How To Identify Transmission By Serial Number
Ever wondered how auto manufacturers keep track of the thousands of transmissions they produce? Or perhaps you're sourcing a replacement for your trusty ride and need to ensure it's the exact right fit. The answer, in many cases, lies hidden in plain sight: the transmission serial number. This seemingly cryptic string of characters is the key to unlocking a wealth of information about your transmission, from its build date and model to its compatibility with specific vehicles. Understanding how to decipher it can save you time, money, and a whole lot of headaches.
The Problem: Decoding the Mystery
Imagine this: your car's transmission has seen better days and requires replacement. You head to your local salvage yard, only to be confronted with a sea of used transmissions. They all look relatively similar, but you know that not all transmissions are created equal. Installing the wrong one could lead to poor performance, premature failure, or even catastrophic engine damage. How do you avoid this costly mistake? The transmission serial number is your first line of defense. But simply finding the number isn't enough; you need to understand what it means.
The Analogy: A VIN for Transmissions
Think of a transmission serial number like the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) for your entire car. The VIN contains information about the vehicle's manufacturer, model, engine, and assembly plant. Similarly, the transmission serial number acts as a unique identifier, providing crucial details about the transmission's specifications and origin. It's a condensed history lesson etched into metal.
How the System Works: A Deep Dive
The exact format and location of the transmission serial number will vary depending on the manufacturer, model year, and type of transmission (automatic or manual). However, the underlying principle remains the same: to provide a traceable record of each unit. Let's break down the typical components you might find in a serial number:
Manufacturer Code:
This identifies the company that manufactured the transmission. It might be a short abbreviation or a unique alphanumeric code. For example, General Motors (GM) uses codes like "TH" for some of their older Turbo-Hydramatic transmissions.
Model Designation:
This section specifies the transmission model, such as a 4L60E (a popular GM automatic transmission) or a TR-3650 (a common manual transmission used in Ford Mustangs). The model designation allows you to quickly determine the type of transmission and its general capabilities.
Assembly Plant Code:
Many manufacturers use a code to indicate the plant where the transmission was assembled. This can be important for tracing potential manufacturing defects or quality control issues.
Date Code:
The date code reveals when the transmission was built. This is usually expressed as a combination of year, month, and sometimes even day. Knowing the build date helps determine compatibility with specific vehicle models and identify potential updates or revisions made during production.
Sequential Serial Number:
This is a unique, sequential number assigned to each individual transmission. It ensures that no two transmissions have the same serial number, providing a definitive way to track a specific unit.
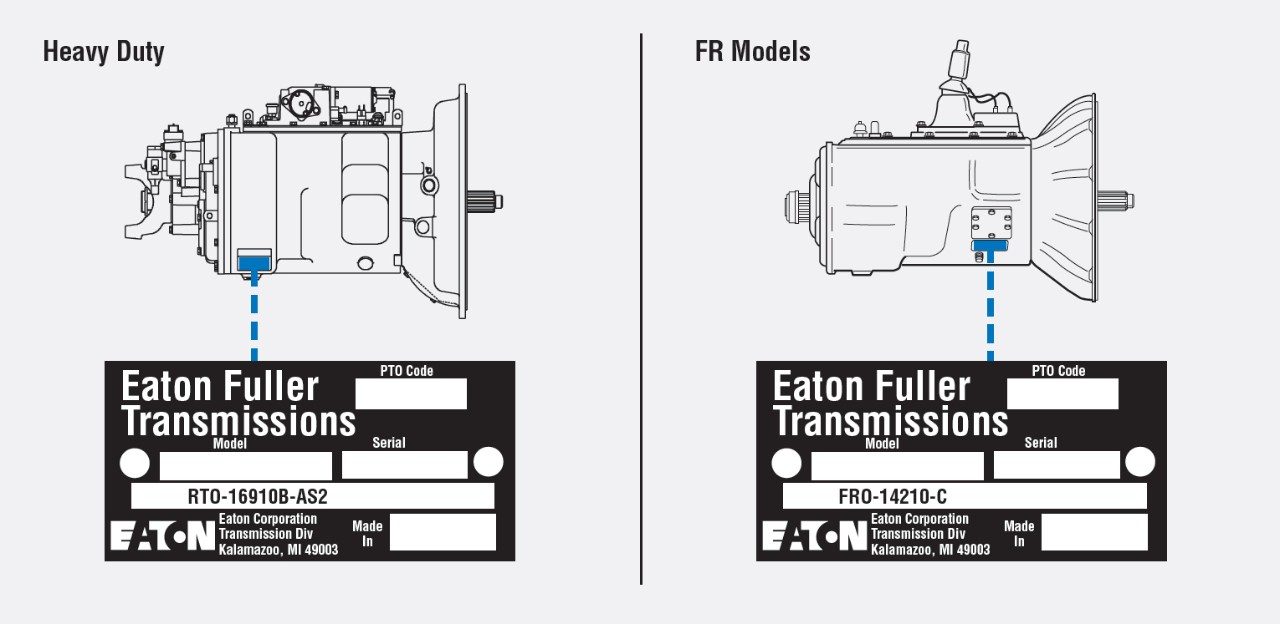
Finding the Serial Number: The serial number is typically stamped or printed on a metal tag or directly onto the transmission case. Common locations include the side, top, or rear of the transmission housing. You might need to use a flashlight and a wire brush to clean the area and make the number visible. Sometimes the tag is bolted or riveted to the case. Be patient and thorough in your search.
