How To Use A 4 Wheel Drive
So, you're looking to get a handle on how your 4-wheel drive (4WD) system works. Excellent choice! Understanding the mechanics behind your vehicle's traction is crucial, whether you're planning off-road adventures, performing maintenance, or just want to troubleshoot potential issues. This article will break down the inner workings of a typical 4WD system, focusing on the core components and how they interact. Consider this your detailed guide to understanding 4WD systems.
Purpose and Understanding
Why delve into the intricacies of 4WD? There are several key reasons:
- Troubleshooting: Understanding the system allows you to diagnose problems like binding, unusual noises, or failure to engage.
- Maintenance: Knowing the components and their lubrication needs can prevent premature wear and costly repairs.
- Modification: Planning on upgrading your system with a lift kit, lockers, or a different transfer case? This knowledge is essential for a successful modification.
- Safe Operation: Knowing the limitations of your system prevents damage and ensures safer driving in challenging conditions.
Think of it as understanding the blueprint of your vehicle's traction. The more you know, the better equipped you'll be to handle any situation.
Key Specs and Main Parts of a 4WD System
A typical 4WD system consists of several key components working in harmony:
- Engine: The source of power for the entire system.
- Transmission: Transfers power from the engine and allows for gear selection.
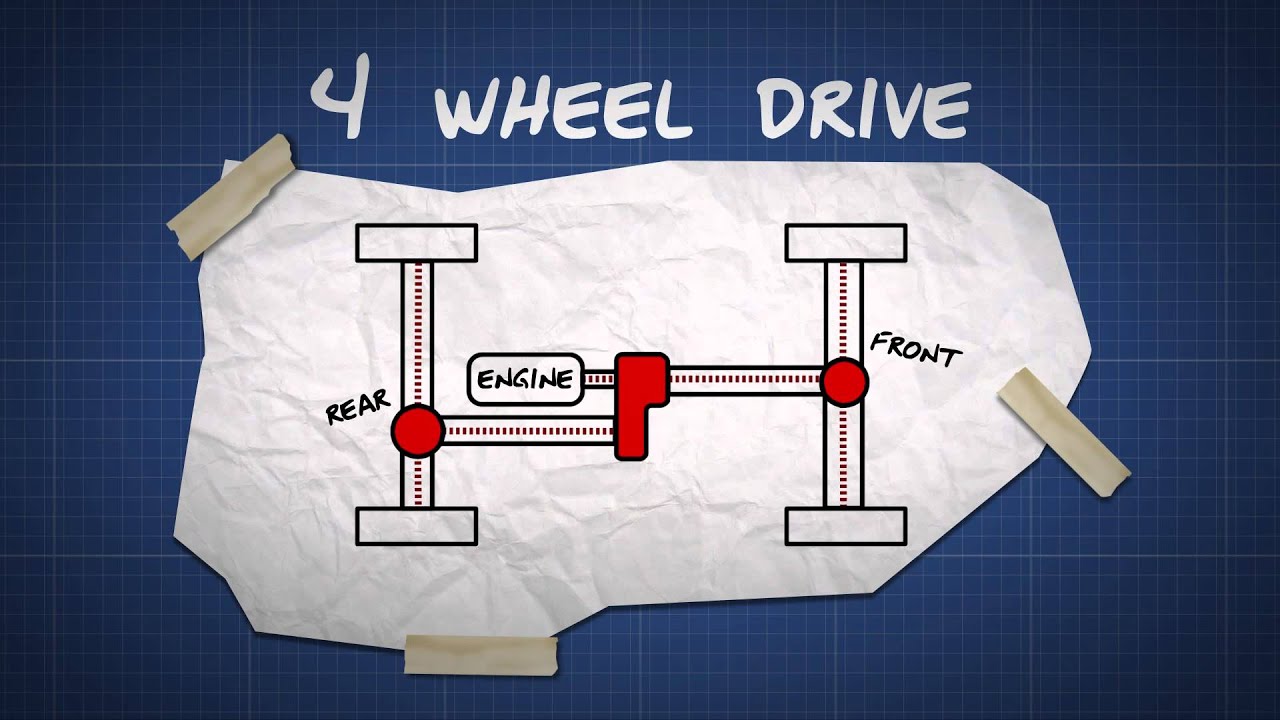
- Transfer Case: This is the heart of the 4WD system. It splits power from the transmission between the front and rear axles. A transfer case typically offers different modes, such as 2WD, 4WD High, and 4WD Low.
