How To Check My Car For Recalls
Okay, so you want to check if your car has any outstanding recalls? Smart move. Ignoring recalls can lead to serious safety issues down the road, and often the repairs are covered by the manufacturer. This article will guide you through the process, giving you the knowledge to understand what a recall *really* means and how to stay on top of them.
Understanding Vehicle Recalls
A vehicle recall is issued when a manufacturer or the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) determines that a vehicle or piece of motor vehicle equipment (like tires or child car seats) creates an unreasonable risk to safety or fails to meet minimum safety standards. Think of it like this: the manufacturer found a potential defect that could cause an accident or injury.
Purpose: Checking for recalls is primarily about your safety and the safety of others on the road. It ensures that any potential manufacturing defects that could lead to accidents or injuries are addressed promptly and, usually, at no cost to you. It also helps maintain the vehicle's value and longevity.
Methods for Checking Recalls
There are several ways to check for recalls on your vehicle. We'll explore each one:
1. Using the NHTSA Website
The most reliable and comprehensive method is using the NHTSA (National Highway Traffic Safety Administration) website. This is a free service.
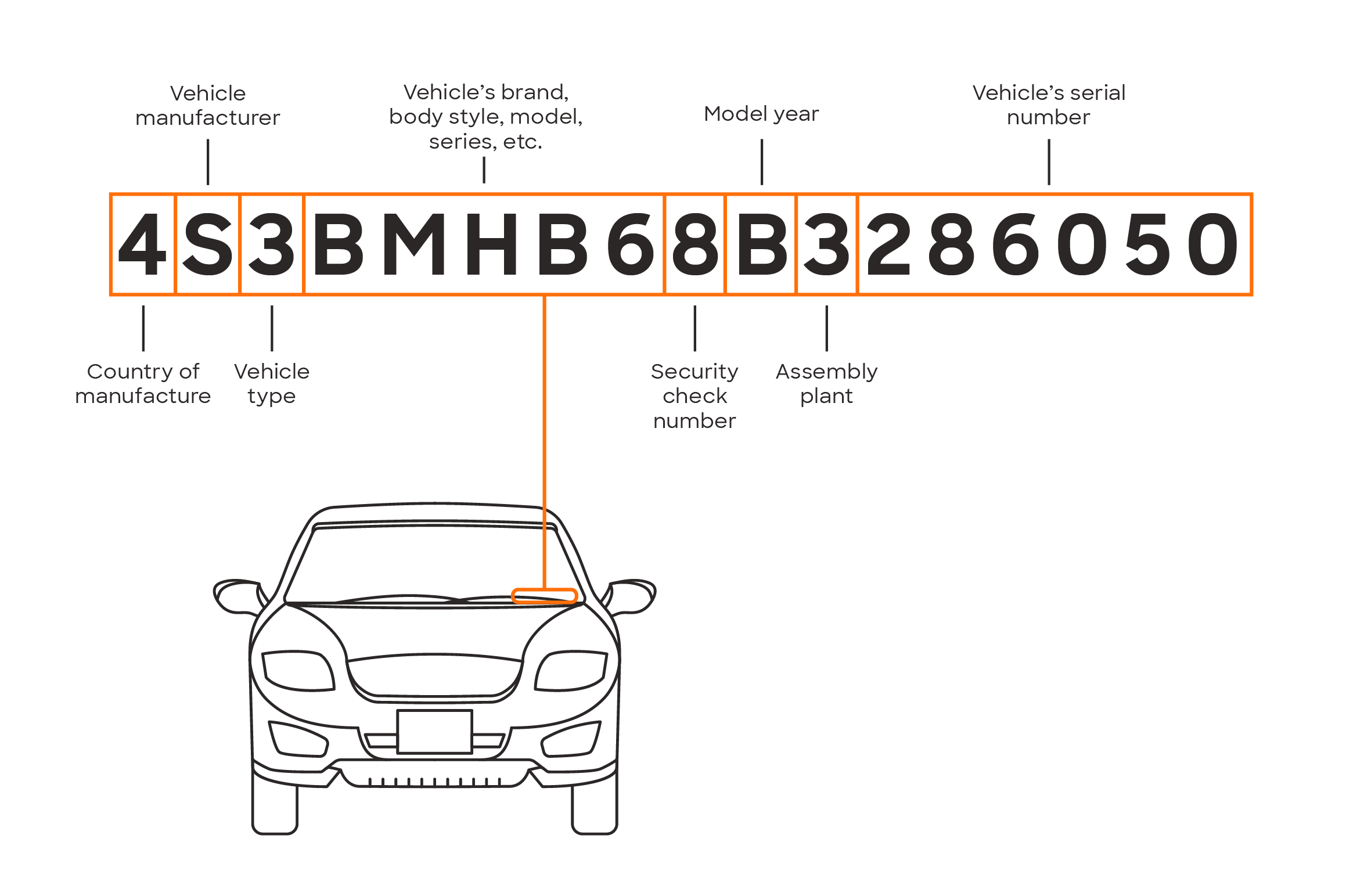
- Locate Your VIN: Your Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) is a 17-character alphanumeric code unique to your vehicle. It's usually found on the driver's side dashboard (visible through the windshield), on your vehicle registration, or in your insurance documents.
