How To Get Apple Carplay To Work
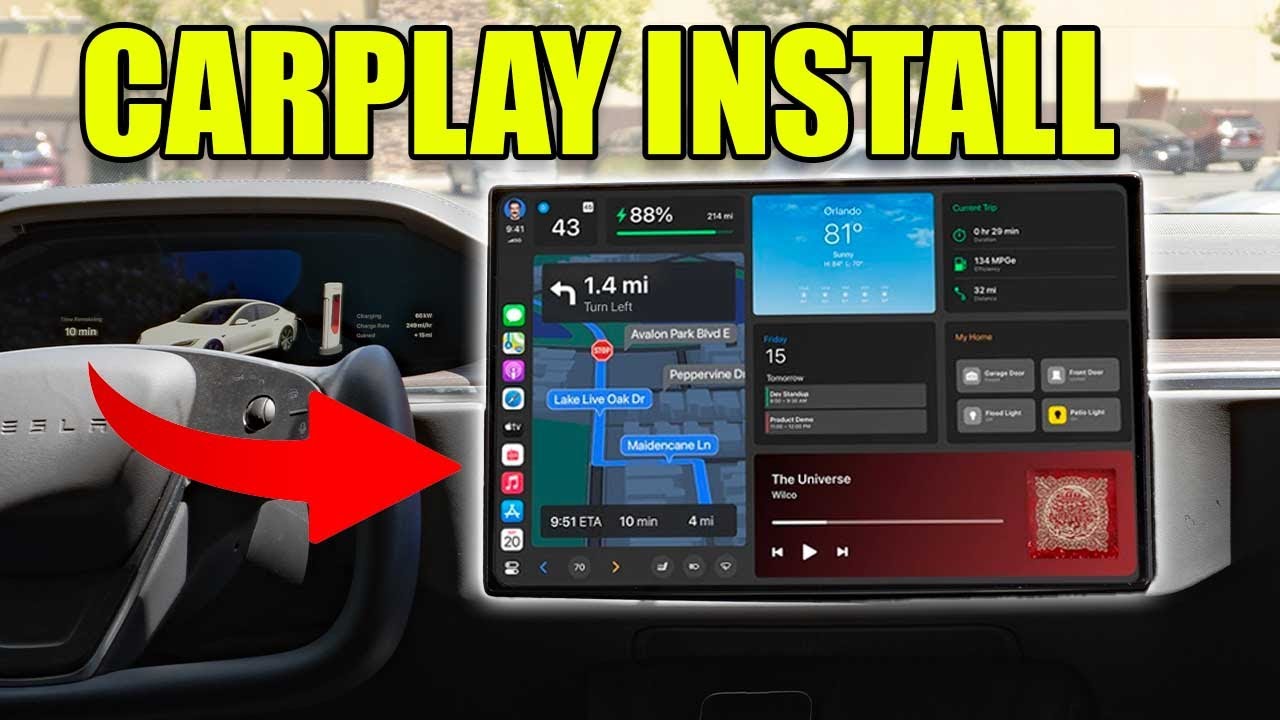
Alright, let's dive into getting Apple CarPlay up and running in your vehicle. This guide is for those who like to tinker, upgrade, and understand the tech behind the scenes. We'll cover everything from the essential components to troubleshooting common issues, assuming you're comfortable with basic car audio modifications.
Understanding the Apple CarPlay Ecosystem
Before we get our hands dirty, let's understand why understanding CarPlay matters. Whether you're upgrading an older vehicle with an aftermarket head unit, diagnosing connectivity problems, or simply curious about how it all works, having a grasp on the CarPlay architecture is invaluable. This guide will essentially provide a simplified functional diagram of the CarPlay system, outlining data flow and connection types.
Key Specs and Main Parts
At its core, CarPlay is a system that allows your iPhone to interface with your car's infotainment system. Think of it as an extension of your iPhone onto your dashboard display. Here are the key components involved:
- iPhone (iOS Device): This is where all the processing power resides. CarPlay essentially streams information from your iPhone to the head unit. Compatibility is crucial; check Apple's CarPlay compatibility list for supported iPhone models and iOS versions.
- Head Unit (Infotainment System): This is the in-dash display and audio control unit. It must be CarPlay-compatible. This can either be factory-installed or an aftermarket unit. Key specs to consider include screen resolution, touch responsiveness, audio output quality, and the presence of physical buttons (which can be very useful).
- USB Connection (Wired CarPlay): The most common method. The USB port needs to support data transfer, not just charging. The protocol used is typically USB 2.0 or 3.0. The cable itself is also critical; a high-quality, Apple-certified cable is recommended.
- Wireless Connection (Wireless CarPlay): A more modern implementation using Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. Bluetooth handles the initial handshake and connection setup, while Wi-Fi handles the high-bandwidth data transfer for audio and video. Requires a head unit and iPhone that both support Wireless CarPlay.
- Lightning/USB-C Port (on iPhone): The physical interface for connecting the iPhone. Check for damage or debris in the port.
