How To Connect Phone To Bluetooth
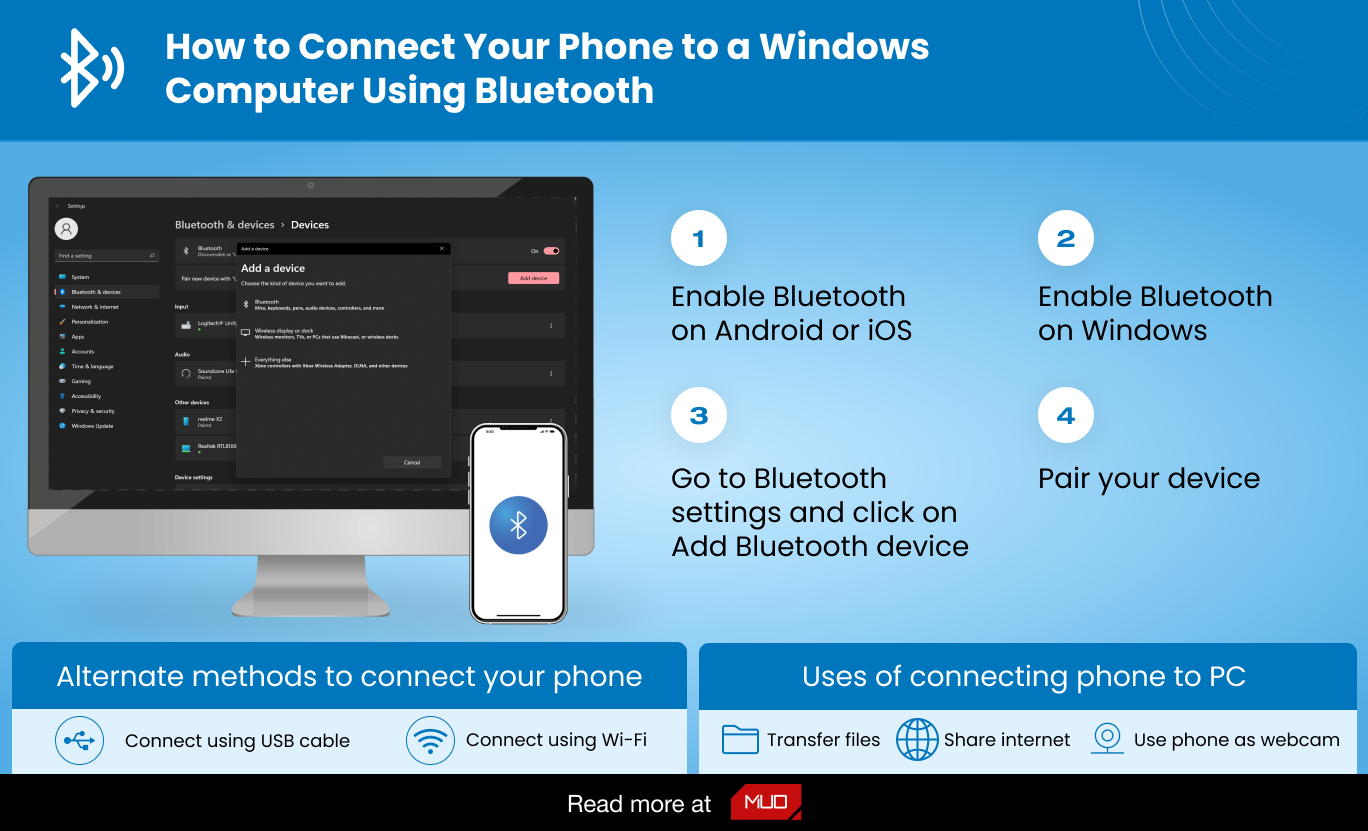
Alright folks, let's talk Bluetooth. Connecting your phone to your car's Bluetooth system is something we all take for granted these days, but understanding the underlying principles and troubleshooting the inevitable connection glitches can save you a ton of frustration. This article is going to break down the process, the key components, and the potential pitfalls, giving you a solid foundation for keeping your mobile life integrated with your driving experience. This knowledge isn't just for convenience; it can be crucial for using hands-free calling features, streaming music, and even accessing diagnostic information from your vehicle via compatible apps. Think of it as another tool in your DIY automotive arsenal.
Key Specs and Main Parts of a Bluetooth Connection
Before we dive into the process, let's define some key terms and components. When we talk about a Bluetooth connection, we're referring to a short-range wireless technology that allows devices to communicate without physical cables. In our context, that’s your smartphone and your car's infotainment system.
Key Specifications:
- Bluetooth Version: The Bluetooth version dictates the features, speed, and security of the connection. Common versions include 4.0, 4.2, 5.0, and 5.2. Newer versions generally offer improved range, data transfer rates, and power efficiency. Your car's system and phone both need to support a compatible version. For example, if your car only supports Bluetooth 4.0, it won't fully utilize the features of a phone with Bluetooth 5.0.
- Bluetooth Profiles: These are standardized sets of protocols that define how devices use Bluetooth technology. Key profiles for car connectivity include:
- HFP (Hands-Free Profile): Enables hands-free calling.
