How To Use Android Auto In Car
So, you're ready to dive into the world of Android Auto? Excellent! This isn’t just about getting Google Maps on your in-car display. It's about integrating your Android smartphone’s functionality seamlessly with your vehicle's infotainment system, providing a safer and more convenient driving experience. Think of this guide as your comprehensive workshop manual for understanding and troubleshooting Android Auto.
Purpose
This guide aims to equip you with the knowledge to confidently set up, use, and diagnose common issues with Android Auto. Whether you’re performing routine updates, troubleshooting connection problems, or even considering aftermarket head unit installations, understanding the technical aspects of Android Auto is crucial. Having a firm grasp on how the system operates will save you time, money, and potentially prevent headaches down the road. Consider this your go-to resource if you're comfortable under the hood and want to extend that knowledge to your car's infotainment system.
Key Specs and Main Parts
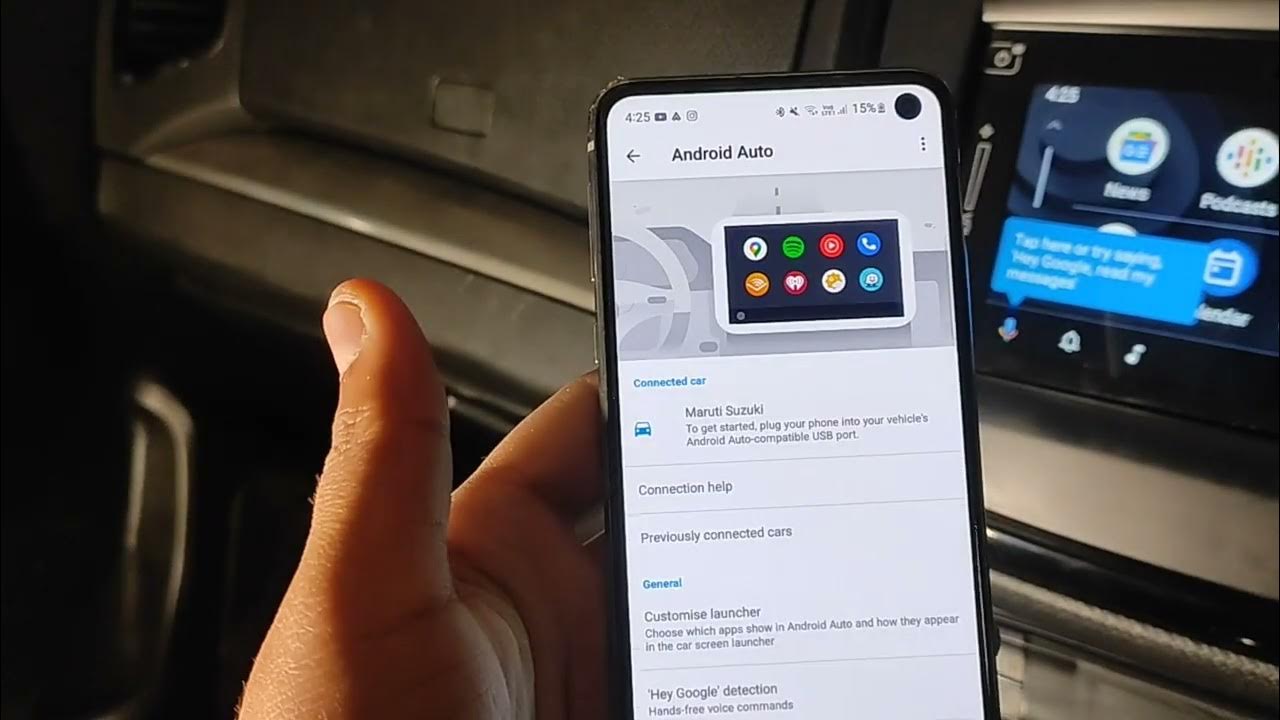
Android Auto isn't a single piece of hardware but rather a software projection from your smartphone to your car's head unit. Here's a breakdown of the key components:
- Android Smartphone: Running Android 8.0 (Oreo) or higher, with a data plan. This is the brain of the operation. The app itself must be installed on the phone, often pre-installed on newer devices.
- Compatible Head Unit: Your car's infotainment system must support Android Auto. This can be factory-installed or an aftermarket unit. Check the manufacturer’s specifications for compatibility. This includes the head unit's hardware specifications, like the processor and memory, which play a crucial role in responsiveness.
- USB Cable: A high-quality USB cable is *essential* for a stable connection, especially if you’re not using Wireless Android Auto. Ideally, use the cable that came with your phone. We’re talking about data transfer rates here; a cheap cable can introduce lag or even disconnects.
