What Cars Have 5x4 5 Bolt Pattern
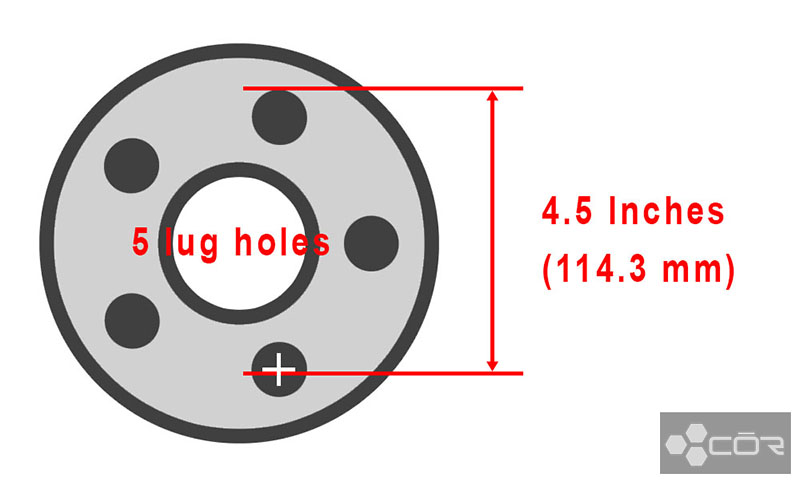
Let's dive into the world of wheel bolt patterns, specifically the 5x4.5" (or 5x114.3mm) configuration. Understanding this spec is crucial for a DIY mechanic or car enthusiast – whether you're replacing worn-out wheels, upgrading to aftermarket options, or simply trying to ensure your vehicle is safe and reliable. This isn't just about aesthetics; it's about safety and proper vehicle operation.
Why Bolt Patterns Matter
Bolt patterns are critical. They determine if a wheel will properly and safely mount to your vehicle's hub. Using the wrong bolt pattern can lead to:
- Wheel Instability: Wheels not sitting flush against the hub.
- Vibration: Uneven load distribution causing uncomfortable driving and potential damage to suspension components.
- Stud/Bolt Failure: Overstressing the studs or bolts, leading to catastrophic failure and wheel separation.
- Damage to Hub and Wheel: Mismatch can damage the hub flange and the wheel itself.
So, taking the time to understand and identify the correct bolt pattern is a worthwhile investment.
Key Specs and Main Parts
Let's break down the 5x4.5" (or 5x114.3mm) bolt pattern:
- 5: This indicates the number of studs or bolts used to secure the wheel to the hub. In this case, there are five.
- 4.5" (or 114.3mm): This is the bolt circle diameter (BCD). It represents the diameter of the imaginary circle that passes through the center of each of the five bolt holes. 4.5 inches is equivalent to 114.3 millimeters; both measurements refer to the same bolt pattern.
Important Components:
- Hub: The central part to which the wheel attaches. It contains the studs (or threaded holes for bolts).
- Studs (or Bolts): The fasteners that secure the wheel to the hub. Studs are permanently mounted on the hub, and lug nuts are tightened onto them. Bolts pass through the wheel and screw into threaded holes in the hub.
- Lug Nuts/Bolts: The hardware used to tighten the wheel to the hub. Lug nuts are used with studs, and lug bolts are used with hubs that have threaded holes.
- Wheel: The rotating component that provides contact with the road. It has corresponding holes that align with the hub's studs/bolts.
- Center Bore: The diameter of the hole in the center of the wheel. This should match or be slightly larger than the hub's center diameter. A mismatch can lead to vibration and wheel imbalance. Hub-centric rings can be used to correct minor size differences.
Common Vehicles with 5x4.5" Bolt Pattern
The 5x4.5" bolt pattern is incredibly common and found on a wide variety of vehicles. Here are some examples:
- Ford: Many Ford vehicles, especially older models and some modern ones, use this pattern. Examples include:
- Ford Mustang (1994-2014)
- Ford Explorer (some generations)
- Ford Ranger (some generations)
- Ford Crown Victoria
- Chrysler/Dodge/Jeep: This bolt pattern is prevalent in many Chrysler products.
