What Does Check Abs System Mean
Alright, let's dive into the "Check ABS System" light and what it really means. Seeing that light illuminate on your dashboard can be a bit unsettling, especially when you're not sure what's causing it. This guide is aimed at helping you, the experienced DIYer, understand the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS), interpret potential issues, and perform some basic troubleshooting. We'll cover the system's purpose, components, how it functions, and some safety considerations. Think of this as a detailed look under the hood – or, in this case, under the brake lines – so you can approach ABS problems with confidence.
Purpose of Understanding the ABS System
Why bother understanding the ABS system? Several reasons. First, it's about safety. ABS prevents wheel lock-up during hard braking, allowing you to maintain steering control in emergency situations. Knowing how it works ensures you can recognize and address problems promptly. Second, it empowers you to perform basic diagnostics and repairs, potentially saving money on mechanic fees. Third, whether you're modifying your vehicle or simply performing routine maintenance, understanding the ABS system allows you to work safely and avoid damaging critical components. Knowing how the system works helps you better understand what's going on when that pesky light comes on, saving you from potentially costly repairs or worse, a dangerous driving situation.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the ABS System
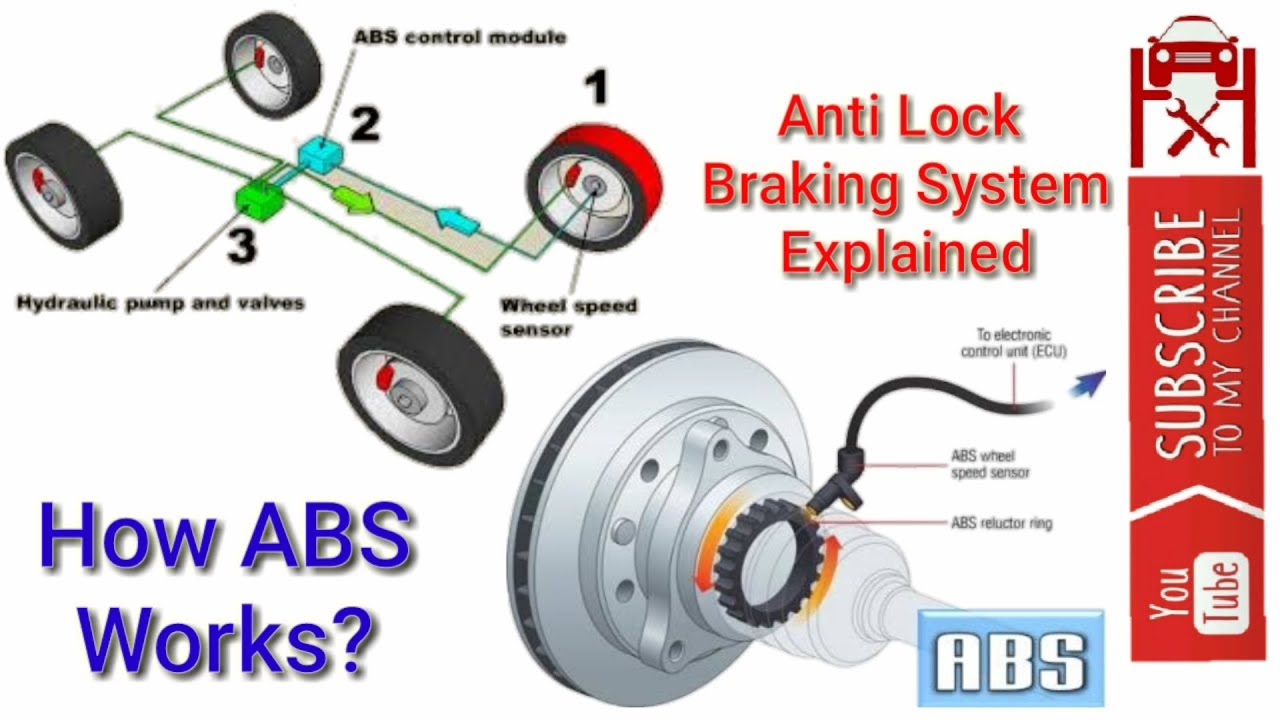
The ABS system, while seemingly complex, relies on a few key components working in harmony. Here's a breakdown:
- Wheel Speed Sensors: These are critical. Each wheel has a sensor (usually inductive or Hall-effect) that monitors its rotational speed. The sensors send a signal to the ABS control module. A faulty sensor is a common cause of the ABS light.
- ABS Control Module (ECU): This is the brains of the operation. It receives data from the wheel speed sensors, determines if a wheel is locking up, and controls the hydraulic unit to adjust brake pressure.
- Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU): This unit contains valves and a pump that modulate brake pressure to each wheel individually. It's the actuator of the system, responding to commands from the ECU.
