How To Replace Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid
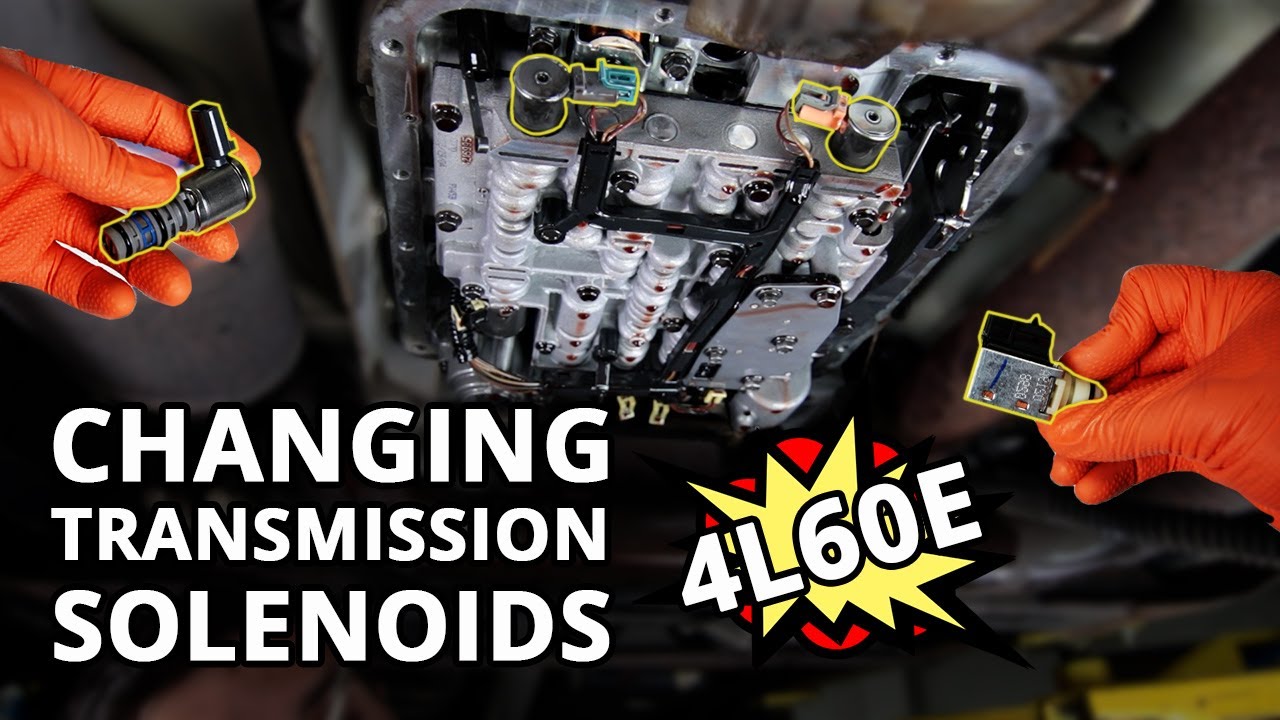
The torque converter clutch (TCC) solenoid is a vital component in your vehicle's automatic transmission. It controls the engagement and disengagement of the torque converter clutch, which, in simple terms, locks the engine and transmission together at higher speeds. Replacing it might sound daunting, but with the right tools, knowledge, and a bit of patience, it's a task you can potentially tackle yourself. This article will guide you through the process of replacing a torque converter clutch solenoid, providing helpful tips and insights along the way.
Why Replacing Your Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid Matters
Understanding the TCC solenoid's function is crucial to appreciating the importance of its proper operation. The torque converter acts as a fluid coupling between the engine and transmission. At lower speeds, this slippage is necessary for smooth starts and stops. However, at cruising speeds, this slippage reduces fuel efficiency. This is where the TCC comes in.
The TCC solenoid, when activated, allows transmission fluid to engage the torque converter clutch, essentially locking the engine and transmission together. This eliminates slippage, resulting in several key benefits:
- Improved Fuel Economy: Eliminating slippage maximizes the transfer of power from the engine to the wheels, reducing fuel consumption.
- Reduced Transmission Heat: Slippage generates heat within the transmission. Locking the torque converter reduces this heat buildup, prolonging transmission life.
- Smoother Highway Driving: When the TCC engages smoothly, it can improve the overall driving experience, particularly on long highway journeys.
A faulty TCC solenoid can manifest in various ways, including:
- Check Engine Light (CEL): A common symptom is the illumination of the CEL, often accompanied by diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the TCC solenoid or torque converter performance.
- Poor Fuel Economy: If the TCC isn't engaging properly, you'll likely notice a decrease in your vehicle's fuel economy.
- Shuddering or Vibration: You might experience a noticeable shuddering or vibration, especially at highway speeds, when the TCC attempts to engage or disengage erratically.
- Stalling: In severe cases, a malfunctioning TCC solenoid can cause the engine to stall, particularly when coming to a stop.
- Transmission Slipping: The transmission might slip or fail to shift properly, indicating a problem with the TCC system.
How to Choose the Right Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid
Selecting the correct replacement TCC solenoid is crucial for a successful repair. Here's what to consider:
- Vehicle Year, Make, and Model: This is the most important factor. TCC solenoids vary significantly between different vehicles. Use a reliable online parts catalog or consult with an auto parts store to ensure you're getting the right one.
- Transmission Type: Different transmissions require different solenoids. Identify your transmission type (e.g., 4L60E, 4R70W) and verify compatibility.
- Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) vs. Aftermarket: OEM solenoids are manufactured by the original vehicle manufacturer and are generally considered to be the highest quality option. Aftermarket solenoids can be a more affordable alternative, but quality can vary. Research the brand and read reviews before purchasing.
