What Is A Subaru Cvt Transmission
So, you want to get under the skin of your Subaru's Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT), huh? Good on you. Understanding this vital component is key for everything from basic maintenance and troubleshooting to more advanced modifications. This isn't just about changing the fluid; it's about grasping the principles behind how this seemingly simple gearbox delivers power to your wheels. We'll break down the key specs, internal workings, and even offer some real-world troubleshooting tips. Plus, we have a detailed diagram available for download (link below) that will serve as your visual guide. Let's dive in.
Purpose: Why Understand Your Subaru CVT?
Why bother learning about the CVT? For several reasons:
- Informed Maintenance: Knowing the inner workings helps you understand the "why" behind maintenance intervals and procedures, leading to better preventative care.
- Troubleshooting: When your Subaru acts up, understanding the CVT's function will help you diagnose the problem accurately, saving time and money. No more blindly replacing parts!
- Modification Awareness: Planning to tune your engine or increase power? Knowing the CVT's limitations is crucial to avoid damage. You need to know the torque limits of the transmission to avoid expensive repairs.
- Repair Insights: While rebuilding a CVT is often best left to specialists, understanding its construction allows you to discuss repairs intelligently with your mechanic and make informed decisions.
Key Specs and Main Parts
Subaru CVTs, like those found in many Impreza, Forester, Outback, and Legacy models, aren't all created equal. They vary in torque capacity, gear ratios, and even internal components depending on the engine and model year. However, the fundamental principles remain the same.
Key specs to consider include:
- Model Designation: Look for the specific CVT model code (e.g., TR580, TR690). This is crucial for finding compatible parts and service information.
- Torque Capacity: This indicates the maximum engine torque the CVT can reliably handle. Exceeding this limit can lead to premature failure.
- Gear Ratio Range: The range from the lowest (highest numerical value) to the highest gear ratio. This determines acceleration and fuel economy.
- Fluid Type: Use the correct CVT fluid specified by Subaru. Using the wrong fluid can cause serious damage.
Main parts of a Subaru CVT:
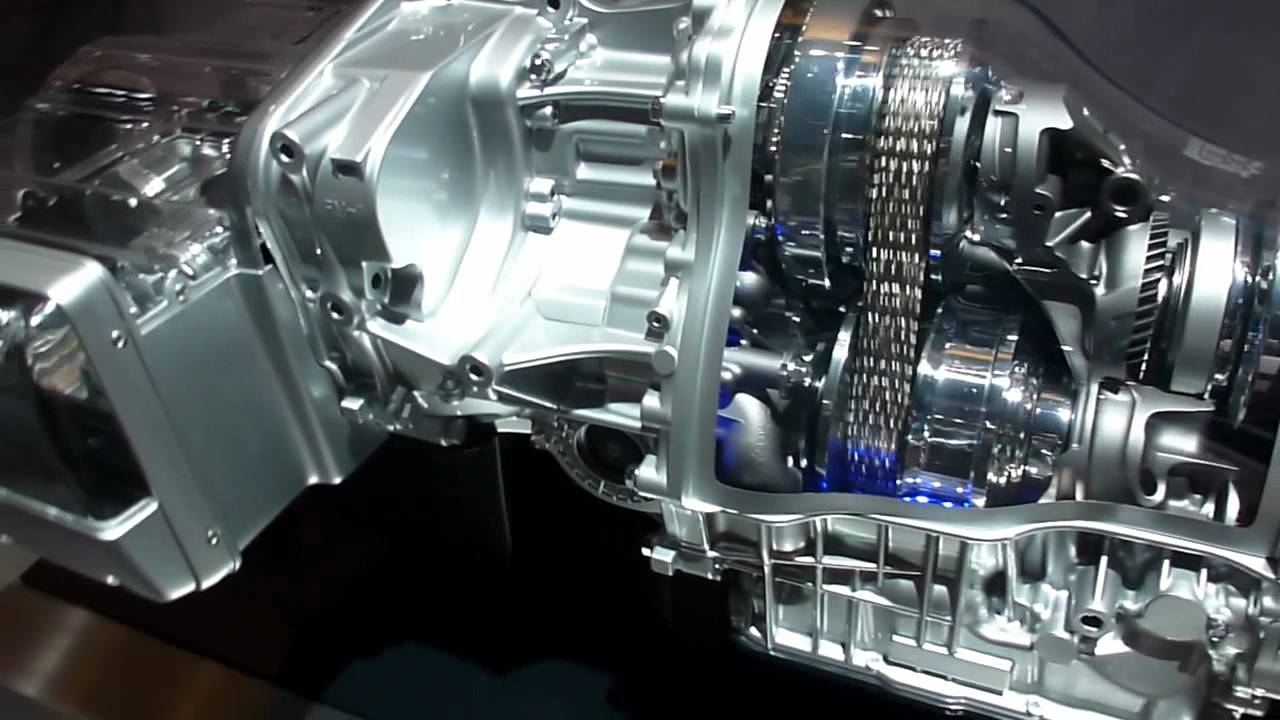
- Torque Converter: This fluid coupling connects the engine to the CVT. It allows the engine to idle while the car is stopped and multiplies torque at low speeds.
