How To Know If My Car Is Awd
So, you're wondering if your car is rocking All-Wheel Drive (AWD)? Good question! Knowing your vehicle's drivetrain is crucial for maintenance, modifications, and even understanding how it handles in different conditions. This guide will walk you through the steps and indicators to determine if you've got an AWD machine. We'll cover the visual clues, identification numbers, and even some mechanical checks you can perform.
Purpose of Understanding Your Drivetrain
Why does knowing if your car is AWD matter? Several reasons:
- Maintenance: AWD vehicles have different maintenance requirements than Front-Wheel Drive (FWD) or Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD) vehicles. Differentials, transfer cases, and extra driveshafts all need specific fluids and service intervals.
- Repairs: Diagnosing drivetrain issues requires knowing exactly what parts your car has. A misdiagnosis can lead to wasted time and money on the wrong components.
- Modifications: Upgrading suspension, tires, or even engine components needs to consider the AWD system. Some modifications that work perfectly on a RWD car can be detrimental to an AWD vehicle.
- Performance: Understanding how your AWD system works allows you to better utilize its capabilities in various driving situations – snow, rain, or even off-roading (if applicable).
- Learning: Deepening your understanding of automotive technology is a worthy pursuit, and drivetrain identification is a fundamental aspect of it.
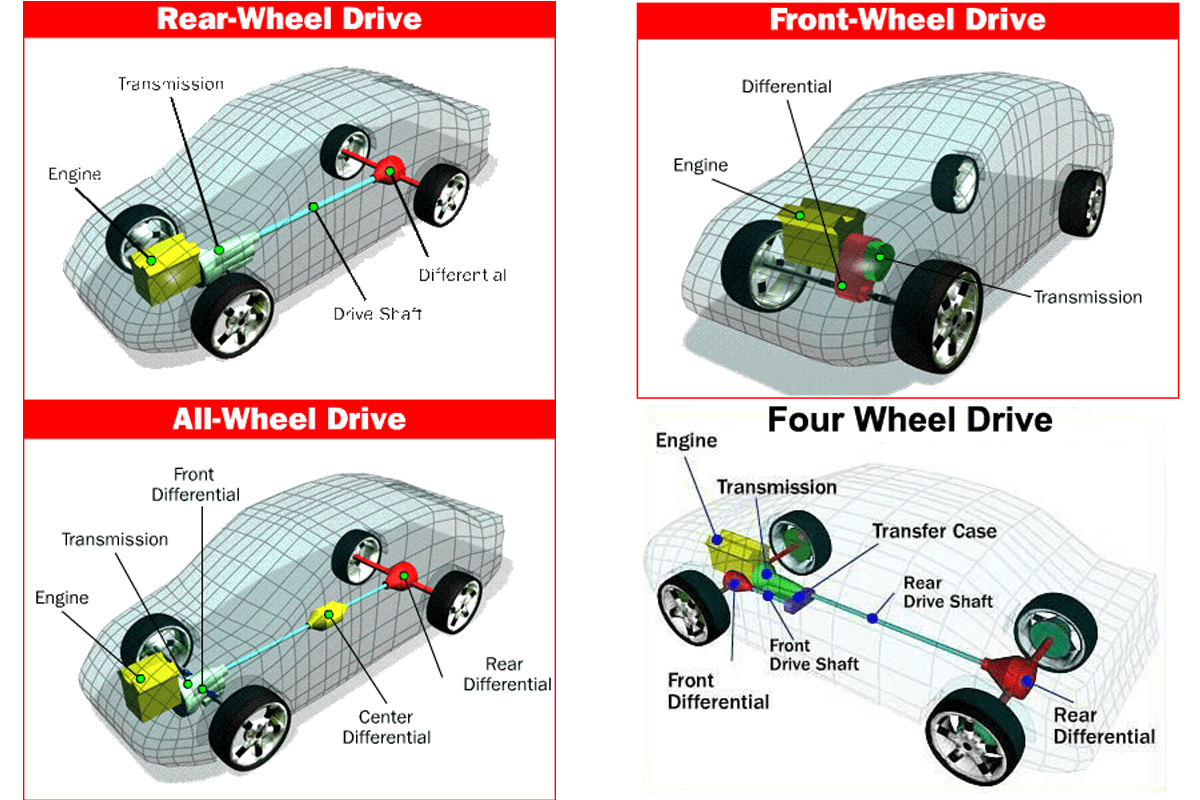
Key Specs and Main Parts of an AWD System
An AWD system distributes power to all four wheels, providing improved traction compared to two-wheel drive vehicles. However, the specific components and operation can vary significantly. Here's a breakdown of the key elements:
- Engine: The source of power. No matter the drivetrain, it all starts here.
- Transmission: Transfers the engine's power and torque.
