What Is A Car Drive Belt
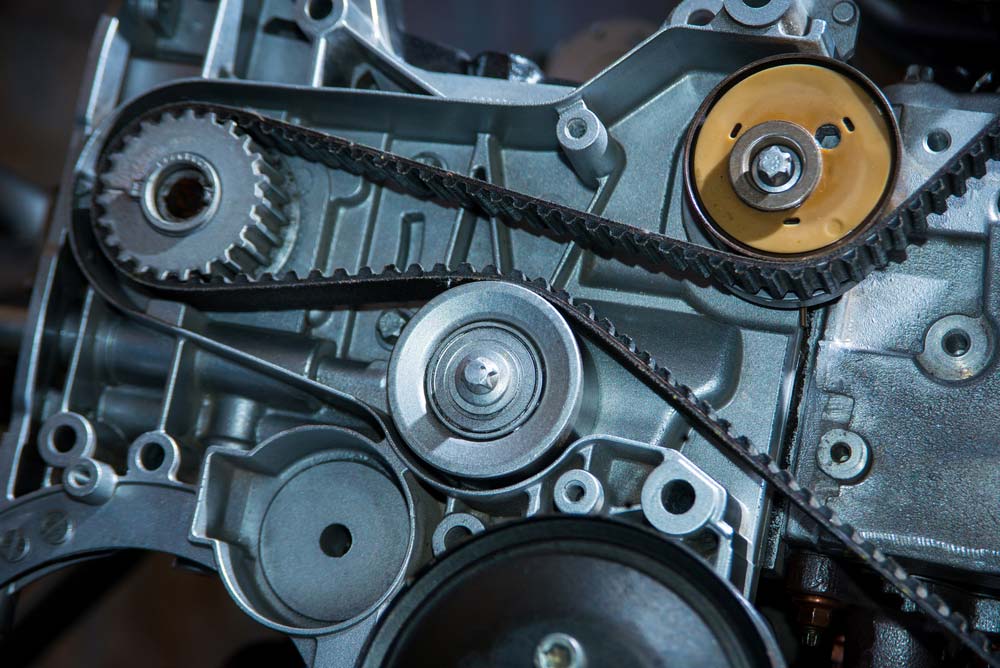
Hey there, fellow gearheads! Today, we're diving deep into the heart of your engine to dissect a component often overlooked but absolutely crucial: the drive belt (sometimes called a serpentine belt). This article is for you – the intermediate DIYer, the aspiring modder, and the mechanically curious – looking to expand your knowledge and maybe even tackle some repairs yourself. Having a solid understanding of the drive belt system empowers you to diagnose issues, perform preventative maintenance, and ultimately, keep your ride running smoothly. We'll cover the purpose, key specs, how it works, troubleshooting, and some essential safety tips. Plus, we've got a detailed diagram of a typical drive belt setup available for you to download – more on that later!
Purpose: Why Understand the Drive Belt?
Think of the drive belt as the unsung hero of your engine. It's a seemingly simple rubber belt, but it's responsible for powering several vital accessories that keep your car functioning correctly. The primary reason to understand the drive belt system is for preventative maintenance and timely repairs. A snapped drive belt can leave you stranded, and it often takes out other components with it. Knowing the warning signs – like cracks, fraying, or squealing – allows you to replace the belt before disaster strikes. Furthermore, if you're planning on upgrading or modifying components like the alternator or power steering pump, you'll need to understand the drive belt's routing and tensioning to ensure proper fit and function. This knowledge is also invaluable when diagnosing problems like a dead battery (could be an alternator not being powered by the belt) or stiff steering (power steering pump issue).
Key Specs and Main Parts
The drive belt system isn't just the belt itself. Here are the main players:
- Drive Belt (Serpentine Belt): The main event! Typically made of reinforced rubber compounds designed to withstand high temperatures, constant flexing, and significant tension. These belts come in various lengths and widths, specific to your vehicle's engine and accessory configuration.
- Crankshaft Pulley: This pulley is directly attached to the crankshaft and driven by the engine's rotation. It's the driving force behind the entire drive belt system.
- Alternator Pulley: Driven by the belt, the alternator generates electricity to charge the battery and power the car's electrical system.
- Power Steering Pump Pulley: This pulley drives the power steering pump, which provides hydraulic assistance to make steering easier.
- Air Conditioning Compressor Pulley: Powers the air conditioning compressor, responsible for cooling the cabin.
- Idler Pulley: Smooth, non-powered pulleys used to guide the belt around the various components and maintain proper wrap angle on other pulleys. They also help prevent belt flutter.
