What Does Cvt Mean In Cars
So, you're diving deeper into the world of automotive mechanics and have stumbled upon the term "CVT." Good on you! Understanding a Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT) is crucial in today's automotive landscape, as they're increasingly common. This article will provide a detailed breakdown of what a CVT is, how it works, its key components, troubleshooting tips, and important safety considerations. Think of this as your expert mechanic friend explaining it all, without the greasy overalls (unless you’re actually in the garage, of course!). This information is valuable whether you're diagnosing a weird noise, planning a repair, or just expanding your automotive knowledge.
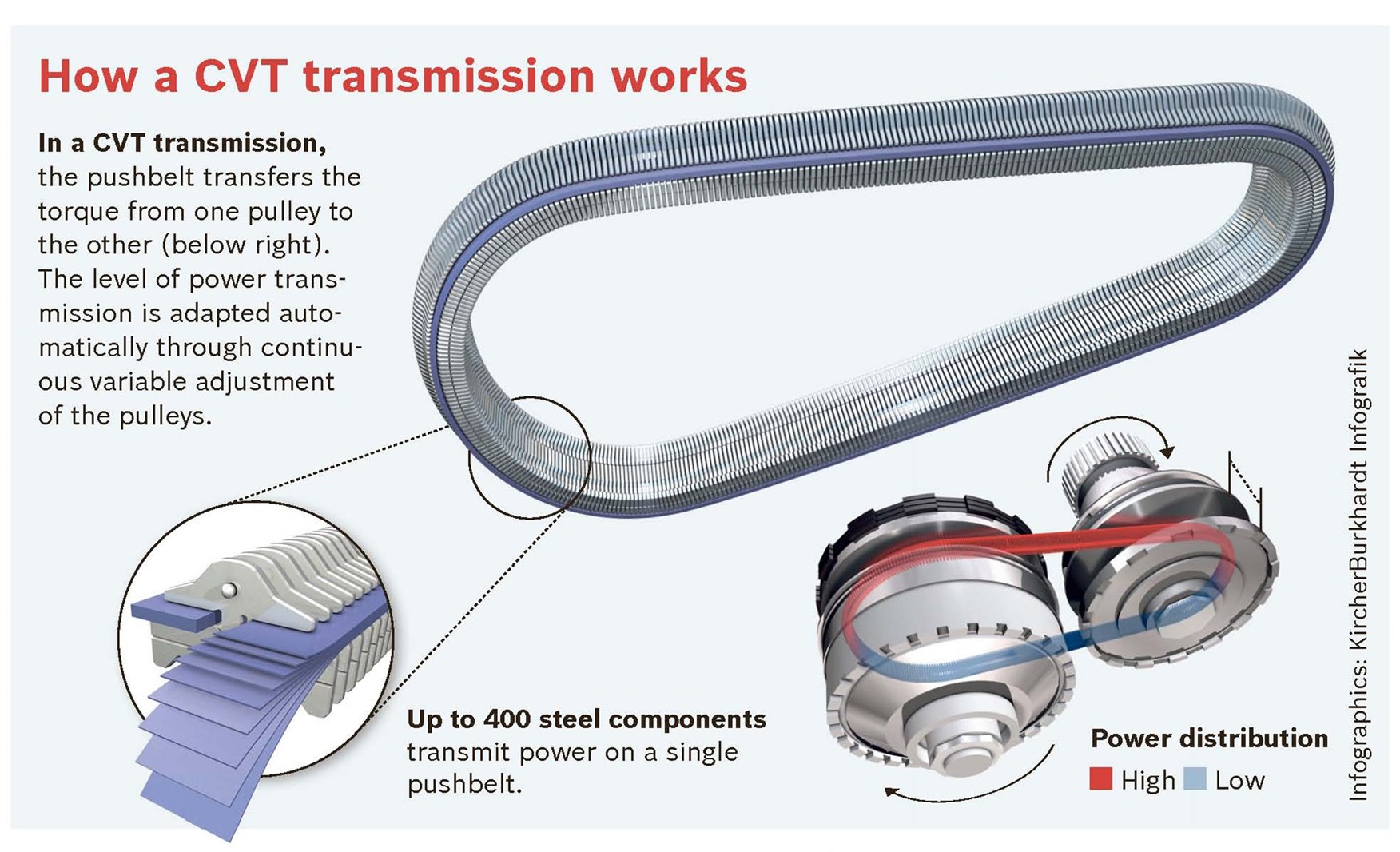
Key Specs and Main Parts of a CVT
Unlike traditional automatic transmissions with fixed gears, a CVT uses a system of pulleys and a belt (or chain) to provide an infinite range of gear ratios within its design limitations. This allows the engine to operate at its most efficient RPM, regardless of vehicle speed. Let's break down the main parts:
- Input Pulley (Primary Pulley): Connected to the engine's crankshaft. This pulley's diameter is adjusted by hydraulic pressure, changing the gear ratio.
