How To Replace A Transmission Speed Sensor
Is your car shifting erratically, hesitating, or just generally acting up? You might be facing a faulty transmission speed sensor. This vital component provides critical data to your car's computer, and when it fails, the consequences can range from annoying to downright dangerous. In this guide, we'll walk you through the process of diagnosing a bad speed sensor and, most importantly, how to replace it yourself. This can save you a significant amount of money compared to taking your vehicle to a shop.
Understanding the Problem: Why a Speed Sensor Matters
The transmission speed sensor (TSS), also sometimes referred to as a vehicle speed sensor (VSS) depending on its location, is responsible for monitoring the rotational speed of either the input shaft or output shaft of your transmission. This information is crucial for the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) or Transmission Control Module (TCM) to properly manage shifting. Without accurate speed readings, the transmission might shift improperly, stay in the wrong gear, or even fail to shift at all. Ignoring a bad speed sensor can lead to further damage to your transmission, potentially resulting in a very costly repair or even a complete transmission replacement.
Symptoms of a Failing Transmission Speed Sensor
Recognizing the symptoms early is key to preventing further damage. Here's a list of common warning signs indicating a potential problem:
- Erratic Shifting: The most common symptom. Your transmission might shift too early, too late, or skip gears altogether.
- Harsh Shifting: Shifts may feel rough and jarring, rather than smooth.
- Hesitation or Stalling: Your vehicle might hesitate when accelerating, or even stall completely.
- Check Engine Light: The check engine light will often illuminate, accompanied by diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the speed sensor. Common codes include P0720, P0721, P0722, P0723, P0715, P0716, and P0717.
- Speedometer Malfunction: While sometimes the speedometer has its own dedicated sensor, on some vehicles the VSS signal is used. An inaccurate or non-functioning speedometer can indicate a speed sensor problem.
- Cruise Control Problems: Cruise control relies on accurate speed information. If the sensor is failing, cruise control may not engage or may disengage unexpectedly.
- Decreased Fuel Efficiency: Inefficient shifting can lead to a noticeable drop in gas mileage.
- Transmission Slipping: This feels like the engine is revving up without the car accelerating properly.
- Limp Mode: In some cases, the PCM will put the transmission into "limp mode" to protect it from further damage. This limits the transmission to a single gear.
Root Cause: Why Speed Sensors Fail
Transmission speed sensors are typically magnetic pickup sensors or Hall-effect sensors. Here’s why they might fail:
- Physical Damage: Road debris, impacts, or accidents can physically damage the sensor.
- Contamination: Metal shavings, dirt, or other debris can interfere with the sensor's ability to accurately read the transmission's rotational speed.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged wiring, corroded connectors, or loose connections can disrupt the signal.
- Sensor Failure: Over time, the sensor itself can simply wear out and fail. This is often due to heat cycling and constant vibration.
- Fluid Leaks: Transmission fluid leaks can damage the sensor or its wiring.
Ignoring the Problem: Potential Consequences
Ignoring a faulty transmission speed sensor can have serious consequences:
- Transmission Damage: Improper shifting can put undue stress on the transmission's internal components, leading to premature wear and failure. This is the most significant risk.
- Safety Hazard: Erratic shifting or sudden loss of power can create dangerous driving conditions.
- Increased Repair Costs: Delaying the repair can lead to more extensive damage, resulting in much higher repair bills down the road.
- Complete Transmission Failure: In the worst-case scenario, a failing speed sensor can contribute to a complete transmission failure, requiring a full replacement.
Recommended Fixes: Replacing the Speed Sensor
Replacing a transmission speed sensor is a relatively straightforward repair that most DIY mechanics can tackle with basic tools. Here's a step-by-step guide:
- Gather Your Tools and Parts:
- New transmission speed sensor (ensure it's the correct one for your vehicle – use your VIN to verify).
- Socket set (metric or standard, depending on your vehicle).
- Wrench set (metric or standard).
- Screwdrivers (Phillips and flathead).
- Jack and jack stands.
- Wheel chocks.
- Penetrating oil (if needed).
- rags or shop towels.
- Scan tool (to clear diagnostic trouble codes).
