How To Track My Car With Onstar
Tracking Your Car with OnStar: A Deep Dive
As experienced DIYers and car enthusiasts, we appreciate understanding the inner workings of our vehicles. Modern cars are increasingly complex, relying heavily on telematics systems like OnStar. While often marketed for safety and convenience, OnStar's core functionality revolves around its ability to track your vehicle. This article provides a technical overview of how OnStar tracking works, enabling you to better understand its capabilities and limitations.
Purpose: Understanding OnStar Tracking
Understanding how OnStar tracks your car is valuable for several reasons:
- Understanding Data Privacy: Knowing what data is collected and how it's transmitted allows you to make informed decisions about your privacy settings and usage of the service.
- Troubleshooting Issues: In some cases, tracking malfunctions can point to underlying electrical or connectivity problems within your vehicle.
- Security Awareness: Familiarizing yourself with the tracking mechanism can help you understand potential vulnerabilities and take steps to protect your vehicle from theft.
- Accident Reconstruction: In unfortunate events, the data collected by OnStar can be crucial for accident reconstruction and insurance claims.
This isn't about circumventing OnStar's intended uses, but rather empowering you with knowledge about a critical aspect of your vehicle's technology.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the OnStar System
The OnStar system comprises several key components working in concert to provide tracking functionality:
- GPS Receiver: The Global Positioning System (GPS) receiver is the heart of the tracking system. It receives signals from GPS satellites orbiting the Earth to determine the vehicle's precise location (latitude, longitude, and altitude). This data is extremely accurate, typically within a few meters.
- Cellular Modem: The cellular modem allows the OnStar system to communicate with the OnStar call center and transmit location data, diagnostic information, and other relevant data. It uses cellular networks (typically 4G LTE or newer) for this communication.
- OnStar Module (Telematics Control Unit - TCU): This is the main processing unit for the OnStar system. It contains the GPS receiver, cellular modem, and a microcontroller that manages all the functions, including data processing, communication, and interaction with other vehicle systems.
- Vehicle Sensors: OnStar can also access data from various vehicle sensors, such as the speedometer, odometer, and airbag deployment sensors. This data can be used to provide additional context to the vehicle's location and status.
- Antennas: Separate antennas are used for GPS and cellular communication. These antennas are typically located on the roof or inside the vehicle's dashboard, and they ensure optimal signal reception.
- Backup Battery: A small backup battery ensures the OnStar system can still function even if the vehicle's main battery is disconnected. This is particularly important in the event of an accident.
Understanding these components is essential for diagnosing potential tracking issues.
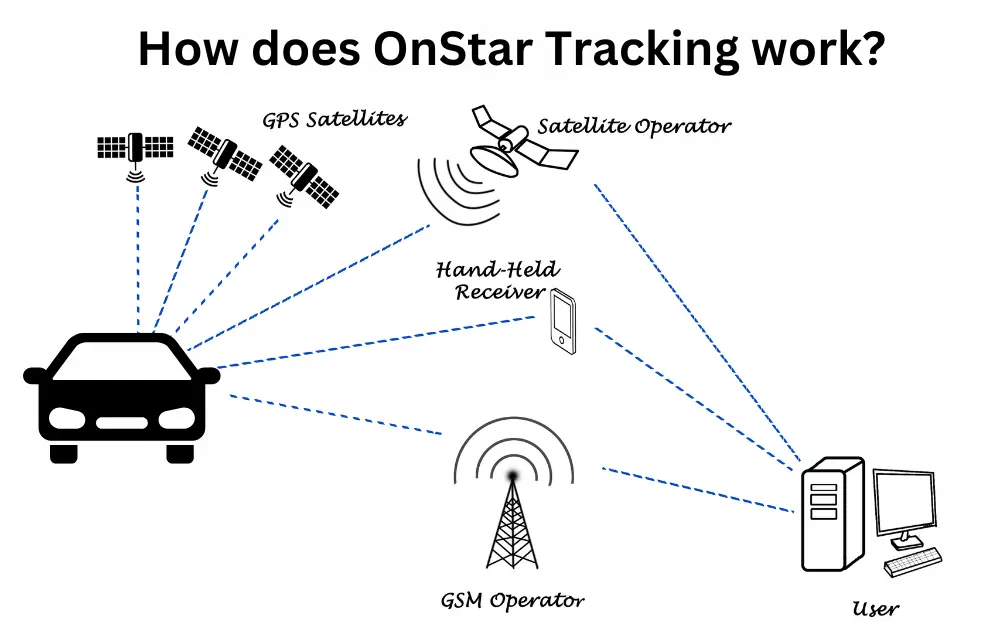
How It Works: The Tracking Process
The OnStar tracking process can be broken down into several steps:
- Location Acquisition: The GPS receiver continuously receives signals from GPS satellites. The OnStar module calculates the vehicle's location based on the timing and distance of these signals.