- Output Pulley (Secondary Pulley): Connected to the differential and ultimately the wheels. Like the input pulley, its diameter is also adjustable.
- Belt or Chain: A strong, flexible band that connects the two pulleys. This belt transmits the power between the input and output pulleys. The material and construction of the belt are critical to the CVT's performance and longevity. Often made of high-strength steel or a composite material.
- Hydraulic Control System: This system uses hydraulic pressure to adjust the diameters of the pulleys. Valves, sensors, and a sophisticated transmission control unit (TCU) manage the hydraulic pressure based on engine load, vehicle speed, and driver input.
- Transmission Control Unit (TCU): The brain of the CVT. It receives data from various sensors (engine speed, vehicle speed, throttle position, etc.) and controls the hydraulic system to optimize the gear ratio.
- Valve Body: Contains a series of valves that control the flow of hydraulic fluid to the pulleys. These valves are often electronically controlled solenoids.
- Fluid Pump: Provides the necessary hydraulic pressure for the CVT to function.
- Fluid Reservoir/Pan: Holds the CVT fluid, which lubricates and cools the internal components.
How a CVT Works
The beauty of a CVT lies in its simplicity and efficiency. Imagine two cones facing each other, connected by a belt. By moving the belt up and down the cones, you effectively change the gear ratio. A CVT essentially does the same thing, but with more sophisticated, hydraulically controlled pulleys. Here's a step-by-step breakdown:
- The engine provides power to the input pulley.
- The TCU monitors engine load, vehicle speed, and driver input.
- Based on this data, the TCU signals the hydraulic control system to adjust the diameters of the input and output pulleys.
- For example, when accelerating from a stop, the input pulley is set to its smallest diameter and the output pulley to its largest diameter. This creates a low gear ratio, providing high torque for initial acceleration.
- As the vehicle gains speed, the TCU gradually increases the diameter of the input pulley and decreases the diameter of the output pulley. This effectively "shifts" to a higher gear ratio, allowing the engine to operate at a more efficient RPM for cruising speed.
- This continuous adjustment of the pulley diameters allows the CVT to provide an infinite number of gear ratios within its range.
Real-World Use – Basic Troubleshooting Tips
CVTs are generally reliable, but they can experience issues. Here are some common problems and basic troubleshooting tips:
- Slipping: If the engine RPM increases without a corresponding increase in vehicle speed, the CVT may be slipping. This could be due to low fluid level, worn belt/chain, or malfunctioning hydraulic components. First, check the CVT fluid level. If it's low, top it off with the correct type of CVT fluid. If the problem persists, it's best to consult a professional.
- Jerky Acceleration: This can be caused by a faulty sensor, a malfunctioning valve in the valve body, or problems with the TCU. A scan tool can help identify any error codes related to the transmission.
- Unusual Noises: Whining or grinding noises can indicate bearing wear or internal damage. These noises often require professional diagnosis and repair.
- Delayed Engagement: If there's a noticeable delay between shifting into drive or reverse and the vehicle actually moving, it could be due to low fluid pressure or internal component failure.
Important Note: CVT fluid is *very* specific. Using the wrong type of fluid can cause serious damage to the transmission. Always consult your vehicle's owner's manual to determine the correct CVT fluid.
Safety – Highlight Risky Components
Working on a CVT involves certain safety risks. Here are some components to be extra careful around:
- High-Pressure Hydraulic System: The hydraulic system operates at high pressure, which can be dangerous if mishandled. Always relieve pressure before disconnecting any hydraulic lines.
- Hot Fluid: CVT fluid can get very hot during operation. Allow the transmission to cool down completely before draining or working on it.
- Moving Parts: Never operate the vehicle with the transmission exposed or with any covers removed. The moving parts can cause serious injury.
- Electrical Components: The TCU and other electrical components can be sensitive to static electricity. Use proper grounding techniques when working on these components.
Warning: CVT repair can be complex. If you're not comfortable working on your own vehicle, it's best to consult a qualified technician. Improper repairs can cause further damage and compromise the safety of your vehicle.
This article provides a foundational understanding of CVT technology. Keep learning, stay safe, and enjoy the journey into the world of automotive mechanics!
We have a detailed CVT diagram available for download. This diagram provides a visual representation of the CVT's components and their relationships. It can be a valuable tool for understanding the CVT's operation and troubleshooting potential problems. Contact us for access to the file.