- Safety First: Chock the rear wheels, engage the parking brake, and lift the front of the vehicle with a jack. Securely support the vehicle with jack stands. Never work under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
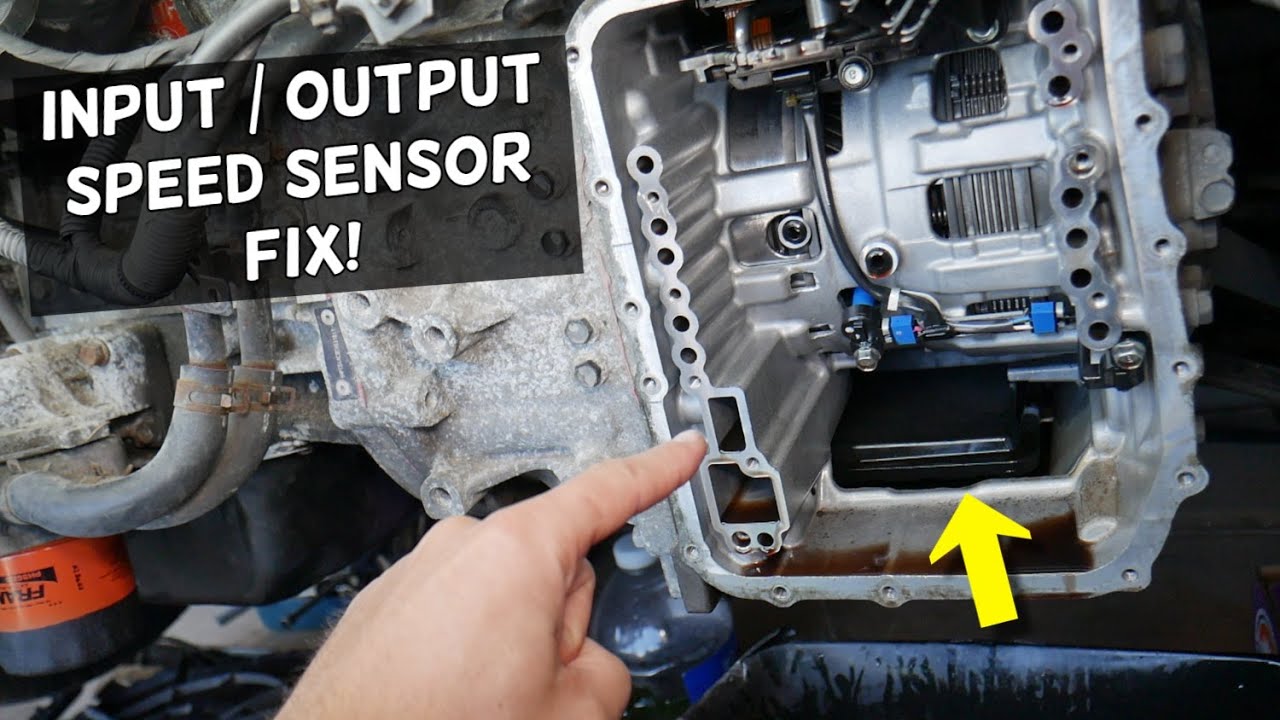
- Locate the Speed Sensor: The location of the speed sensor varies depending on the vehicle make and model. It's typically found on the transmission housing, near the input shaft or output shaft. Consult your vehicle's repair manual or search online for specific instructions for your vehicle. Look for the sensor and follow the wiring to make sure you find the right one.
- Disconnect the Electrical Connector: Carefully disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor. You may need to press a release tab. Inspect the connector for corrosion or damage. If there is corrosion clean it with electrical contact cleaner.
- Remove the Old Sensor: Use a socket or wrench to remove the sensor from the transmission housing. Some sensors are held in place with a bolt, while others simply twist and pull out. If the sensor is stuck, apply penetrating oil and let it soak for a few minutes. Be careful not to damage the transmission housing.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new sensor in the reverse order of removal. Ensure it is properly seated and tightened to the manufacturer's specifications (if available). Be careful not to overtighten, as this can damage the sensor or the transmission housing.
- Reconnect the Electrical Connector: Reconnect the electrical connector to the new sensor, ensuring it clicks into place.
- Lower the Vehicle: Carefully lower the vehicle from the jack stands.
- Clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Use a scan tool to clear any diagnostic trouble codes related to the speed sensor.
- Test Drive: Take the vehicle for a test drive to ensure the transmission is shifting properly and the speedometer is functioning correctly.
Cost Estimates and Shop Advice
The cost of a transmission speed sensor typically ranges from $20 to $100, depending on the make and model of your vehicle and the brand of the sensor. If you choose to have a professional mechanic perform the replacement, labor costs can add an additional $50 to $200, bringing the total cost to between $70 and $300.
If you're comfortable working on your car, replacing the speed sensor yourself is a great way to save money. However, if you're not mechanically inclined or if you're unsure about any part of the process, it's best to take your vehicle to a trusted mechanic. When choosing a shop, be sure to get a written estimate and ask about their warranty policy.
Important Note: It's always a good idea to diagnose the problem accurately before replacing any parts. Use a scan tool to read the diagnostic trouble codes and verify that the speed sensor is indeed the culprit. Also, check the wiring and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion. Sometimes, a simple wiring repair can resolve the issue without the need for a new sensor.
Credibility and Common Failure Points
Several factors can contribute to the failure of a transmission speed sensor. Some manufacturers have even issued Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) addressing common speed sensor problems in specific vehicle models. For example, some vehicles are prone to speed sensor failures due to excessive heat or vibration, while others may experience issues with the wiring harness.
Anecdotal data from online forums and automotive communities suggests that speed sensors typically begin to fail around 80,000 to 150,000 miles. However, this can vary depending on driving conditions and maintenance habits. Regular transmission fluid changes can help to prolong the life of the speed sensor by reducing the amount of debris and contaminants that can damage the sensor.
By understanding the symptoms, causes, and consequences of a faulty transmission speed sensor, you can take proactive steps to diagnose and repair the problem before it leads to more serious damage. Whether you choose to tackle the repair yourself or entrust it to a professional, knowing what to expect can help you save time, money, and potential headaches.