- Microphone: Essential for Siri voice commands and phone calls. Usually integrated into the head unit or steering wheel controls.
Decoding the Connections: Symbols and Data Flow
Think of the CarPlay system as a network. Here's a breakdown of how the data flows and how to interpret a simplified diagram:
- Solid Lines: Represent a physical connection, usually the USB cable. In a diagram, a thick solid line might indicate a primary data path.
- Dashed Lines: Represent a wireless connection (Wi-Fi or Bluetooth). The thickness of the dashed line can sometimes indicate signal strength or bandwidth.
- Arrows: Indicate the direction of data flow. From iPhone to Head Unit means data is being sent for display and audio output. From Head Unit to iPhone means the head unit is sending commands or input (e.g., button presses).
- Icons: Standard icons represent different components: iPhone, Head Unit, GPS antenna (if relevant for navigation), Microphone. Look for consistency in these icons across different diagrams.
- Colors: Can represent different types of data. For example, blue might represent audio, red might represent video, and green might represent control signals.
In a CarPlay diagram, you'll see a clear path from the iPhone, through the USB or wireless connection, to the Head Unit. Control signals travel in both directions, allowing the head unit to send commands to the iPhone and vice versa.
How Apple CarPlay Works: A Deep Dive
The magic of CarPlay lies in its ability to offload the processing to your iPhone. The head unit essentially becomes a display and input device for your iPhone. Here's the process:
- Connection Establishment: For wired CarPlay, connecting your iPhone via USB triggers a handshake. The head unit identifies the iPhone as a CarPlay device. For wireless CarPlay, Bluetooth is used for the initial connection. The iPhone searches for available CarPlay devices, and once paired, it switches to Wi-Fi for data transfer.
- Authentication: The iPhone and head unit authenticate each other to ensure a secure connection.
- Data Transfer: The iPhone streams audio, video, and user interface data to the head unit. Your touches on the head unit screen are sent back to the iPhone as commands. The iPhone processes these commands and updates the display accordingly.
- Audio Routing: Audio from CarPlay apps (music, podcasts, phone calls) is routed through the car's audio system. The head unit controls volume and playback.
- Siri Integration: The microphone allows you to use Siri voice commands. These commands are processed on your iPhone, and the results are displayed on the head unit.
Think of it this way: your iPhone is the brain, and the head unit is the eyes and ears. The connection, whether wired or wireless, is the nervous system transmitting information between them.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting
Encountering issues? Here are some common troubleshooting tips:
- CarPlay Not Starting:
- Check your iPhone's compatibility with CarPlay.
- Ensure CarPlay is enabled in your iPhone's settings (Settings > General > CarPlay).
- Try a different USB cable (for wired CarPlay).
- Restart your iPhone and head unit.
- Check for software updates on both your iPhone and head unit.
- For wireless CarPlay, make sure Bluetooth and Wi-Fi are enabled on both devices and that they are properly paired. Forget the device and re-pair if necessary.
- Connection Issues:
- Ensure the USB port on your car supports data transfer (some only provide charging).
- Check for debris or damage in the Lightning/USB-C port on your iPhone.
- For wireless CarPlay, try moving your iPhone closer to the head unit to improve Wi-Fi signal strength.
- Audio Problems:
- Check the volume settings on both your iPhone and head unit.
- Ensure the correct audio source is selected on your head unit (CarPlay, USB, etc.).
- Try a different audio app to rule out app-specific issues.
- Siri Not Working:
- Make sure Siri is enabled on your iPhone (Settings > Siri & Search).
- Check the microphone connection.
- Ensure the microphone isn't muted in the CarPlay interface.
If all else fails, consult your head unit's manual or contact the manufacturer for support. A factory reset of the head unit might also be necessary in some cases (but proceed with caution, as this will erase all your settings).
Safety First: Handling Risky Components
Working with car electronics involves some inherent risks. Always remember these safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical components, disconnect the negative terminal of your car battery. This prevents accidental shorts and electrical damage.
- Proper Grounding: Ensure all grounding connections are secure. Poor grounding can cause electrical noise and malfunctions.
- Avoid Tampering with Airbag Systems: Airbag systems are highly sensitive. Do not attempt to modify or repair any airbag components. This could result in serious injury.
- Use Proper Tools: Use the correct tools for the job. Forcing screws or connectors can damage components.
- Refer to the Head Unit's Manual: Always consult the head unit's manual for specific installation and safety instructions.
Caution: The head unit itself can be a potential fire hazard if improperly installed or wired. Always use appropriately sized fuses and wiring.
Modifying your car's electrical system can void your warranty. Proceed with caution and at your own risk. If you're not comfortable with any of these procedures, consult a qualified professional.
Remember, this guide provides a general overview. Specific procedures may vary depending on your vehicle and head unit.
We have a simplified block diagram outlining the Apple CarPlay system architecture. Feel free to download it for a clearer visual representation of the concepts discussed.
