What Are Recalls On A Car
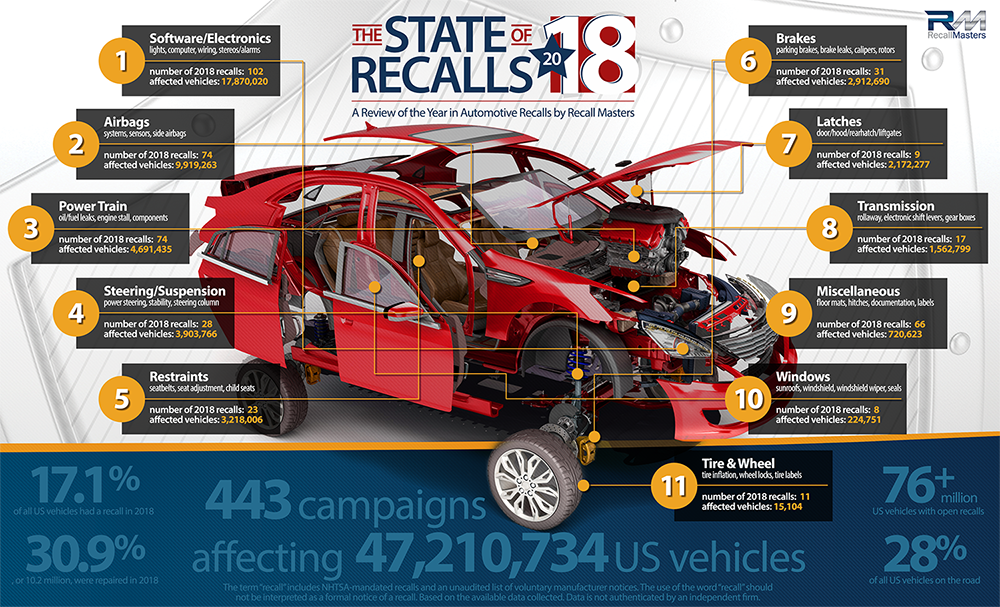
Let's talk about something crucial for every car owner, modder, and DIY mechanic: vehicle recalls. You might think it's just a notice in the mail, but understanding the technical aspects of a recall can empower you to keep your ride safe and reliable. Think of this as a deep dive into the "why" and "how" behind those recall notices.
What is a Vehicle Recall?
A vehicle recall is essentially a notification from a vehicle manufacturer or the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) that a specific safety-related defect exists in a certain make and model of vehicle. This defect could compromise the safety of the driver, passengers, or other road users. It's important to understand that a recall isn't just about minor inconveniences; it's about potential safety risks.
Purpose – Why Understanding Recalls Matters
Understanding recalls is critical for several reasons:
- Safety: The primary purpose is, of course, to ensure your safety and the safety of others. Knowing the specifics of a recall allows you to understand the potential hazard and take action to mitigate it.
- Informed Repairs: If you're a DIY mechanic, knowing the details of a recall lets you inspect the affected components yourself. While the recall repair is typically free at a dealership, understanding the issue can help you diagnose similar problems down the line.
- Preventative Maintenance: Even if your vehicle isn't currently showing symptoms related to the recall, addressing it promptly can prevent a future failure that could lead to an accident.
- Learning and Modification: For modders and enthusiasts, understanding the engineering flaws that led to the recall can inform your own modifications and ensure you're not inadvertently recreating a known safety issue.
Key Specs and Main Parts Involved in a Recall
The specifics of a recall depend entirely on the defect. However, some common components are frequently involved. Here are a few examples:
- Airbags: Defective airbags, especially those manufactured by Takata, have been the subject of massive recalls due to the risk of explosion and shrapnel injuries. The key components here are the inflator, the airbag itself, and the electronic control unit (ECU) that triggers deployment.
- Brakes: Brake-related recalls can involve issues with the brake lines, master cylinder, calipers, or even the anti-lock braking system (ABS) module. These are critical safety components, and any defect can lead to reduced stopping power or complete brake failure.
- Steering: Problems with the steering system, such as a faulty power steering pump, loose steering column bolts, or a defective steering gear, can lead to loss of steering control.
- Fuel System: Fuel leaks, faulty fuel pumps, or issues with the fuel tank can pose a fire hazard.
- Electrical System: Wiring harnesses, connectors, and electronic control modules (ECMs) can be affected by recalls due to shorts, corrosion, or software glitches. These can cause a variety of problems, from engine stalling to airbag malfunctions.
- Suspension: Recalls can involve issues with suspension components like ball joints, control arms, or shocks. These can lead to instability and loss of control.