- A2DP (Advanced Audio Distribution Profile): Enables streaming audio (music, podcasts, etc.).
- AVRCP (Audio/Video Remote Control Profile): Allows you to control audio playback (pause, play, skip tracks) from your car's controls.
- PBAP (Phone Book Access Profile): Enables your car to access and display your phone's contacts.
- Frequency Band: Bluetooth operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM (Industrial, Scientific, and Medical) band. This band is also used by Wi-Fi and other wireless devices, which can sometimes lead to interference.
Main Parts:
- Smartphone: The source device, equipped with a Bluetooth transceiver (transmitter/receiver). Its Bluetooth software stack handles the communication protocols.
- Car's Infotainment System: The receiving device, also with a Bluetooth transceiver. This system interprets the Bluetooth signals and relays them to the audio system, display, and other vehicle functions.
- Bluetooth Chipset: A dedicated integrated circuit within both devices that handles the Bluetooth communication protocol.
- Antenna: A small antenna, usually internal, within both devices that radiates and receives the Bluetooth radio waves.
How It Works: Pairing and Connecting
The process of connecting your phone to your car's Bluetooth system involves two main steps: pairing and connecting. Pairing is a one-time process where the two devices "introduce" themselves and establish a secure connection. Connecting is the process of re-establishing that connection each time you enter your car.
- Enable Bluetooth: On both your smartphone and your car's infotainment system, ensure Bluetooth is enabled. Typically, this is done through the settings menu on both devices.
- Enter Pairing Mode: On your car's infotainment system, navigate to the Bluetooth settings and select the option to "Pair Device" or "Add Device." This puts the car's system into discoverable mode, meaning it's broadcasting its presence to other Bluetooth devices.
- Search for Devices: On your smartphone, scan for available Bluetooth devices. Your car's system should appear in the list (often with the car's make and model as the name).
- Initiate Pairing: Select your car's system from the list of available devices on your smartphone.
- Authentication: You'll likely be prompted to enter a PIN code or confirm a passkey on both devices. This ensures that you're connecting to the correct device and prevents unauthorized access. The passkey is generally displayed on the car's screen and you will be prompted to confirm it on your phone.
- Grant Permissions: Your smartphone may ask for permission to access your contacts, call history, and other information. Granting these permissions is necessary for features like hands-free calling and contact synchronization.
- Automatic Connection: Once paired, your phone and car should automatically connect whenever they are within range and Bluetooth is enabled. This process is usually handled automatically by the devices.
Real-World Use and Basic Troubleshooting
Even with a seemingly simple process, things can go wrong. Here are some common issues and troubleshooting tips:
- Pairing Fails:
- Problem: The devices can't find each other.
- Solution: Make sure both devices are in pairing mode and within close proximity (a few feet). Ensure that Bluetooth is actually enabled on both and hasn’t inadvertently been switched off.
- Solution: Clear the Bluetooth cache on your phone. This can sometimes resolve issues with corrupted Bluetooth data. On Android, go to Settings > Apps > Show System Apps > Bluetooth Share > Storage > Clear Cache. The process will be different on iPhones.
- Connection Drops:
- Problem: The connection frequently disconnects.
- Solution: Check for interference from other devices operating in the 2.4 GHz band, such as Wi-Fi routers or microwave ovens. Try moving your phone to a different location in the car.
- Solution: Ensure your phone's operating system and your car's infotainment system are up to date. Software updates often include bug fixes and performance improvements.
- Solution: "Forget" the paired device on both your phone and your car, and then re-pair them. This can sometimes resolve persistent connection issues.
- Audio Quality Issues:
- Problem: Distorted or low-quality audio.
- Solution: Check the Bluetooth audio settings on your phone and car. Ensure that the audio codec being used (e.g., SBC, AAC, aptX) is supported by both devices.
- Solution: Close any other apps on your phone that are using Bluetooth audio.
- Phonebook issues:
- Problem: Contacts not syncing or appearing correctly.
- Solution: Ensure that PBAP permissions are granted. Check the car's infotainment system's settings to ensure contact syncing is enabled.
- Solution: Try manually syncing the contact list via the car's infotainment system if that feature is available.
Safety Considerations
While Bluetooth itself is relatively safe, it's important to remember that using your phone while driving can be extremely dangerous. Always prioritize safe driving practices. Hands-free calling can help, but minimize distractions and keep your attention focused on the road.
Important Note: Never attempt to disassemble or modify your car's infotainment system unless you are a qualified technician. The internal components can be sensitive and potentially dangerous. Mishandling them can lead to electrical shock, damage to the vehicle, or even personal injury.
Conclusion
Mastering Bluetooth connectivity in your car is about more than just playing music; it's about leveraging technology for safer and more convenient driving. By understanding the fundamentals, you can troubleshoot common issues and keep your devices seamlessly connected.
Remember, we have a detailed technical diagram of a generic automotive Bluetooth system available for download. This diagram visually illustrates the components, signal flow, and protocols involved. This tool, combined with the information in this article, should give you a comprehensive understanding of automotive Bluetooth systems.