- Front and Rear Driveshafts: Rotating shafts that transmit power from the transfer case to the front and rear differentials.
- Front and Rear Differentials: These allow each wheel on an axle to rotate at different speeds, which is essential for turning. Standard (open) differentials distribute torque equally, which can lead to wheel spin in low-traction situations.
- Axles: The shafts that connect the differential to the wheels.
- Hubs (if applicable): Some 4WD systems use manual or automatic hubs to engage or disengage the front wheels from the axles.
Key Specifications to consider include gear ratios in the transfer case (especially the low range ratio), axle ratios, and the type of differential (open, limited-slip, or locking).
How It Works: Power Flow and Engagement
Let's trace the flow of power in a typical part-time 4WD system (the most common type):
- The engine generates power, which is sent to the transmission.
- The transmission, controlled by the driver, selects the appropriate gear based on speed and load.
- The transmission output shaft connects to the transfer case input shaft.
- When 4WD is engaged (typically by a lever or electronic switch), the transfer case locks the front and rear driveshafts together.
- Power is then split between the front and rear driveshafts. In most part-time systems, this split is a fixed 50/50.
- The driveshafts transmit power to the front and rear differentials.
- The differentials allow the wheels on each axle to rotate at different speeds, while still transmitting power.
- Finally, the axles transfer the rotational force from the differentials to the wheels, propelling the vehicle forward.
In 4WD High, the transfer case engages both axles, providing increased traction at higher speeds. 4WD Low utilizes a gear reduction within the transfer case. This significantly increases torque to the wheels, ideal for slow-speed, high-obstacle situations. The lower gear ratio multiplies the engine's torque output, allowing you to crawl over rocks or through mud. However, it limits your speed substantially.
Real-World Use and Troubleshooting
Here are some basic troubleshooting tips for common 4WD issues:
- Difficulty Engaging/Disengaging: This could be due to a sticky linkage in the transfer case, low vacuum (if vacuum-actuated), or a faulty electronic actuator. Try shifting into neutral and engaging/disengaging the system while moving slowly.
- Binding: This occurs when the front and rear axles are forced to rotate at different speeds on a hard surface. It's most common in part-time 4WD systems used on pavement. Avoid using 4WD on dry pavement to prevent this.
- Unusual Noises: Grinding or clunking noises from the transfer case or differentials could indicate worn gears, low fluid levels, or damaged bearings. Check fluid levels and inspect for leaks.
- Failure to Engage: This can be caused by a blown fuse, a faulty sensor, or a malfunctioning shift motor. Check the fuse box and consult your vehicle's repair manual for sensor locations and testing procedures.
Regular maintenance, including fluid changes in the transfer case and differentials, is crucial for preventing these issues.
Safety Considerations
Working on a 4WD system involves inherent risks. Here are some key safety precautions:
- Always disconnect the battery before working on any electrical components.
- Use jack stands to support the vehicle securely. Never work under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
- Be cautious of rotating components, such as driveshafts, when the engine is running. Keep hands and clothing clear.
- Release pressure in hydraulic systems before disconnecting lines.
- Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris.
- The driveshaft is a high-speed rotating component that can cause serious injury if it fails or is accidentally engaged during maintenance.
Specifically, the transfer case can be heavy and awkward to handle. Use proper lifting techniques and consider using a transmission jack for removal and installation. The differentials contain gears that can have sharp edges. Wear gloves to protect your hands.
Final Thoughts
Understanding your 4WD system empowers you to maintain, troubleshoot, and even modify your vehicle for improved performance and reliability. Remember to always prioritize safety and consult your vehicle's service manual for specific instructions and torque specifications. This knowledge will not only save you money on repairs but also enhance your overall driving experience.
We have a detailed 4WD system diagram available for download, illustrating the components and their connections. This diagram can be a valuable resource for understanding the layout and function of your 4WD system. [Download Diagram Here]
