesitation or stalling during acceleration: The TPS tells the ECU how quickly you're pressing the accelerator. A bad sensor can cause the engine to hesitate or stall when you try to accelerate.
- Check engine light: A malfunctioning TPS will often trigger the check engine light on your dashboard, storing diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the sensor.
- Surging or jerking: Inconsistent TPS signals can cause the engine to surge or jerk, making for an unpleasant driving experience.
- Difficulty starting: In some cases, a severely faulty TPS can even prevent the engine from starting.
Regularly checking your TPS sensor can help you identify and address these issues before they escalate into more serious and costly repairs. It's a proactive step that can save you time, money, and headaches in the long run.
How to Check a TPS Sensor: A Step-by-Step Guide
There are several methods you can use to check your TPS sensor. We'll cover both basic visual inspections and more advanced electrical testing.
Method 1: Visual Inspection
This is the simplest check and involves visually inspecting the sensor and its wiring for any obvious damage.
- Locate the TPS sensor: The TPS is typically mounted on the throttle body, which is located near the intake manifold. Refer to your vehicle's repair manual or online resources to pinpoint its exact location.
- Inspect the wiring: Carefully examine the wiring harness and connector leading to the TPS. Look for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires, cracked insulation, or corroded terminals.
- Check the sensor body: Look for any cracks, breaks, or other physical damage to the sensor housing.
- Check the throttle linkage: Ensure the throttle linkage moves freely and is properly connected to the TPS. If the linkage is loose or binding, it can affect the sensor's readings.
If you find any obvious damage during the visual inspection, replacing the TPS sensor or repairing the wiring may be necessary.
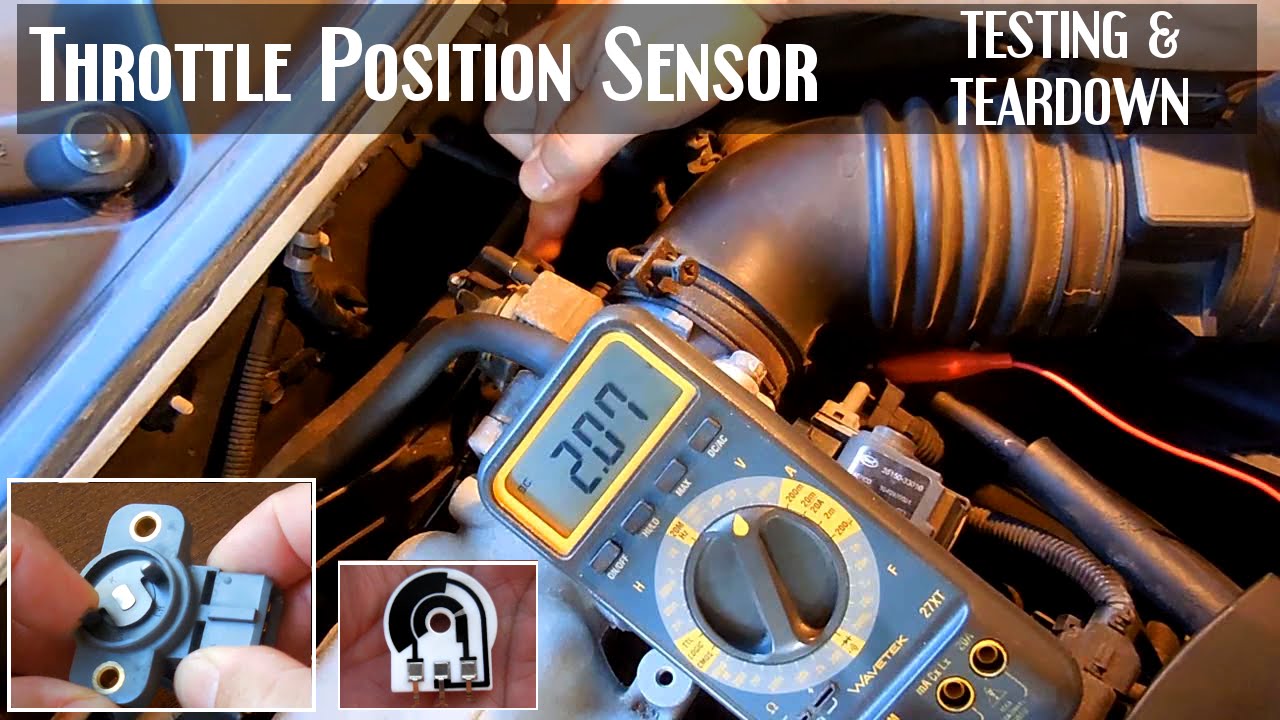
Method 2: Using a Multimeter (Voltage Test)
This method involves using a multimeter to measure the voltage output of the TPS sensor at different throttle positions. This is a more accurate way to assess the sensor's functionality.
- Gather your tools: You'll need a multimeter, a set of jumper wires, and your vehicle's repair manual or wiring diagram.
- Identify the TPS sensor wires: Use your vehicle's wiring diagram to identify the signal wire, ground wire, and power wire on the TPS sensor connector.