Deciphering the Code: Once you've located the serial number, you'll need a reference guide or online resource to decipher its meaning. Many manufacturers publish lists of their transmission codes. You can also find helpful databases and forums online where enthusiasts share their knowledge. Start by identifying the manufacturer's code and then work your way through the remaining components. Pay close attention to the model designation and date code, as these are critical for determining compatibility.
Pros and Cons of Using Serial Numbers
Pros:
- Accurate Identification: Serial numbers provide the most accurate way to identify a specific transmission model and its compatibility with different vehicles.
- Traceability: They allow you to trace the transmission back to its origin, including the manufacturer, assembly plant, and build date.
- Troubleshooting: Serial numbers can be helpful for troubleshooting issues, as they can reveal specific design flaws or revisions associated with certain production batches.
- Parts Ordering: Identifying the correct transmission by serial number ensures that you order the correct replacement parts.
Cons:
- Location and Visibility: Serial numbers can be difficult to locate and may be obscured by dirt, grease, or corrosion.
- Decoding Complexity: Deciphering the serial number requires knowledge of the manufacturer's coding system, which can be complex and vary over time.
- Database Availability: Comprehensive databases of transmission serial numbers and their meanings may not always be readily available or up-to-date.
- Tampering: Serial number tags can be removed, damaged, or altered, making it difficult to identify the transmission accurately.
Use Cases
- Transmission Replacement: As discussed earlier, serial numbers are essential for ensuring that you install the correct replacement transmission in your vehicle.
- Performance Upgrades: When upgrading your transmission for performance purposes, the serial number helps you identify compatible aftermarket components and modifications.
- Vehicle Restoration: During a vehicle restoration project, the serial number can help you source an original or period-correct transmission.
- Salvage Operations: Salvage yards rely on serial numbers to accurately catalog and sell used transmissions.
- Warranty Claims: Manufacturers may require the serial number to process warranty claims related to transmission failures.
Manufacturer Examples
Let's look at a couple of examples to illustrate how different manufacturers use serial numbers:
General Motors (GM):
GM transmissions often have a serial number stamped on a metal tag attached to the transmission case. For example, a 4L60E transmission might have a serial number that includes codes for the model (4L60E), the build date (e.g., "991122," meaning 1999, November, 22nd), and a sequential production number. Other codes can indicate which plant the transmission was assembled at.
Ford:
Ford transmissions typically have a part number and a date code stamped directly onto the case. The part number identifies the specific transmission model, while the date code indicates the build date. These numbers can be found on various locations depending on the model.
Aisin Warner (Aisin):
Aisin Warner transmissions, commonly found in many Japanese vehicles (Toyota, Lexus), often have a serial number etched onto the transmission case, usually near the bellhousing. These serial numbers are often long and alphanumeric, encoding a combination of production date, model variant, and sequential number.
Real-World Insights and Recommendations
Based on real-world use and experience, here are a few key insights and recommendations when dealing with transmission serial numbers:
- Document Everything: Before removing a transmission, take clear photos of the serial number and its location on the case. This will be invaluable if the tag gets damaged or lost.
- Double-Check Information: Always verify the information obtained from the serial number with other sources, such as your vehicle's VIN or the manufacturer's specifications.
- Seek Expert Advice: If you're unsure about deciphering a serial number or determining transmission compatibility, consult with a qualified mechanic or transmission specialist.
- Beware of Counterfeits: Be cautious when purchasing used transmissions, especially from unknown sources. Inspect the serial number tag carefully for signs of tampering or alteration.
- Clean the Area: Before attempting to read any numbers on your transmission, use a wire brush and degreaser to clean off any dirt or grime. A clean surface allows for better visibility and more accurate reading.
In conclusion, understanding how to identify a transmission by its serial number is a valuable skill for anyone working with cars. While the process can be challenging, the rewards – accurate identification, informed decision-making, and peace of mind – are well worth the effort. Remember, the seemingly random string of characters holds the key to unlocking your transmission's secrets. By taking the time to decipher it, you can ensure that you're making the right choices for your vehicle.
