What Does A Bursa Look Like
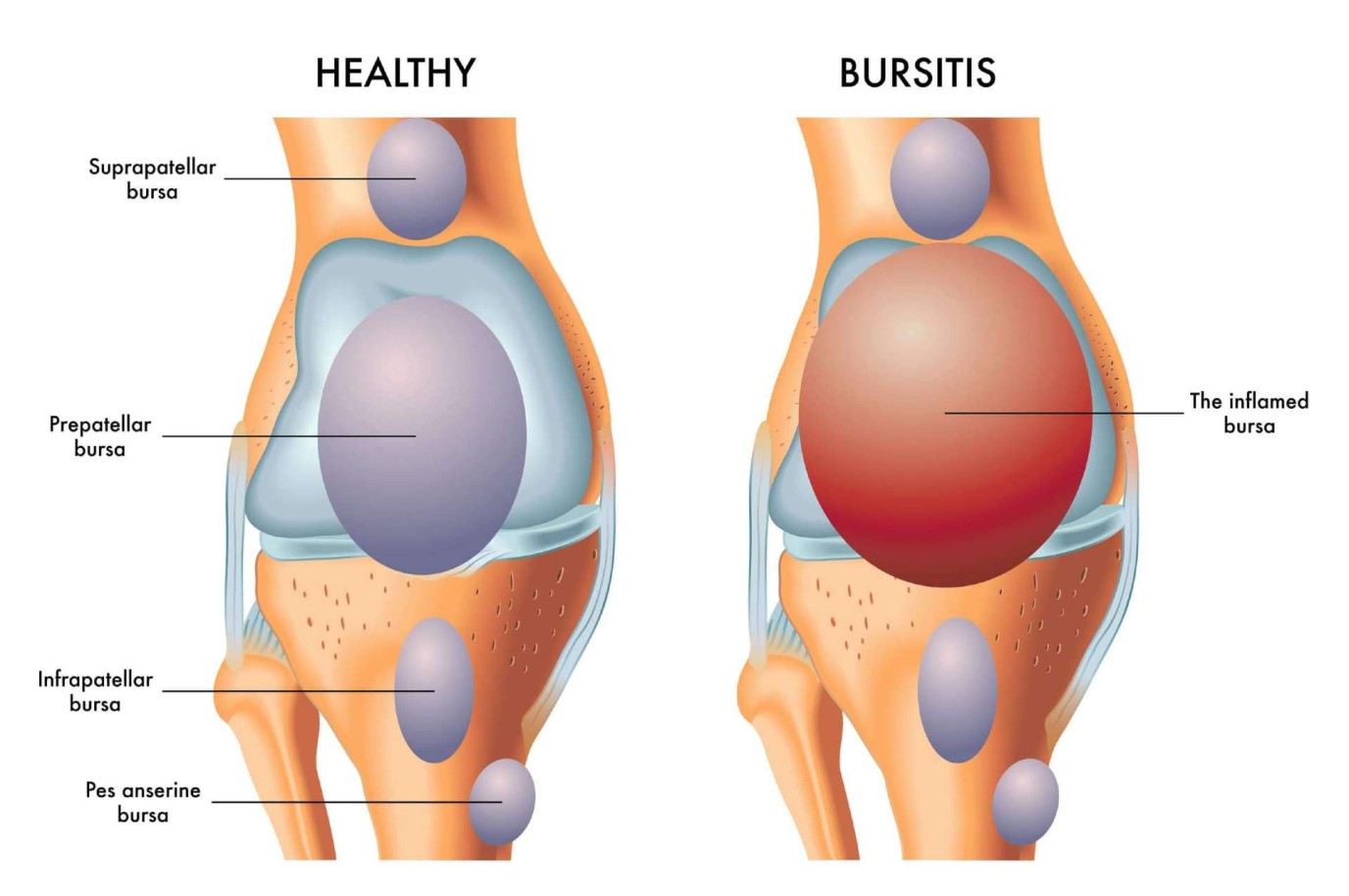
Alright, let's dive into the anatomy of a bursa. No, we're not talking about stock market data; in automotive terms, a bursa is a crucial component, especially when dealing with suspension and drivetrain systems. Understanding what a bursa looks like, its function, and potential issues is incredibly valuable, whether you're tackling a suspension rebuild, diagnosing a mysterious clunk, or simply expanding your automotive knowledge.
Why This Matters: Diagnosing and Repairing Problems
Having a mental image, or better yet, a detailed diagram, of a bursa is essential for several reasons:
- Accurate Diagnosis: Many suspension and joint noises can be traced back to damaged or dry bursae. Knowing their location and expected condition allows for quicker and more accurate diagnoses.
- Proper Repair and Replacement: Identifying the correct bursa type and size is crucial for a successful repair. Using the wrong replacement part can lead to further damage and compromise safety.
- Preventative Maintenance: Checking the condition of bursae during routine maintenance can help prevent costly repairs down the road. Catching a tear or leak early allows you to address the issue before it escalates.
