What Are Trim Levels On A Car
Alright, let's dive into the often-overlooked but crucial aspect of car ownership: trim levels. Think of them as different configurations of the same basic car, each offering varying levels of features, performance, and styling. Understanding trim levels is essential for everything from buying a car to sourcing the right parts for repairs or modifications. It's like knowing the different flavors of your favorite ice cream – they all start with the same base, but the added ingredients make all the difference.
Purpose of Understanding Trim Levels
Why bother learning about trim levels? Well, consider these scenarios:
- Buying a Car: You might be drawn to a specific model, but the base trim might lack features you consider essential. Conversely, the top-of-the-line trim might include options you'll never use, leading you to overspend.
- Parts Sourcing: A seemingly minor component, like a suspension spring or even interior trim, can be different between trim levels. Ordering the wrong part can lead to compatibility issues and frustration.
- Modifications and Upgrades: Understanding your current trim level helps you plan informed upgrades. For example, upgrading the audio system in a base trim might require more extensive wiring than upgrading the same system in a higher trim that already has some premium audio components.
- Repair and Maintenance: Some diagnostic procedures and repair steps can differ slightly based on trim level, particularly regarding electronic components and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
Essentially, knowing your car's trim level is like knowing its DNA. It provides crucial context for almost everything you do with it.
Key Specs and Main Parts Differentiation by Trim
Trim levels are identified by specific designations – often a combination of letters and numbers (e.g., LX, EX, Limited, Sport, etc.). These designations vary widely between manufacturers, so there's no universal standard. Here's a breakdown of common areas where trim levels differ:
Powertrain
While the basic engine might be the same across several trims, higher trims often offer more powerful engine options or upgraded transmissions. For instance, a base model might have a naturally aspirated 2.0L engine, while a higher trim offers a turbocharged 2.0L or even a V6.
Suspension and Brakes
Sportier trims often feature stiffer suspensions, larger brakes, and performance tires. These differences affect handling and stopping power. A base trim might have standard coil springs and dampers, while a higher trim could boast adaptive dampers or even air suspension.
Interior Features
This is where trim levels often show the most significant differences. Base trims might have cloth seats, manual climate control, and a basic audio system. Higher trims could offer leather seats, dual-zone automatic climate control, a premium sound system, and advanced infotainment features like navigation and a larger touchscreen.
Exterior Styling
Exterior differences can include different wheel designs, chrome trim, fog lights, sunroofs, and even different front and rear fascias. Sportier trims might have rear spoilers or ground effects.
Technology and Safety Features
Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) like lane departure warning, blind-spot monitoring, and adaptive cruise control are often reserved for higher trims. Similarly, features like keyless entry, push-button start, and remote start might only be available on specific trim levels.
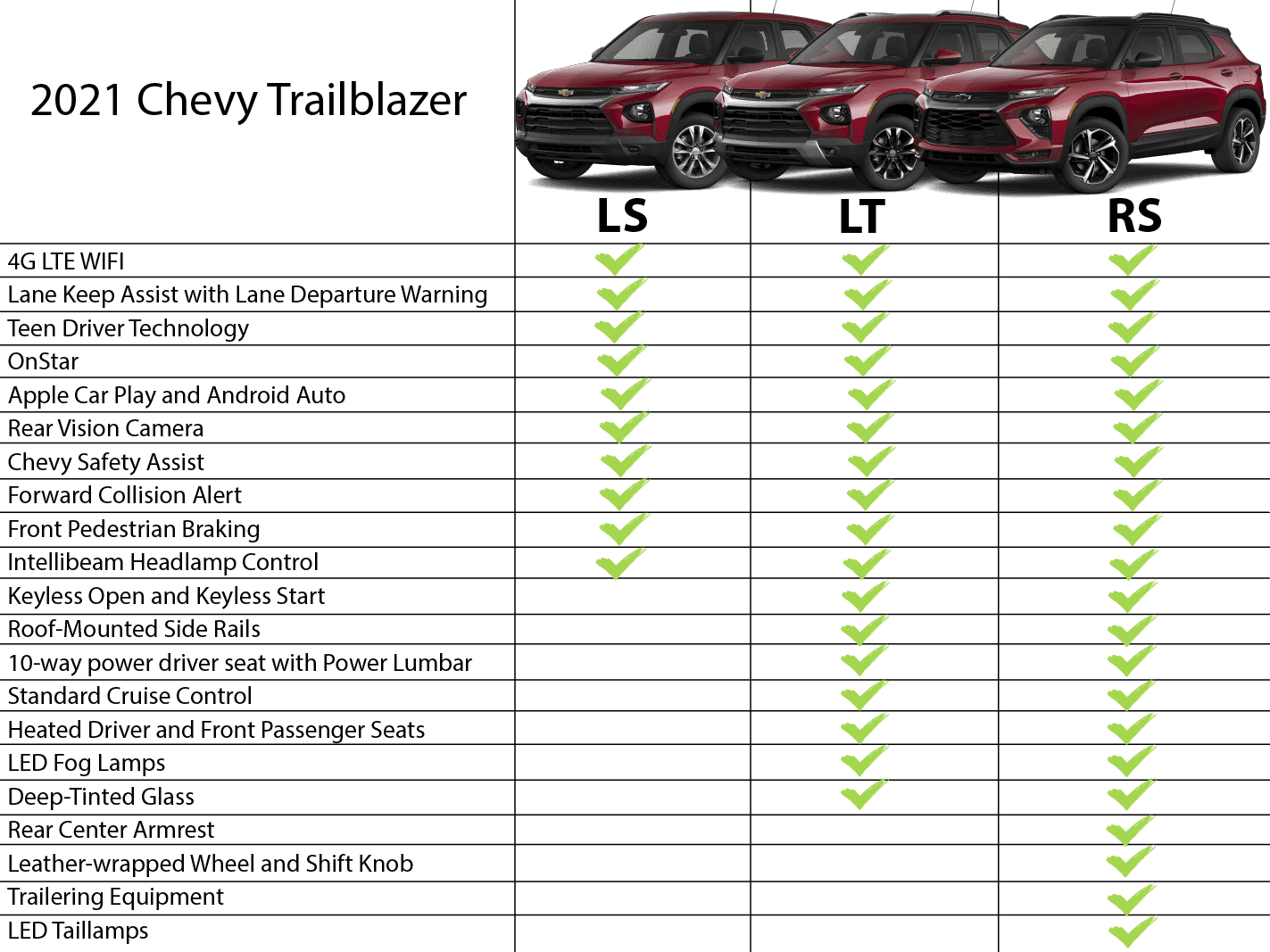
Example Table of Feature Differences
Let's illustrate with a hypothetical example, the "Acme Sedan":
| Feature | Base (LX) | Mid-Range (EX) | Top-Tier (Limited) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engine | 2.0L I4 | 2.0L I4 | 2.0L Turbo I4 |
| Wheels | 16" Steel | 17" Alloy | 18" Alloy |
| Seats | Cloth | Cloth with Leatherette Bolsters | Leather |