- Transfer Case (Part-Time AWD): This component is unique to part-time AWD systems. It splits power between the front and rear axles and allows the driver to engage or disengage AWD. Think of it like a gear box specifically for the AWD system. It typically includes a shift lever or electronic switch.
- Center Differential (Full-Time AWD): Found in full-time AWD systems, a center differential (or viscous coupling or electronic clutch in some systems) allows the front and rear axles to rotate at different speeds. This is crucial for driving on pavement without binding or damaging the drivetrain. This allows the wheels to independently manage slippage.
- Front Differential: Distributes power to the front wheels.
- Rear Differential: Distributes power to the rear wheels.
- Driveshafts/Axle Shafts: These connect the differentials to the wheels, transmitting power. The number and configuration can provide immediate clues.
Visual Inspection: Finding the Obvious Clues
The easiest way to start is with a visual inspection. Here's what to look for:
- Driveshaft to the Rear: Look under the vehicle. If you see a driveshaft running from the transmission or transfer case to the rear axle, it's a strong indicator of AWD or RWD. If the vehicle is FWD, you won't see this shaft running to the rear.
- Front Axle Shafts: Examine the front wheels. Do you see axle shafts (also called half-shafts) connecting to the front wheels? If so, power is definitely going to the front. Even if you *do* see a rear driveshaft, you also need front half-shafts to confirm AWD.
- Transfer Case Shift Lever/Button: Some older AWD vehicles (usually trucks and SUVs) have a lever or button inside the cabin that allows you to switch between 2WD and 4WD (which is technically a type of AWD). If you see such a control, it confirms an AWD (or 4WD) system. Modern systems are mostly automatic and engage based on driving conditions.
- Wheel Hubs: Check the front wheel hubs. Look for a CV joint (Constant Velocity joint) near the wheel hub. This confirms a powered front axle.
Decoding Vehicle Identification: VIN and Badges
If a visual inspection isn't definitive, try these methods:
- VIN Decoder: The Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) contains information about your vehicle's specifications. Many online VIN decoders (easily found with a search engine) can tell you the drivetrain configuration. Just enter your VIN, and the decoder will reveal details about your car.
- Manufacturer's Website: Check the manufacturer's website (e.g., Toyota, Honda, Ford). You can often enter your VIN or vehicle details to access the original specifications.
- Badges and Emblems: Some vehicles have badges or emblems indicating the drivetrain (e.g., "AWD," "4Matic," "Quattro"). However, be cautious, as these badges can be added or removed. Always verify with other methods.
- Owner's Manual: Your owner's manual should clearly state the drivetrain configuration.
The Mechanical Test: A Simple Check
If you're still unsure, you can perform a simple, albeit potentially slightly risky, mechanical test. Proceed with caution and ensure you have a safe environment with plenty of space and no obstructions.
- Find a Loose Surface: Find a patch of gravel, dirt, or grass.
- Engage Low Gear (if applicable): If your vehicle has a low-range gear, engage it.
- Accelerate Gently: Slowly accelerate. Have an assistant watch the wheels.
- Observe Wheel Spin: If it's an AWD system, *all* wheels should spin or try to spin simultaneously. If only the front or rear wheels spin, it's likely a 2WD vehicle. Do not attempt to power through extreme conditions; this test is only to see the initial response to slippage.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Knowing your drivetrain is essential for diagnosing problems. Here are some basic troubleshooting tips:
- Unusual Noises: Grinding, clunking, or whining noises from the drivetrain area can indicate problems with differentials, the transfer case, or driveshafts.
- Vibrations: Excessive vibrations, especially at certain speeds, can be caused by worn U-joints on driveshafts or imbalanced tires.
- Fluid Leaks: Check for fluid leaks around differentials and the transfer case. Leaking fluid can lead to component failure.
- AWD System Light: If your vehicle has an AWD system warning light, consult your owner's manual for possible causes and diagnostic procedures.
Safety Considerations
Working on drivetrain components can be risky. Keep these safety tips in mind:
- Support the Vehicle Properly: Always use jack stands when working under a vehicle. Never rely solely on a jack.
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnecting the battery prevents accidental starting.
- Use the Right Tools: Use the correct tools for the job to avoid damaging components or injuring yourself.
- Torque Specifications: Always tighten bolts to the manufacturer's specified torque to ensure proper clamping force.
- Differentials and Transfer Cases: These components contain complex gears and can be heavy. Use caution when handling them.
- Driveshafts: Rotating driveshafts can be dangerous. Never start the engine with the vehicle raised and the wheels free to spin.
Identifying your car's drivetrain is a crucial step in understanding and maintaining your vehicle. By using the visual clues, identification numbers, and mechanical checks outlined above, you can confidently determine if your car is AWD.
We have a detailed diagram of a typical AWD system that you can download. This diagram illustrates the components and their relationships, providing a visual aid for your understanding. This diagram clarifies the flow of power and helps you identify key components in your specific vehicle. Contact us for access to the file.
