How To Check Ac Compressor Clutch
So, you're tackling an AC issue in your car, and you suspect the compressor clutch might be the culprit. Smart move! Diagnosing this component can save you a bundle compared to blindly replacing the entire AC system. This article will walk you through checking your AC compressor clutch like a pro, covering everything from understanding the system to using common troubleshooting techniques.
Why Bother Checking the AC Compressor Clutch?
Understanding the AC compressor clutch and how to diagnose its problems is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it’s a common failure point in automotive AC systems. Replacing it (or even just the coil) is significantly cheaper than replacing the entire compressor. Secondly, accurate diagnosis prevents unnecessary repairs, saving you time and money. Finally, learning how the system works gives you a deeper understanding of your car's mechanics, empowering you to tackle more complex repairs down the road.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the AC Compressor Clutch System
Let’s break down the main components:
- Compressor Clutch: This is an electromagnetic clutch that engages and disengages the compressor pulley from the compressor shaft, allowing the compressor to cycle on and off as needed.
- Compressor Pulley: A constantly spinning pulley driven by the engine's serpentine belt. It’s always turning when the engine is running.
- Clutch Plate (or Armature Plate): The part that makes physical contact with the pulley when the clutch is engaged. This plate is drawn to the pulley when the electromagnetic coil is energized.
- Electromagnetic Coil: This coil, when energized, creates a magnetic field that pulls the clutch plate towards the pulley. This is powered by 12V DC.
- Air Gap: The small space between the clutch plate and the pulley when the clutch is disengaged. Maintaining the correct air gap is critical for proper clutch operation. Too large of a gap, and the magnetic field won't be strong enough to engage the clutch. Too small, and the clutch may drag.
- Shims: These are small washers placed behind the clutch plate that adjust the air gap.
- AC Pressure Switch(es): These switches monitor the refrigerant pressure in the system. If the pressure is too high or too low, the switch will prevent the compressor clutch from engaging to protect the system from damage.
- Relay: A relay acts as a switch, using a small current from the AC control panel to control a larger current to the clutch coil.
- Fuse: Protects the electrical circuit powering the clutch.
Key specs you might be interested in are the air gap (usually between 0.020" and 0.040", but check your vehicle's service manual), and the coil resistance (typically between 3 and 5 ohms).
How the AC Compressor Clutch Works
The AC compressor clutch system operates on a relatively simple principle. When you turn on your AC, the AC control panel signals the AC relay. The relay, if all safety conditions are met (proper refrigerant pressure detected by the pressure switches), closes the circuit, sending 12V DC to the electromagnetic coil in the compressor clutch. This energized coil creates a magnetic field, which pulls the clutch plate towards the spinning pulley. When the clutch plate makes contact with the pulley, it locks the pulley to the compressor shaft, causing the compressor to spin and compress the refrigerant.
When the AC system reaches the desired temperature, or if the refrigerant pressure drops too low or rises too high, the AC control panel will de-energize the relay, cutting power to the coil. The magnetic field collapses, and a spring pushes the clutch plate away from the pulley, disengaging the compressor. This cycle repeats continuously to maintain the desired temperature in the cabin.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some basic troubleshooting steps you can take:
Visual Inspection:
Look for any visible damage to the clutch, pulley, or wiring. Check the condition of the serpentine belt. Is it cracked, frayed, or loose? Make sure the pulley spins freely when the engine is off. If the pulley is seized or difficult to turn, the compressor itself might be the problem, not just the clutch.
Check the Air Gap:
Use a feeler gauge to measure the air gap between the clutch plate and the pulley. If the gap is outside the specified range (usually 0.020" to 0.040"), you'll need to adjust it by adding or removing shims behind the clutch plate.