| Infotainment | 7" Touchscreen | 8" Touchscreen with Apple CarPlay/Android Auto | 10" Touchscreen with Navigation |
| ADAS | None | Blind-Spot Monitoring | Adaptive Cruise Control, Lane Keep Assist |
Symbols, Abbreviations and Jargon
Automotive documentation often uses specific abbreviations and jargon related to trim levels. Here are a few common ones:
- MSRP: Manufacturer's Suggested Retail Price – the base price before options and taxes. Varies greatly with trim.
- VIN: Vehicle Identification Number – a unique identifier for each vehicle. The VIN can be decoded to reveal the trim level and other specific details about the car's configuration.
- Packages/Options: Individual options or groups of options offered on top of the base trim level. These effectively create sub-trims.
- FWD/RWD/AWD: Front-Wheel Drive, Rear-Wheel Drive, All-Wheel Drive. The drivetrain configuration can vary between trim levels, especially on trucks and SUVs.
- Engine Codes: Specific codes that identify the exact engine model installed in the vehicle. These codes are crucial for sourcing the correct replacement parts.
How It Works
Manufacturers create trim levels to cater to a wider range of customers with different budgets and preferences. By offering several trim levels, they can attract buyers who are looking for a basic, affordable vehicle, as well as those who are willing to pay more for added features and luxury. The trim levels are strategically priced to maximize sales volume and market share.
Real-World Use – Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are a few scenarios where understanding trim levels can help with troubleshooting:
- "My heated seats aren't working!" First, verify that your trim level actually includes heated seats. It might seem obvious, but double-check!
- "My car won't start after installing a new aftermarket stereo." Check the wiring diagrams specific to your trim level. Higher trims with premium audio systems might have more complex wiring that needs to be bypassed or properly integrated with the aftermarket unit.
- "I ordered a replacement suspension spring, but it's too short!" Ensure you ordered the correct spring for your specific trim level and drivetrain. Sportier trims often have stiffer and shorter springs.
Safety – Highlight Risky Components
Working on certain components can be particularly risky, especially on higher trim levels with advanced features:
- Airbags: Deactivating and working around airbags requires specialized knowledge and tools. Incorrect handling can lead to accidental deployment and serious injury. Always disconnect the battery and follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully.
- High-Voltage Systems (Hybrid/Electric Vehicles): These systems contain potentially lethal voltages. Only qualified technicians should work on these systems. Identify if your trim level comes with a hybrid or electric drivetrain.
- ADAS Sensors: Sensors for blind-spot monitoring, lane departure warning, and adaptive cruise control are often located in bumpers and mirrors. Be careful not to damage these sensors during repairs or modifications, as they can be expensive to replace and require recalibration.
- Brake Systems with ABS/Traction Control: These systems can require specialized diagnostic tools and procedures. Improper bleeding of the brake lines can compromise the system's functionality. Remember that higher trims often have enhanced braking systems, such as larger rotors, and are more sensitive to improper maintenance.
Remember, if you're unsure about any repair or modification, it's always best to consult a qualified mechanic.
We have a detailed trim level guide available as a downloadable PDF. This guide includes comprehensive information on identifying trim levels, key feature differences, and troubleshooting tips. Download it to take your knowledge of vehicle trims to the next level.