- Backprobe the connector: With the TPS sensor connected, carefully insert backprobes into the connector to access the wires without disconnecting them. Alternatively, use a breakout box if available.
- Set the multimeter: Set your multimeter to measure DC voltage.
- Connect the multimeter: Connect the multimeter's positive lead to the signal wire and the negative lead to the ground wire.
- Turn on the ignition: Turn the ignition key to the "on" position, but do not start the engine.
- Measure the voltage at closed throttle: Note the voltage reading with the throttle fully closed. The reading should typically be between 0.5 and 1.0 volts. Consult your vehicle's repair manual for the specific voltage range for your vehicle.
- Slowly open the throttle: Gradually open the throttle, observing the voltage reading on the multimeter. The voltage should increase smoothly and linearly as the throttle opens.
- Measure the voltage at wide open throttle (WOT): Note the voltage reading with the throttle fully open. The reading should typically be between 4.0 and 5.0 volts. Again, consult your vehicle's repair manual for the specific voltage range.
- Analyze the results: If the voltage readings are outside the specified range, fluctuate erratically, or don't increase smoothly, the TPS sensor is likely faulty and needs to be replaced.
Method 3: Using a Scan Tool
A scan tool can provide valuable information about the TPS sensor's performance and any related diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Connect the scan tool: Plug the scan tool into the OBD-II port on your vehicle. This port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver's side.
- Turn on the ignition: Turn the ignition key to the "on" position, but do not start the engine.
- Read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs): Use the scan tool to read any stored DTCs. If there are any codes related to the TPS sensor, such as P0120, P0121, P0122, or P0123, it indicates a potential problem with the sensor.
- View live data: Use the scan tool to view live data related to the TPS sensor. This will allow you to monitor the sensor's voltage or percentage reading in real-time as you open and close the throttle.
- Analyze the data: Observe the TPS sensor readings as you slowly open the throttle. The readings should increase smoothly and linearly. If the readings are erratic, jump around, or don't change at all, the TPS sensor is likely faulty.
How to Choose the Right TPS Sensor Replacement
If you've determined that your TPS sensor needs to be replaced, it's important to choose the right replacement sensor for your vehicle. Here are some factors to consider:
- Compatibility: Ensure that the replacement TPS sensor is compatible with your vehicle's make, model, and year. Check the part number to verify compatibility.
- Quality: Opt for a high-quality TPS sensor from a reputable manufacturer. Cheap aftermarket sensors may not be as reliable or accurate. Brands like Bosch, Delphi, and Denso are generally considered to be reliable.
- Warranty: Look for a TPS sensor that comes with a warranty. This will protect you in case the sensor fails prematurely.
- Reviews: Read online reviews from other vehicle owners to get an idea of the sensor's performance and reliability.
When replacing the TPS sensor, follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully. You may need to adjust the sensor's position to ensure it's properly calibrated. Some vehicles require a scan tool to relearn the new TPS sensor.
Real-World Owner Experiences
Many vehicle owners have shared their experiences with faulty TPS sensors. Some common symptoms they've reported include:
- "My car was idling really rough and stalling at stoplights. Replacing the TPS sensor fixed the problem completely."
- "I was getting terrible gas mileage and my check engine light was on. A scan tool revealed a TPS sensor code. After replacing the sensor, my gas mileage improved significantly."
- "My car was hesitating badly when I tried to accelerate. The TPS sensor was the culprit. Replacing it made a huge difference in my car's performance."
These experiences highlight the importance of diagnosing and addressing TPS sensor issues promptly. Ignoring a faulty TPS sensor can lead to a variety of drivability problems and potentially damage other engine components.
FAQs About TPS Sensors
What does a TPS sensor do?
The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) monitors the position of the throttle plate and sends this information to the engine control unit (ECU). The ECU uses this data to determine how much fuel to inject and when to adjust ignition timing.
How do I know if my TPS sensor is bad?
Common symptoms of a bad TPS sensor include rough idling, hesitation during acceleration, poor fuel economy, stalling, and a check engine light.
Can I drive with a bad TPS sensor?
While you *can* technically drive with a bad TPS sensor, it's not recommended. The vehicle's performance will be compromised, and it could potentially damage other engine components. It's best to address the issue as soon as possible.
How much does it cost to replace a TPS sensor?
The cost to replace a TPS sensor can vary depending on the vehicle make and model, as well as the labor rates in your area. Generally, you can expect to pay between $100 and $300 for the parts and labor.
Can I replace a TPS sensor myself?
Yes, replacing a TPS sensor is a relatively straightforward repair that many DIY mechanics can handle. However, it's important to have the necessary tools and knowledge, including a multimeter and your vehicle's repair manual. Some vehicles may also require a scan tool to relearn the new TPS sensor.
Do I need to calibrate a new TPS sensor?
Some TPS sensors require calibration after installation. Consult your vehicle's repair manual or the sensor manufacturer's instructions to determine if calibration is necessary and how to perform it.
By following these steps and understanding the importance of a properly functioning TPS sensor, you can keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently. Regular maintenance and prompt attention to warning signs are key to preventing costly repairs and ensuring a safe and enjoyable driving experience.