- Jeep Cherokee (XJ)
- Jeep Wrangler (YJ, TJ)
- Dodge Dakota (some generations)
- Dodge Caravan/Grand Caravan (some generations)
- Chrysler Town & Country (some generations)
- Toyota: Certain Toyota models also utilize this pattern.
- Toyota Tacoma (6-lug models *do not* use this pattern, check for 5-lug versions)
- Toyota MR2 (some generations)
- Nissan/Infiniti: Some Nissan and Infiniti vehicles use the 5x4.5" bolt pattern.
- Nissan 240SX
- Infiniti G35 (sedan models)
Note: This is not an exhaustive list, and specific years and trims can vary. Always verify the bolt pattern of your vehicle before purchasing wheels.
How It Works
The principle is simple: the wheel's bolt holes must perfectly align with the studs (or bolt holes) on the hub. When the lug nuts (or bolts) are tightened, they clamp the wheel firmly against the hub, creating a friction fit that transmits torque from the hub to the wheel, allowing the vehicle to move.
The precise fit is crucial for several reasons:
- Load Distribution: Proper alignment ensures that the load is evenly distributed across all studs/bolts, preventing stress concentrations.
- Concentricity: The wheel must be perfectly centered on the hub to prevent vibrations and ensure smooth rotation.
- Shear Strength: The studs/bolts must be strong enough to withstand the shear forces generated during acceleration, braking, and cornering.
Real-World Use – Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some common problems you might encounter and how to address them:
- Difficulty Mounting the Wheel: If the wheel doesn't easily slide onto the studs, double-check the bolt pattern. If the pattern is correct, inspect the studs and wheel holes for damage or debris.
- Vibration After Wheel Installation: This could indicate a bent wheel, an improperly torqued lug nut, or a mismatch between the wheel's center bore and the hub's center diameter. Re-torque the lug nuts to the manufacturer's specification in a star pattern. Consider using hub-centric rings if the center bore is slightly too large.
- Stripped Studs/Bolts: Over-tightening lug nuts/bolts is a common cause of stripped threads. Replace damaged studs or bolts immediately. When installing new studs, use a stud installer tool to avoid damaging the threads.
- Lug Nut Loosening: Always re-torque lug nuts after driving a short distance (e.g., 50-100 miles) after a wheel change. This allows the wheel to seat properly against the hub.
Safety – Highlight Risky Components
The wheel mounting system is a critical safety component. Here are some potential hazards:
- Over-Torquing Lug Nuts/Bolts: This can stretch or break the studs/bolts, leading to wheel separation. Always use a torque wrench and tighten to the manufacturer's specified torque.
- Under-Torquing Lug Nuts/Bolts: This can allow the wheel to loosen, leading to vibration and eventual wheel separation.
- Using Incorrect Lug Nuts/Bolts: Different wheel types may require specific lug nut styles (e.g., conical, ball seat, flat seat). Using the wrong type can damage the wheel and prevent proper clamping.
- Damaged Studs/Bolts: Replace any studs or bolts that are bent, corroded, or have damaged threads.
- Wheel Spacers: While wheel spacers can be used to improve appearance or clear suspension components, they can also introduce stress and increase the risk of stud failure, especially if low-quality spacers are used. Use high-quality, hub-centric spacers and ensure they are properly installed. Extended studs may be required.
Never take shortcuts when it comes to wheel safety. If you're unsure about any aspect of wheel installation, consult a qualified mechanic.
Diagram File Availability
For a more detailed visual representation, we have a downloadable diagram illustrating the 5x4.5" bolt pattern, including key dimensions and measurement techniques. It's a handy reference tool for your garage. Contact us, and we can provide you with the diagram file.
By understanding the intricacies of wheel bolt patterns, you can ensure your vehicle's safety and performance, whether you're performing routine maintenance or upgrading your wheels. Remember, safety is paramount. When in doubt, consult a professional.