Each recall notice will specify the exact components involved and the nature of the defect. The notice will also provide the VIN (Vehicle Identification Number) range affected, so you can check if your vehicle is included.
Understanding Recall Documentation and Diagrams
While the recall notice itself will provide a basic description of the problem, more detailed information is often available to technicians performing the recall repair. This documentation may include diagrams, technical service bulletins (TSBs), and step-by-step repair instructions. Let's break down what you might encounter:
- Exploded View Diagrams: These diagrams show the disassembled view of the affected component. Each part is numbered, and a corresponding parts list identifies each component by name and part number.
- Wiring Diagrams: For electrical recalls, wiring diagrams are essential for understanding the circuit affected by the defect. These diagrams use symbols to represent electrical components like resistors, capacitors, diodes, and transistors. Lines represent wires, and different colors may indicate different wire gauges or functions.
- Flowcharts: Some recalls involve software updates to the engine control unit (ECU) or other electronic modules. Flowcharts illustrate the steps involved in the reprogramming process.
- Torque Specifications: These specify the correct tightening torque for bolts and nuts during the repair. Using the wrong torque can lead to component failure or damage.
Symbols in Diagrams
Understanding the symbols used in automotive diagrams is crucial. Here are a few common examples:
- Ground Symbol: Represents a connection to the vehicle's chassis, providing a common reference point for electrical circuits.
- Resistor Symbol: A zig-zag line representing a component that opposes the flow of current.
- Capacitor Symbol: Two parallel lines representing a component that stores electrical energy.
- Diode Symbol: A triangle pointing to a line representing a component that allows current to flow in only one direction.
- Fuse Symbol: A squiggly line inside a rectangle representing a protective device that breaks the circuit if the current exceeds a certain limit.
- Relay Symbol: A coil of wire and a switch representing a component that uses a small current to control a larger current.
Lines in diagrams represent wires, hoses, or mechanical linkages. Colors are often used to distinguish different circuits or fluid types. Icons represent various components like sensors, actuators, and pumps.
How a Recall "Works" – From Detection to Resolution
The recall process typically begins with the manufacturer identifying a potential safety defect. This can happen through internal testing, reports from dealerships, or complaints from customers. NHTSA also plays a crucial role in monitoring vehicle safety and can initiate a recall investigation based on consumer complaints or accident data.
Once a defect is confirmed, the manufacturer is required to notify NHTSA and develop a remedy. This remedy could involve replacing a defective component, reprogramming the vehicle's software, or performing a specific repair procedure.
The manufacturer then sends out recall notices to registered owners of the affected vehicles. The notice will explain the nature of the defect, the potential hazards, and the steps needed to get the vehicle repaired. The repair is typically performed free of charge at an authorized dealership.
Real-World Use – Basic Troubleshooting Tips
While you should always take your vehicle to a dealership for a recall repair, understanding the details of the recall can help you troubleshoot related problems. For example:
- Check for Symptoms: If your vehicle is included in a recall, pay close attention to any symptoms described in the recall notice. Even if you haven't received a notice, research recalls for your make and model online.
- Inspect the Affected Component: If you're comfortable working on your car, you can visually inspect the affected component. Look for signs of damage, corrosion, or wear. However, never attempt to repair a component if you are not qualified to do so.
- Research Online: Search online forums and technical websites for information about the recall and related problems. Other owners may have experienced similar issues and can offer helpful advice.
Safety – Risky Components and Precautions
Working on certain components can be extremely dangerous. Here are a few to be particularly cautious of:
- Airbags: Never attempt to disassemble or repair an airbag yourself. These devices contain explosive charges and can cause serious injury or death if mishandled.
- Fuel System: Fuel leaks can create a fire hazard. Always disconnect the battery and work in a well-ventilated area when working on the fuel system.
- Electrical System: Disconnecting the battery is always a good practice when working on the electrical system to prevent short circuits. Be careful when working with high-voltage components like the ignition system.
- Braking System: Brake fluid can be corrosive and harmful if ingested. Wear gloves and eye protection when working on the braking system.
Always consult a qualified technician if you are unsure about any aspect of a recall repair.
Recalls are a vital part of vehicle safety. By understanding the technical aspects of recalls, you can be a more informed and proactive car owner, ensuring the safety and reliability of your vehicle.
To help you further, we have access to a detailed diagram relevant to common recall procedures. Feel free to download the diagram below for your reference:
Download Recall Diagram
(Note: Please replace "Download Recall Diagram" with an actual downloadable file.)