- Brake Lines and Hydraulics: Standard brake lines are used to deliver brake fluid from the master cylinder to the wheels. The HCU intercepts these lines to provide ABS functionality.
- Warning Light: The "Check ABS System" light on your dashboard indicates a detected fault in the system.
Some advanced systems may include additional features like Electronic Brakeforce Distribution (EBD) and Traction Control (TCS), which are often integrated into the ABS control module.
Understanding ABS System Symbols and Diagrams
While we don't have a diagram to visually demonstrate, let's talk about how they are usually presented and how to read one. If you get hold of a diagram (and we have the file available for you to download later), here's what to look for:
- Lines: Solid lines typically represent hydraulic lines, while dashed lines often represent electrical wiring.
- Colors: Wire colors are usually indicated on the diagram (e.g., BLK for black, RED for red). Hydraulic lines may be differentiated by color to indicate pressure levels or fluid flow direction.
- Icons: Specific components, like the wheel speed sensors, ABS control module, and hydraulic unit, are represented by standardized symbols. Refer to the diagram's legend for clarification. Common symbols include rectangles for electronic modules, circles for sensors, and valve symbols for the HCU.
- Connectors: Electrical connectors are often depicted as small rectangles with numbers indicating the pin assignments. This is critical for troubleshooting wiring issues.
Pay close attention to the ground connections (usually indicated by a grounding symbol), as a poor ground can cause intermittent ABS problems.
How the ABS System Works
The ABS system's primary function is to prevent wheel lock-up during braking. Here's how it achieves this:
- Monitoring Wheel Speed: Wheel speed sensors constantly monitor the rotational speed of each wheel. This data is transmitted to the ABS control module.
- Detecting Lock-Up: The ABS control module analyzes the wheel speed data. If it detects that a wheel is decelerating rapidly (a sign of impending lock-up), it intervenes.
- Modulating Brake Pressure: The ABS control module signals the hydraulic control unit (HCU) to reduce brake pressure to the affected wheel. The HCU uses valves to isolate the wheel from the master cylinder and then either hold or release pressure as needed.
- Repeating the Cycle: This process of pressure modulation occurs rapidly and repeatedly (several times per second). You may feel a pulsating sensation in the brake pedal during ABS activation, which is normal.
- Restoring Normal Braking: Once the wheel speed stabilizes (i.e., the wheel is no longer at risk of locking up), the ABS control module restores normal braking function.
Essentially, the ABS system acts as an electronic pump, rapidly applying and releasing the brakes to maintain optimal traction.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
When the "Check ABS System" light illuminates, don't panic. Here are some basic troubleshooting steps you can take:
- Check Brake Fluid Level: Low brake fluid can sometimes trigger the ABS light. Top it off and see if the light goes out (but be aware of potential leaks).
- Inspect Wheel Speed Sensors: Visually inspect the wheel speed sensors and their wiring harnesses for damage or corrosion. Clean the sensors and connectors with electrical contact cleaner.
- Check ABS Fuses: Locate the ABS fuse(s) in your vehicle's fuse box and check if they are blown. Replace any blown fuses with the correct amperage rating.
- Scan for Trouble Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner that can read ABS codes. This will provide specific information about the fault detected by the ABS control module. Common codes relate to wheel speed sensors, hydraulic unit malfunctions, or control module failures.
- Check the Tone Rings: The tone rings are toothed wheels located on the axles, which the wheel speed sensors use to determine wheel speed. Damage to these rings can cause the ABS light to illuminate. Visually inspect the tone rings for cracks or damage.
Important Note: ABS troubleshooting can sometimes require specialized tools and diagnostic equipment. If you're not comfortable performing these steps, it's best to consult a qualified mechanic.
For example, a common code might be "C0035," indicating a fault with the front right wheel speed sensor. After confirming the code, you would inspect the sensor, its wiring, and the tone ring for damage. Replacing the sensor often resolves this issue.
Safety Considerations
Working on the ABS system requires caution. Here are some important safety points:
- Brake Fluid: Brake fluid is corrosive and can damage painted surfaces. Wear gloves and eye protection when handling it.
- Electrical Components: Always disconnect the battery before working on electrical components of the ABS system.
- Hydraulic Pressure: Be aware that the hydraulic control unit contains pressurized brake fluid. Depressurize the system according to the manufacturer's instructions before disconnecting any hydraulic lines. Improper handling can lead to serious injury.
- Torque Specifications: When reassembling components, use the correct torque specifications to ensure proper function and prevent damage.
Warning: Never attempt to disable or bypass the ABS system. Doing so can significantly reduce your vehicle's braking performance and compromise your safety. If you are unsure about any aspect of ABS system repair, seek professional assistance.
Remember, even experienced DIYers should exercise caution and prioritize safety when working on critical systems like ABS.
We have the ABS system diagram we referred to available for download. Please contact us through [link to contact page or email address] to request the file.