Check for Power to the Clutch:
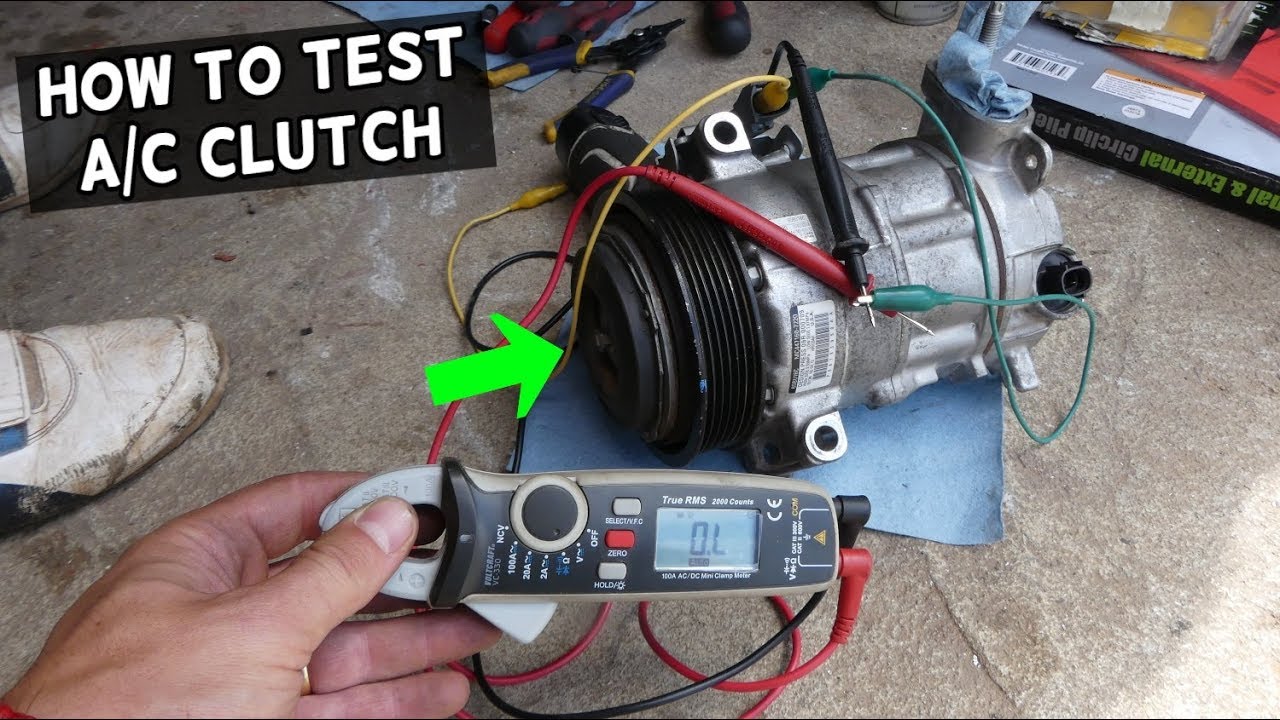
With the engine running and the AC turned on max, use a multimeter to check for 12V DC at the connector leading to the clutch coil. If you're not getting power, the problem lies upstream – likely the relay, fuse, pressure switch, or wiring.
Check Clutch Coil Resistance:
Disconnect the wiring harness from the clutch coil. Set your multimeter to measure resistance (ohms). Connect the multimeter probes to the two terminals on the clutch coil. A healthy coil should typically read between 3 and 5 ohms. A reading of 0 ohms indicates a short circuit, while an infinite reading indicates an open circuit – both meaning the coil is faulty.
Listen for the Click:
With the engine running and the AC turned on, listen carefully near the compressor. You should hear a distinct "click" sound when the clutch engages. If you don't hear the click, even with power applied, the clutch coil may be bad or the clutch plate might be seized.
Safety: Highlighting Risky Components
Working on automotive AC systems can be dangerous. Here's what to watch out for:
- High-Pressure Refrigerant: The refrigerant in your AC system is under high pressure. Never attempt to open any part of the sealed AC system without recovering the refrigerant first using proper equipment. Releasing refrigerant into the atmosphere is illegal and harmful to the environment.
- Moving Parts: Keep your hands and clothing clear of the serpentine belt and pulleys when the engine is running. The belt can cause serious injury if it catches on something.
- Electrical System: Disconnect the negative battery cable before working on any electrical components of the AC system to prevent accidental short circuits.
Additional Resources
For more advanced diagnostics and repairs, you’ll need a detailed wiring diagram specific to your vehicle. These diagrams illustrate the complete electrical circuit for the AC system, showing the location of relays, fuses, switches, and wiring connections. Having this diagram significantly simplifies troubleshooting, allowing you to pinpoint the exact location of any electrical faults. We have a generic AC compressor clutch wiring diagram available for download. It's not a substitute for a vehicle-specific diagram, but it can provide a general overview of the circuit.
With a bit of knowledge and the right tools, you can confidently diagnose and potentially repair your AC compressor clutch, saving yourself time and money. Remember to always prioritize safety and consult your vehicle's service manual for specific instructions and specifications.