- Enter the VIN: Go to the NHTSA recall website and enter your VIN in the designated field.
- Review the Results: The website will display any open recalls associated with your VIN. It will also provide details about the recall, including the affected component, the potential hazard, and the remedy.
2. Using the Manufacturer's Website
Most major automotive manufacturers also have recall lookup tools on their websites. The process is similar to using the NHTSA website: locate your VIN and enter it into the tool.
Key Specs and Main Parts: The core component here is the VIN. It's the key to unlocking recall information specific to your vehicle. Other specs, such as the year, make, and model, are helpful if you don't have the VIN readily available but are generally less accurate. The main "part" of this process is the database that NHTSA or the manufacturer maintains, linking VINs to recall notices.
3. Signing Up for Recall Alerts
NHTSA and some manufacturers allow you to sign up for email alerts regarding recalls. This proactive approach ensures you're notified as soon as a recall is issued for your vehicle.
4. Waiting for a Recall Notice
If a recall is issued for your vehicle, the manufacturer is legally obligated to notify you by mail. However, relying solely on this method can be risky, as recall notices can get lost in the mail or overlooked. Also, this requires the manufacturer to have your current address on file. If you've moved and haven't updated your address with the manufacturer, you might miss the notice.
Understanding Recall Information
When you receive a recall notice (either online or by mail), it will contain the following information:
- Recall Campaign Number: A unique identifier for the recall.
- Affected Vehicles: The specific makes, models, and years affected by the recall.
- Component Affected: The specific part of the vehicle that is defective. For example, the airbag inflator, fuel pump, or brake system.
- Description of the Defect: A detailed explanation of the problem.
- Potential Hazard: What could happen if the defect is not addressed. This might include increased risk of accidents, injuries, or fires.
- Remedy: The steps the manufacturer will take to fix the problem. This usually involves replacing the defective part or making necessary repairs, free of charge.
- Instructions: How to schedule an appointment with a dealer to have the recall work performed.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Let's say you check your VIN on the NHTSA website and find an open recall for your car's airbag inflator. Here's what you should do:
- Read the Recall Notice Carefully: Understand the specific defect, the potential hazard, and the remedy.
- Contact Your Local Dealer: Call your local dealership of the same make and model. Provide them with the recall campaign number and your VIN.
- Schedule an Appointment: Schedule an appointment to have the recall work performed. The dealer should be able to confirm that your vehicle is indeed affected by the recall and that the necessary parts are in stock.
- Document Everything: Keep copies of the recall notice, the service order, and any other paperwork related to the recall repair.
Important Note: Dealers are legally obligated to perform recall repairs free of charge. If a dealer tries to charge you for a recall repair, contact the manufacturer directly or file a complaint with NHTSA.
Safety Considerations
Some recalls involve components that pose an immediate safety risk. For example, a recall related to faulty brakes or airbags should be addressed immediately.
Safety – Highlight Risky Components: The components most often associated with high-risk recalls involve systems critical to vehicle control and safety. These include, but aren't limited to: brakes (malfunctioning calipers, rotors, or brake lines), steering (power steering failures, tie rod issues), airbags (Takata airbag inflators are a prime example), fuel systems (leaks that could lead to fires), and throttle control systems (unintended acceleration). If a recall relates to any of these, treat it with utmost urgency.
If a recall poses an immediate safety risk, the manufacturer may offer alternative transportation or a loaner vehicle while the repair is being performed. Don't hesitate to inquire about these options if you feel unsafe driving your vehicle.
Beyond the Basics: DIY Considerations
While recall repairs are typically performed by dealerships, some experienced DIYers might consider tackling certain recalls themselves, particularly if the remedy involves a simple component replacement. However, this is generally not recommended for safety-critical components like airbags or brake systems.
If you *do* choose to attempt a DIY recall repair, make sure you have the necessary tools, technical expertise, and access to accurate repair information. Obtain the correct replacement parts from a reputable source and follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully. Document your work meticulously. It's also a good idea to inform the manufacturer that you performed the repair yourself, providing them with documentation. This helps maintain accurate records.
Manufacturer Responsibility
It is crucial to remember that manufacturers are legally responsible for addressing safety defects in their vehicles. Don't hesitate to contact the manufacturer directly if you encounter any difficulties in getting a recall repaired or if you believe the repair was not performed correctly.
Staying Informed
Checking for recalls should be a routine part of your vehicle maintenance schedule. Make it a habit to check the NHTSA website or the manufacturer's website every few months to ensure you're aware of any new recalls that may affect your vehicle.
By proactively checking for recalls, you can help ensure your safety, the safety of your passengers, and the safety of others on the road. Don't take recalls lightly; they are issued for a reason.
We've prepared a detailed guide on interpreting common vehicle maintenance diagrams, which can be invaluable for understanding the specific components affected by a recall. This guide covers everything from electrical schematics to hydraulic system layouts, helping you visualize the potential problems. You can download the diagram here.