- Primary Pulley (Input Pulley): Connected to the torque converter, this pulley receives power from the engine.
- Secondary Pulley (Output Pulley): Connected to the differential, this pulley sends power to the wheels.
- Steel Belt or Chain: Connects the primary and secondary pulleys, transmitting power between them. This is a critical component responsible for the continuously variable ratios.
- Hydraulic Control System: This complex system uses hydraulic pressure to control the position of the pulley sheaves, thereby changing the gear ratio. It includes valves, solenoids, and sensors.
- Transmission Control Unit (TCU): The "brain" of the CVT, the TCU monitors sensor inputs and controls the hydraulic system to achieve the desired gear ratio.
- Oil Pump: Provides the necessary hydraulic pressure for the control system and lubrication of the CVT's internal components.
How a Subaru CVT Works
The core principle behind a CVT is to provide a *seemingly* infinite number of gear ratios within a specific range. Unlike traditional automatic transmissions with fixed gears, the CVT uses a belt or chain running between two variable-diameter pulleys. Think of it like a bicycle derailleur system, but instead of discrete steps, the ratio changes smoothly and continuously.
Here's the breakdown:
- Engine Power Input: The engine turns the torque converter, which in turn rotates the primary pulley.
- Ratio Adjustment: The TCU monitors various parameters (engine speed, vehicle speed, throttle position, etc.) and commands the hydraulic control system to adjust the effective diameters of the pulleys. Hydraulic pressure pushes the pulley sheaves together or allows them to separate.
- Belt/Chain Movement: As the pulley diameters change, the steel belt or chain rides higher or lower on the pulleys, effectively changing the gear ratio. For example, if the primary pulley diameter is small and the secondary pulley diameter is large, the CVT is in a "low gear" for acceleration. Conversely, if the primary pulley diameter is large and the secondary pulley diameter is small, the CVT is in a "high gear" for fuel efficiency.
- Power Output: The secondary pulley, now rotating at the desired speed, transmits power to the differential and then to the wheels.
This continuous ratio adjustment allows the engine to operate at its optimal efficiency point for any given speed, resulting in improved fuel economy and smoother acceleration compared to traditional automatic transmissions. Some Subaru CVTs also feature pre-programmed "steps" to simulate traditional gears during aggressive driving, giving a more engaging feel.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting
Here are a few common CVT issues and some basic troubleshooting steps:
- Shuddering or Jerking: This can indicate low or contaminated CVT fluid. Check the fluid level and condition. If it's dark or smells burnt, a fluid change is necessary. *Always* use the correct fluid specified for your Subaru CVT.
- Delayed Engagement: A delay between shifting into drive or reverse and the car actually moving can point to low fluid pressure or a failing torque converter.
- Whining Noise: A whining noise, especially under acceleration, could indicate a worn belt or chain, or a failing oil pump.
- Warning Lights: A warning light on the dashboard (e.g., transmission light) is a serious issue that requires immediate attention. Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve the trouble codes and diagnose the problem. Common codes relate to solenoid malfunctions, pressure sensor issues, or slipping.
Important: CVT diagnostics often require specialized equipment and knowledge. If you're not comfortable working on your CVT, it's best to consult a qualified technician.
Safety: Highlighting Risky Components
Working on a CVT involves inherent risks. Here are some areas to be particularly cautious of:
- High Pressure: The hydraulic control system operates under high pressure. Never disconnect any hydraulic lines while the engine is running or the system is pressurized. Depressurize the system according to the service manual before attempting any repairs.
- Hot Fluid: CVT fluid can get very hot during operation. Allow the CVT to cool down completely before draining or handling the fluid.
- Moving Parts: The CVT contains many rapidly rotating parts. Never operate the engine with the CVT exposed. Keep hands and clothing clear of moving components.
- Fluid Type: As mentioned, using the wrong CVT fluid can cause irreversible damage. Always double-check the fluid specification before adding or replacing fluid.
- Torque Converter: Removing and installing the torque converter can be tricky. Ensure it's properly seated in the transmission before bolting the transmission to the engine. Improper installation can damage the torque converter and the transmission.
Symbols and the Diagram
The diagram (available for download below) uses standard hydraulic and electrical symbols. Lines represent hydraulic lines, with different types of lines indicating different pressure levels (e.g., solid lines for high pressure, dashed lines for low pressure). Electrical symbols represent solenoids, sensors, and the TCU. Different colors are often used to differentiate between different fluid circuits or electrical signals.
Take some time to familiarize yourself with these symbols. Understanding the diagram will significantly enhance your ability to troubleshoot and understand the CVT's operation.
We have the full diagram available for you to download. It shows the locations of all the sensors, the hydraulic lines, and the electrical connections. Please use it as a reference when working on your vehicle.
We hope this article has provided you with a solid foundation for understanding your Subaru's CVT. Remember, knowledge is power! The more you understand your car, the better equipped you'll be to maintain it, troubleshoot problems, and even explore performance modifications responsibly.