- Android Auto App: Installed on your smartphone, this app facilitates the connection and data transfer to your head unit. While often pre-installed, it's crucial to ensure you have the latest version from the Google Play Store.
A key specification to understand is the protocol used for communication between your phone and the head unit. Android Auto primarily utilizes the Media Transfer Protocol (MTP) for data transfer. Understanding this is crucial when troubleshooting connection issues, as firewall or driver problems on either end can disrupt MTP communication.
How It Works
Android Auto uses a mirroring process. Your phone runs the apps, processes the data (navigation, music playback, voice commands), and then sends a visual representation to your car's display. Think of it as your phone acting as the remote server, and your car's screen displaying the output. Let's break down the steps:
- Connection Establishment: When you plug your phone into the compatible USB port on your car, or initiate a Wireless Android Auto connection via Bluetooth/Wi-Fi Direct, the head unit recognizes the connected device.
- Handshake and Authentication: The head unit and phone exchange information to verify compatibility and establish a secure connection. This "handshake" is crucial for ensuring proper communication.
- Data Transfer: The Android Auto app on your phone takes over. It essentially projects its user interface onto the car's display. All input (touch, voice commands) is relayed back to the phone for processing.
- App Execution: The phone runs the designated Android Auto-compatible apps (Google Maps, Spotify, etc.) and sends video and audio streams to the head unit.
Wireless Android Auto operates slightly differently. It leverages both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi Direct. Bluetooth is used for initial pairing and control signals, while Wi-Fi Direct provides the high-bandwidth connection needed for audio and video streaming. The key advantage is eliminating the need for a USB cable, but it requires both the phone and the head unit to support the Wireless Android Auto protocol.
Real-World Use – Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Even with a well-configured system, issues can arise. Here's how to diagnose and address common problems:
- Problem: Android Auto won't connect.
- Solution:
- Check your USB cable. Try a different cable, preferably the one that came with your phone. Damaged or low-quality cables are a common culprit.
- Ensure Android Auto is enabled in both your phone's settings and your car's head unit settings.
- Restart both your phone and your car's infotainment system. A simple reboot can often resolve temporary glitches.
- Update the Android Auto app on your phone and ensure your car's head unit firmware is up to date. Outdated software can cause compatibility issues.
- Check USB debugging settings on your phone's developer options. Some Android Auto versions are finicky about debugging being enabled/disabled.
- Solution:
- Problem: Laggy performance or frequent disconnects.
- Solution:
- Close unnecessary apps on your phone. Android Auto relies on your phone's processing power, so freeing up resources can improve performance.
- Check your phone's battery optimization settings. Ensure that Android Auto isn't being aggressively backgrounded by your phone's battery management system.
- If using Wireless Android Auto, ensure a strong Wi-Fi signal is available. Interference or weak signals can lead to dropped connections.
- Consider a factory reset of your head unit (consult your car's manual first!). This can clear out any lingering software issues that may be affecting performance.
- Solution:
- Problem: Audio issues (no sound, distorted sound).
- Solution:
- Check your car's audio settings and ensure that Android Auto is selected as the audio source.
- Adjust the volume levels on both your phone and your car's infotainment system.
- Ensure that your phone isn't connected to any other Bluetooth devices that might be interfering with the audio output.
- Solution:
Safety
While Android Auto is designed to enhance safety by minimizing distractions, it's crucial to use it responsibly. Never interact with the system while driving, especially beyond simple voice commands. Remember:
- Distraction is dangerous: Keep your eyes on the road and your hands on the wheel. Use voice commands whenever possible.
- Beware of "bricked" head units: Attempting to modify the firmware of your head unit without proper knowledge can render it unusable. Exercise extreme caution when performing any updates or modifications.
- Data security: Be mindful of the information you share with Android Auto. While Google employs security measures, it's always prudent to be cautious about personal data.
- Aftermarket Installations: When installing aftermarket head units supporting Android Auto, ensure professional installation and proper wiring. Incorrect wiring can damage your car's electrical system.
Also, remember that continuous use of Android Auto, especially GPS navigation, can significantly drain your phone's battery. Keep a car charger handy for longer trips.
By understanding the underlying technology and following these guidelines, you can maximize the benefits of Android Auto while ensuring a safe and enjoyable driving experience.
We have a comprehensive Android Auto diagram available for download, illustrating the data flow and connections in detail. This diagram will give you even more insights to help you keep your Android Auto up and running. Contact us to gain access to that diagram.