- Solenoid Location and Appearance: Compare the physical appearance of the new solenoid with the old one. Check the connector type and mounting points to ensure they match.
Important Safety Note: Before starting any automotive repair, disconnect the negative battery terminal to prevent electrical shock. Wear safety glasses and gloves to protect yourself.
Tools and Materials You'll Need:
- New TCC solenoid
- Socket set and wrenches
- Screwdrivers (various sizes)
- Torque wrench
- Jack and jack stands
- Wheel chocks
- Drain pan
- Transmission fluid (compatible with your vehicle)
- Rags or shop towels
- Penetrating oil (optional)
- Multimeter (optional, for testing)
- Vehicle repair manual or online service information
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing the TCC Solenoid:
- Preparation: Chock the rear wheels and jack up the front of the vehicle. Securely support it with jack stands.
- Locate the Transmission: Identify the transmission pan. The TCC solenoid is usually located inside the transmission, accessible after removing the pan.
- Drain the Transmission Fluid: Position the drain pan under the transmission pan. Loosen the pan bolts gradually, starting from the rear, to allow the fluid to drain slowly. Be prepared for a mess!
- Remove the Transmission Pan: Once most of the fluid has drained, carefully remove the remaining pan bolts and lower the pan. Be careful not to spill any remaining fluid.
- Locate the TCC Solenoid: The TCC solenoid is typically mounted to the valve body inside the transmission. Refer to your vehicle's repair manual or online service information to pinpoint its exact location.
- Disconnect the Electrical Connector: Carefully disconnect the electrical connector from the TCC solenoid. Some connectors may have a locking mechanism.
- Remove the Old Solenoid: Remove the bolts or clips that secure the TCC solenoid to the valve body. Use penetrating oil if necessary to loosen any corroded fasteners. Pay attention to the orientation of the solenoid as you remove it.
- Install the New Solenoid: Install the new TCC solenoid in the reverse order of removal. Ensure the electrical connector is properly seated and locked. Torque the mounting bolts to the manufacturer's specifications using a torque wrench. Over-tightening can damage the valve body.
- Clean the Transmission Pan: Thoroughly clean the transmission pan and magnet, removing any debris or metal particles.
- Install a New Transmission Pan Gasket: Install a new transmission pan gasket to ensure a proper seal.
- Reinstall the Transmission Pan: Reinstall the transmission pan, tightening the bolts in a crisscross pattern to ensure even pressure. Torque the pan bolts to the manufacturer's specifications.
- Refill the Transmission Fluid: Add the correct type and amount of transmission fluid as specified in your vehicle's owner's manual. Use a funnel to avoid spills.
- Check the Fluid Level: Start the engine and let it run for a few minutes. Check the transmission fluid level using the dipstick (if equipped) or following the manufacturer's instructions. Add more fluid as needed.
- Test Drive: Take the vehicle for a test drive to ensure the TCC solenoid is functioning properly. Pay attention to any unusual noises or vibrations.
- Check for Leaks: Inspect the transmission pan for any leaks.
- Clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): If the Check Engine Light is still on, you may need to clear the DTCs using an OBD-II scanner.
Real-World Owner Experiences
Many car owners have successfully replaced their TCC solenoids themselves, saving money on labor costs. Here are a few common themes from their experiences:
- Accurate Diagnosis is Key: It's crucial to properly diagnose the problem before replacing the TCC solenoid. A mechanic can use a scan tool to confirm that the solenoid is the culprit.
- Cleanliness is Essential: Maintaining cleanliness throughout the repair process is vital to prevent contamination of the transmission fluid and internal components.
- Follow Instructions Carefully: Refer to a reliable repair manual or online resource for specific instructions for your vehicle.
- Don't Over-Tighten Bolts: Over-tightening the transmission pan or solenoid mounting bolts can damage the components. Use a torque wrench and follow the manufacturer's specifications.
- Patience is Rewarded: Replacing the TCC solenoid can be a time-consuming task. Don't rush the process, and take breaks when needed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How much does it cost to replace a TCC solenoid?
The cost can vary depending on the vehicle and whether you do it yourself or hire a mechanic. The solenoid itself can range from $50 to $200. Labor costs can add another $200 to $500 or more.
Q: Can I drive with a bad TCC solenoid?
While you *can* drive with a bad TCC solenoid, it's not recommended. It can lead to poor fuel economy, transmission overheating, and potentially further damage to the transmission. Get it fixed as soon as possible.
Q: How do I know if my TCC solenoid is bad?
Common symptoms include a Check Engine Light, poor fuel economy, shuddering at highway speeds, stalling, and transmission slipping.
Q: Where is the TCC solenoid located?
The TCC solenoid is typically located inside the transmission, mounted to the valve body. It's usually accessible after removing the transmission pan.
Q: Is it difficult to replace a TCC solenoid?
The difficulty level varies depending on your mechanical skills and the vehicle. It's generally considered a moderate DIY project for those with some experience working on cars. If you're not comfortable working on your car, it's best to have a professional mechanic do it.
Q: Do I need to reprogram the computer after replacing the TCC solenoid?
In most cases, you do not need to reprogram the computer after replacing the TCC solenoid. However, some vehicles may require a relearn procedure. Consult your vehicle's repair manual or a mechanic for specific instructions.
Q: What happens if I don't replace the TCC solenoid?
Ignoring a bad TCC solenoid can lead to further damage to the transmission, potentially requiring a more expensive repair or even a complete transmission replacement. It will also result in reduced fuel economy.