- Data Logging: The OnStar module logs the vehicle's location, speed, and other relevant data at regular intervals (typically every few seconds or minutes). The frequency of logging can vary depending on the OnStar subscription plan and specific events (e.g., a crash).
- Data Transmission: The OnStar module periodically transmits the logged data to the OnStar call center using the cellular modem. The data is encrypted to protect privacy.
- Data Processing and Storage: The OnStar call center receives the data, decrypts it, and stores it in a secure database. The data can be accessed by OnStar advisors, law enforcement (with a warrant), or the vehicle owner (through the OnStar mobile app or website).
The Telematics Control Unit (TCU) is crucial in handling and transmitting data. The cellular modem uses protocols like TCP/IP and HTTPS to communicate with OnStar servers. The GPS receiver relies on satellite signals operating in the L1 band (1575.42 MHz) for location information.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
If you suspect your OnStar tracking is malfunctioning, consider the following troubleshooting steps:
- Check OnStar Subscription: Ensure your OnStar subscription is active. An expired subscription will disable tracking functionality.
- Verify Cellular Coverage: OnStar relies on cellular networks. If you are in an area with poor cellular coverage, tracking may be intermittent or unavailable.
- Inspect Antennas: Check the antennas for damage or obstructions. A damaged antenna can significantly reduce signal strength.
- Check Vehicle Battery Voltage: A weak vehicle battery can sometimes affect the performance of the OnStar system. Ensure your battery is in good condition.
- Contact OnStar Support: If you have ruled out basic issues, contact OnStar support for assistance. They may be able to diagnose the problem remotely or recommend a visit to a certified repair technician.
For example, if you're getting a "GPS signal not available" error, the GPS antenna might be damaged or disconnected. Use a multimeter to check the antenna cable for continuity.
Safety: Risky Components and Precautions
Working with the OnStar system can involve dealing with electrical components and sensitive data. Take the following precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical components, disconnect the vehicle's battery to prevent accidental shocks or damage.
- Handle Antennas Carefully: Antennas can be fragile. Avoid bending or breaking them.
- Protect Your Privacy: Be mindful of the data collected by OnStar. Review your privacy settings and disable features you are not comfortable with.
- Do not attempt to tamper with the OnStar system without proper knowledge. Doing so could compromise the vehicle's safety and security systems.
- Be aware of FCC regulations regarding radio frequency devices if working with antennas or wireless modules.
The TCU can be sensitive to electrostatic discharge (ESD). Use an anti-static wrist strap when handling it.
By understanding the technical aspects of OnStar tracking, you can better understand how your vehicle functions and take steps to ensure its safe and secure operation. Remember to always consult with a qualified mechanic or OnStar support if you encounter any complex issues.
We have a detailed technical diagram of the OnStar system available for download. This diagram includes component locations, wiring schematics, and other valuable information for advanced troubleshooting and repair. Contact us to receive the file.