- Modifications and Upgrades: When modifying your suspension or drivetrain, understanding the role of bursae is essential for ensuring proper function and avoiding unexpected problems.
Key Specs and Main Parts of a Bursa
A bursa (plural: bursae) is essentially a small, fluid-filled sac lined by synovial membrane. Its primary function is to reduce friction between bones, tendons, and muscles near joints. Think of it as a natural lubricant and shock absorber.
Here's a breakdown of the key components:
- Synovial Membrane: This inner lining secretes synovial fluid.
- Synovial Fluid: A viscous, clear fluid that lubricates the bursa and reduces friction. Its composition is similar to joint fluid.
- Bursal Wall: The outer layer of the bursa, typically composed of connective tissue. This provides structural integrity.
- Location (variable): Bursae are located near joints, between tendons and bones, or between muscles. Common locations include the shoulder, hip, knee, and elbow. In automotive applications, they are often found near suspension joints and other moving parts.
While the basic structure is consistent, the size and shape of bursae vary significantly depending on their location and function. Some bursae are quite small and discreet, while others are larger and more prominent. In the automotive world, you often find "bursae-like" components, sometimes referred to as boots, protecting CV joints and other articulation points. These aren't technically bursae in the biological sense, but they serve a similar purpose of protecting moving parts and preventing debris from entering.
Symbols and Diagram Conventions
When looking at a schematic diagram of a suspension or drivetrain system, bursae (or similar protective boots) are typically represented as follows:
- Outline: A simple curved or rounded shape that represents the bursa. The outline may be solid or dashed, depending on the diagram's style.
- Fill: Often shaded or colored to indicate the presence of fluid or material within the bursa. Different colors might denote different types of fluid or grease.
- Lines: Solid lines typically represent the outer wall of the bursa. Dashed lines may indicate internal structures or the interface between the bursa and surrounding components.
- Arrows: Arrows may be used to indicate the direction of movement or force acting on the bursa.
- Labels: Bursae are usually labeled with abbreviations or acronyms, such as "Bursa," "Boot," or "CV Boot." The label may also include a number or code to identify the specific location of the bursa in the system.
How It Works: Reducing Friction and Protecting Joints
The bursa's primary function is to reduce friction between moving parts. The synovial fluid within the bursa acts as a lubricant, allowing tendons, muscles, and bones to slide smoothly past each other. This prevents wear and tear on the joint and reduces the risk of injury.
In automotive applications, the "bursae-like" boots protecting CV joints and ball joints serve a similar purpose. They prevent dirt, water, and other contaminants from entering the joint, which would cause excessive wear and premature failure. The boot also retains grease within the joint, ensuring proper lubrication.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some basic troubleshooting tips related to bursae and protective boots in automotive systems:
- Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect the boots for signs of damage, such as cracks, tears, or leaks. Pay close attention to areas where the boot is flexed or stretched.
- Grease Leaks: If you notice grease leaking from a boot, it's a sign that the boot is damaged and needs to be replaced. Ignoring this can lead to rapid joint wear and failure.
- Unusual Noises: Clicking, popping, or grinding noises from the suspension or drivetrain can indicate a damaged or dry joint. This may be caused by a torn boot that has allowed contaminants to enter the joint.
- Excessive Play: Excessive play or looseness in a joint can also be a sign of a damaged boot or joint.
For example, a common issue is a torn CV boot. You'll notice grease splattered around the wheel well and a clicking noise when turning. This indicates the CV joint is no longer properly lubricated and is likely ingesting dirt and debris. The solution is to replace the CV boot (or the entire CV axle, depending on the severity of the damage).
Safety: Handling Risky Components
While bursae themselves aren't inherently dangerous, the components they protect often are. When working on suspension or drivetrain systems, always take the following precautions:
- Support the Vehicle Properly: Use jack stands to support the vehicle before working underneath. Never rely solely on a jack.
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative battery terminal to prevent accidental electrical shocks.
- Wear Safety Glasses: Protect your eyes from debris.
- Use Gloves: Protect your hands from grease, oil, and sharp edges.
- Be Aware of Spring Tension: Suspension springs can store a significant amount of energy. Use appropriate spring compressors when working on suspension components.
- Properly Torque Fasteners: Use a torque wrench to ensure that all fasteners are tightened to the correct specifications.
Specifically regarding CV Joints, be careful when handling them as they can be covered in old, potentially contaminated grease. Dispose of the old boot and grease responsibly.
Understanding the function and location of bursae, and related components like CV boots, is crucial for maintaining and repairing your vehicle's suspension and drivetrain systems. By performing regular inspections and addressing problems promptly, you can prevent costly repairs and ensure the safe operation of your vehicle.
To further aid in your understanding, we have a detailed diagram available for download. This diagram illustrates the location and structure of typical automotive bursae and related protective components. With it, you will be able to effectively identify and address problems in your vehicle.