- Tensioner Pulley: A spring-loaded pulley that automatically maintains the correct tension on the drive belt. Crucial for proper operation and belt longevity. A failing tensioner is a common cause of belt noise and premature failure.
- Water Pump Pulley: (Sometimes driven by the drive belt) Circulates coolant throughout the engine to prevent overheating. Note that some vehicles have water pumps driven by the timing belt instead.
Key specifications you might encounter include belt length (measured in inches or millimeters), belt width, and the number of ribs (the V-shaped grooves on the belt that grip the pulleys). These specifications are critical when selecting a replacement belt. Always consult your vehicle's service manual or a reputable parts supplier to ensure you get the correct belt.
Symbols: Interpreting the Drive Belt Diagram
Understanding the diagram is key to working on the system. Here's a breakdown of common symbols:
- Solid Lines: Represent the actual drive belt path around the pulleys. Follow these lines carefully when routing a new belt.
- Dashed Lines: May indicate the "backside" of the belt contacting a pulley (when the smooth side of the belt is used for driving a particular accessory) or alternative routing options.
- Arrows: Indicate the direction of rotation of each pulley. This is important for understanding how the belt is driven and how each accessory functions.
- Icons/Labels: Pulleys are typically labeled with abbreviations such as ALT (alternator), P/S (power steering), A/C (air conditioning), CRANK (crankshaft), IDLER, and TENSIONER.
- Colors: While not always present, some diagrams use colors to differentiate between different sections of the belt or to highlight specific components.
Pay close attention to the routing diagram! Incorrect routing can cause the belt to slip, damage accessories, or even break. Before removing the old belt, take a picture or make a sketch of its routing to ensure you can reinstall the new belt correctly.
How It Works
The magic starts at the crankshaft. As the engine turns, the crankshaft pulley spins, driving the drive belt. The belt, under tension maintained by the tensioner pulley, transfers this rotational force to all the other pulleys connected to essential accessories. This coordinated rotation powers the alternator to charge the battery, the power steering pump for effortless steering, the air conditioning compressor to keep you cool, and (sometimes) the water pump to regulate engine temperature. Without a properly functioning drive belt, these accessories would grind to a halt, leaving you stranded or severely impacting your driving experience.
The tensioner pulley plays a vital role. It uses a spring to maintain consistent tension on the belt, preventing slippage and ensuring efficient power transfer. Over time, the tensioner's spring can weaken, leading to belt slippage and noise. A worn tensioner can also cause the belt to vibrate excessively, shortening its lifespan and potentially damaging other components.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are a few common drive belt problems and how to diagnose them:
- Squealing Noise: Often indicates a slipping belt. Could be due to a worn belt, a loose tensioner, or oil contamination on the belt or pulleys. Inspect the belt for cracks, fraying, or glazing. Check the tensioner for smooth operation and proper tension. Clean the belt and pulleys with a degreaser if necessary.
- Cracked or Frayed Belt: Sign of an aging or damaged belt. Replace the belt immediately. Also, inspect the pulleys for any signs of damage or misalignment that may be contributing to the belt wear.
- Belt Slippage: Can cause dimming headlights, difficulty steering, or poor air conditioning performance. Check the belt tension and condition. A slipping belt may also indicate a failing accessory, such as a seizing alternator.
- Visible Damage to Pulleys: Damage to pulleys may mean they should be replaced. A damaged pulley will quickly destroy a new belt.
Before starting any troubleshooting, always consult your vehicle's service manual for specific instructions and torque specifications.
Safety: Handling Risky Components
Working around the drive belt system can be hazardous. Here are some crucial safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any part of the drive belt system, disconnect the negative battery cable to prevent accidental starting of the engine.
- Hot Engine: Never work on the drive belt system when the engine is hot. Allow the engine to cool completely before starting any repairs.
- Moving Parts: Keep your hands, hair, and clothing clear of the drive belt and pulleys when the engine is running. A spinning drive belt can cause serious injury.
- Proper Tools: Use the correct tools for the job. A belt tensioner tool is essential for releasing the tension on the belt during removal and installation.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris and flying particles.
The rotating components of the drive belt system operate at high speeds and can cause severe injury if contacted while the engine is running. Always exercise caution and follow safety guidelines when working on this system.
So there you have it – a comprehensive overview of the car drive belt system. By understanding its purpose, components, and operation, you'll be well-equipped to diagnose problems, perform preventative maintenance, and keep your engine humming along smoothly. And as promised, we have a detailed diagram of a typical drive belt setup available for you. Just [link to download] download it for a handy reference during your next project. Good luck, and happy wrenching!
